* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Egypt Study Guide
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian language wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
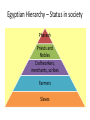
Egypt Study Guide Vocabulary • Delta – the lowlands formed by the silt left at the mouth of a river • Silt – the rich fertile soil left behind on the land from floodwaters • Inundation – one of the three seasons in Egypt – when the Nile River floods the land • Canals – channels dug into the land to carry and help control the floodwaters Vocabulary • Pharaoh – the ruler of Egypt who controlled all of the land and all of the people • Hieroglyphics – Egyptian writing • Papyrus – a paperlike material made from reeds • Pyramid – a tomb for ancient Egyptian rulers • Obelisks - Obelisks • Egyptian Obelisks What is an obelisk and what is its purpose? Obelisk Definition: An obelisk is a monumental tapering column carved from a single block of stone, with a square crosssection and capped with a pointed top called a pyramidion. Obelisks were set in pairs, at the entrances of temples, and to some Old Kingdom tombs and closely related to the cult of the Sun God Ra also known as Atum. Obelisks symbolized the stability and the creative force of Atum. Obelisks were believed to act as magical protection to the monuments such as temples and tombs. Obelisk of Hatshepsut Obelisk at Karnak Hatshepsut • The only woman in Egypt to rule as pharaoh Amenhotep IV • Ruled during the New Kingdom and introduced Egyptians to the single God, Aton Alexander The Great • Greek ruler who conquered the Persian Empire and gained control of Egypt. He was undefeated in battle and created of one of the largest empires in history stretching from the Mediterranean to the Himalaya. Problems with the waters from the Nile River • Too much water on the land • Too little water on the land What are some solutions? Solutions for too much water • • • • Divert water away from farmland Build reservoirs for holding water Build dams and dikes for controlling the water Can you think of any more? Now, which is the best solution, and why? Solutions for too little water • • • • • Dance a rain dance Dig wells Build water storage sites Irrigate with Nile river water Can you think of any more? Now, which is the best solution and why? Achievements and changes during Egyptian History • Old Kingdom – Started a colony in Lower Nubia to get resources there – Traders were sent farther south in Africa – Technology to construct the pyramids – Development of mummification Achievements and changes during Egyptian History • Middle Kingdom – Conquered all of Nubia – Expanded Egyptian trade – Change in society – rights that had once been for pharaohs alone were now for all Egyptians – Changes in government – pharaoh appointed governors for the nomes. This gave paraohs more control • New Kingdom – First woman ruler Hatshepsut – Egypt’s first full-time army began – Egyptian Empire grew to largest size – Worship focused on one god – the Aton – Used hidden tombs to bury pharaohs Egyptian Hierarchy – Status in society Pharaoh Priests and Nobles Craftworkers, merchants, scribes Farmers Slaves Study for your test! Don’t forget to look at your book notes, papers, maps, and sites on the wiki! Credits • http://www.pushindaisies.com/candypress/sc ripts/prodView.asp?idproduct=513 • http://www.bibleufo.com/ancconstobelegy.ht m • http://www.rainbowcrystal.com/atext/egypt1 2.html • http://achanjati.wordpress.com/category/ame nhotep-iv/page/3/ • http://gardenofpraise.com/ibdalex.htm