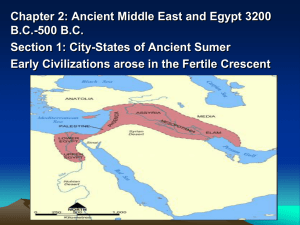
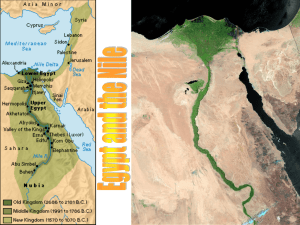
Bellringer
... • Hatshepsut was one of the many famous Egyptian pharaohs, or king, to rule Egypt • The history of ancient Egypt is the history of each of its dynasties- series of rulers from the same family • Had 31 dynasties until it was conquered by the Greek ruler Alexander the Great in 332 B.C. ...
... • Hatshepsut was one of the many famous Egyptian pharaohs, or king, to rule Egypt • The history of ancient Egypt is the history of each of its dynasties- series of rulers from the same family • Had 31 dynasties until it was conquered by the Greek ruler Alexander the Great in 332 B.C. ...
Ancient Egypt Test (Part A) 30 Marks Name Multiple Choice (One
... Fill in the blanks (one mark each) 11. Pharaoh ______________________ expanded trade further than any other pharaoh 12. Egyptians origin story begins with Osiris and Isis and their son ________________ 13. The Nile River is ______________ miles long and flows into the _____________________ sea 14. _ ...
... Fill in the blanks (one mark each) 11. Pharaoh ______________________ expanded trade further than any other pharaoh 12. Egyptians origin story begins with Osiris and Isis and their son ________________ 13. The Nile River is ______________ miles long and flows into the _____________________ sea 14. _ ...
The Double Crown of Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes
... Menes, the King who united Upper and Lower Egypt. Early on, Memphis was more likely a fortress from which Menes controlled the land and water routes between Upper Egypt and the Delta. Having probably originated in Upper Egypt, from Memphis he could control the conquered people of Lower Egypt. Howeve ...
... Menes, the King who united Upper and Lower Egypt. Early on, Memphis was more likely a fortress from which Menes controlled the land and water routes between Upper Egypt and the Delta. Having probably originated in Upper Egypt, from Memphis he could control the conquered people of Lower Egypt. Howeve ...
Ancient Nile Kingdoms
... The river also served as a trade route. Egyptian merchants traveled up and down the Nile in sailboats and barges, exchanging the products of Africa, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean world. ...
... The river also served as a trade route. Egyptian merchants traveled up and down the Nile in sailboats and barges, exchanging the products of Africa, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean world. ...
Ancient Egypt ABC Book
... and agricultural practices and products flourished as a result of favorable geographic characteristics. The cultural practices and products of these early civilizations can be used to help understand the Eastern Hemisphere ...
... and agricultural practices and products flourished as a result of favorable geographic characteristics. The cultural practices and products of these early civilizations can be used to help understand the Eastern Hemisphere ...
Ancient Egypt - WORLD HISTORY Coach Pearce
... and considerable intellectual and cultural activity. The Intermediate periods were between the periods of stability and were ages of political chaos and invasion. ...
... and considerable intellectual and cultural activity. The Intermediate periods were between the periods of stability and were ages of political chaos and invasion. ...
test alert - TeacherWeb
... 5. Why did the Kushites move their capital to Meroë? 6. Who tried to give the Egyptians a new religion? 7. What are two things that resulted from the Nile River’s flooding? 8. Today we call it Sudan. The ancient Egyptians called it __________________. 9. Who was the female pharaoh who concentrated o ...
... 5. Why did the Kushites move their capital to Meroë? 6. Who tried to give the Egyptians a new religion? 7. What are two things that resulted from the Nile River’s flooding? 8. Today we call it Sudan. The ancient Egyptians called it __________________. 9. Who was the female pharaoh who concentrated o ...
History 110B World History 1500 to the Present
... Ancient Egypt Three Eras: 1) The Old Kingdom 2) The Middle Kingdom 3) The New Kingdom Each period was followed by a break-down in order called the First, Second and Third Intermediate Periods, respectively Terms: Ma’at, Pharaoh ...
... Ancient Egypt Three Eras: 1) The Old Kingdom 2) The Middle Kingdom 3) The New Kingdom Each period was followed by a break-down in order called the First, Second and Third Intermediate Periods, respectively Terms: Ma’at, Pharaoh ...
Kingdoms of Ancient Africa
... People settle next to the Nile between 10 - 7000BC Upper (south, upriver) and Lower ...
... People settle next to the Nile between 10 - 7000BC Upper (south, upriver) and Lower ...
Ancient Egypt - World History
... Predynastic Egypt--Unification 3100 BC—King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt By 3000 BC—Characteristics of Egypt have ...
... Predynastic Egypt--Unification 3100 BC—King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt By 3000 BC—Characteristics of Egypt have ...
Chapter 5 – Lesson 3 The Pyramid Builders
... • Legend says a king, Narmer, united Upper and Lower Egypt while some other historians believe several rulers united Egypt • ruler of united Egypt wore the double crown • dynasty—line of rulers from same family • when a king died, he was usually replaced by one of his children • succession—order in ...
... • Legend says a king, Narmer, united Upper and Lower Egypt while some other historians believe several rulers united Egypt • ruler of united Egypt wore the double crown • dynasty—line of rulers from same family • when a king died, he was usually replaced by one of his children • succession—order in ...
The Later Middle Ages
... and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) 4. ________________________ wrote and copied religious and literary texts. (Artisans/Scribes) 5. In Egyptian art, ________________________ were u ...
... and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) 4. ________________________ wrote and copied religious and literary texts. (Artisans/Scribes) 5. In Egyptian art, ________________________ were u ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide – EGYPT
... What physical features/geographical barriers surround the Nile? Be specific. ...
... What physical features/geographical barriers surround the Nile? Be specific. ...
Ancient Egypt
... 2. How did the role of Egyptian pharaohs differ from the role of Mesopotamian rulers? (pg. 37) 3. Why did the Egyptians build great pyramids for their Kings? (pg. 37-38) 4. How did Egyptian religious beliefs compare with those of the Mesopotamians? (pg. 38) 5. What social classes made up Egyptian so ...
... 2. How did the role of Egyptian pharaohs differ from the role of Mesopotamian rulers? (pg. 37) 3. Why did the Egyptians build great pyramids for their Kings? (pg. 37-38) 4. How did Egyptian religious beliefs compare with those of the Mesopotamians? (pg. 38) 5. What social classes made up Egyptian so ...
New Freshmen Chap 2
... • The pyramids were built during the Old Kingdom in necropolises (cemeteries) • The Turbulent Middle Kingdom • The Old Kingdom collapsed due to power struggles and the cost of building the pyramids • The Middle Kingdom was plagued by problems • In 1700 b.c. foreign invaders known as Hyksos invaded a ...
... • The pyramids were built during the Old Kingdom in necropolises (cemeteries) • The Turbulent Middle Kingdom • The Old Kingdom collapsed due to power struggles and the cost of building the pyramids • The Middle Kingdom was plagued by problems • In 1700 b.c. foreign invaders known as Hyksos invaded a ...
IV. ANCIENT EGYPT A. Geography 1. The Nile River – the
... but they were most likely a nomadic tribe from western Asia. They had horses, chariots and stronger bows than the Egyptians. 6. Second Intermediate Period (ca.1780-1570 B.C.) – Hyksos pharaohs ruled Egypt for about 200 years. This time period was a great humiliation for the Egyptians, so they destro ...
... but they were most likely a nomadic tribe from western Asia. They had horses, chariots and stronger bows than the Egyptians. 6. Second Intermediate Period (ca.1780-1570 B.C.) – Hyksos pharaohs ruled Egypt for about 200 years. This time period was a great humiliation for the Egyptians, so they destro ...
File - History with Mr. Davis!
... • Cataracts - Wild rapids in the Nile River than allow for only the last 650 miles where it flows through Egypt. • Shortly before the Nile reaches the Mediterranean Sea, it branches out over fertile soil called a delta. • On both sides of the Nile lie desert. To the west is the Sahara, the largest ...
... • Cataracts - Wild rapids in the Nile River than allow for only the last 650 miles where it flows through Egypt. • Shortly before the Nile reaches the Mediterranean Sea, it branches out over fertile soil called a delta. • On both sides of the Nile lie desert. To the west is the Sahara, the largest ...
Egypt
... characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
... characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
Name: Ancient Egypt Study Guide USE YOUR BOOK and NOTES
... 13. True or False. The surplus of food led to the development of permanent villages. True 14. Describe the importance of Osiris, Isis, Re and Horus in Egyptian religion. Osiris was the god of the underworld that judged the souls of the dead Isis was Osiris’ wife and goddess of magic, fertility Re wa ...
... 13. True or False. The surplus of food led to the development of permanent villages. True 14. Describe the importance of Osiris, Isis, Re and Horus in Egyptian religion. Osiris was the god of the underworld that judged the souls of the dead Isis was Osiris’ wife and goddess of magic, fertility Re wa ...
Ancient Egypt Test
... The Nile River allowed for the development of Ancient Egypt in the Sahara Desert. 2. What caused the soil in the Nile River Valley to become more fertile? The silt from the Nile River caused the soil to become fertile. 3. In what ways did the ancient Egyptians utilize the Nile River? The Ancient Egy ...
... The Nile River allowed for the development of Ancient Egypt in the Sahara Desert. 2. What caused the soil in the Nile River Valley to become more fertile? The silt from the Nile River caused the soil to become fertile. 3. In what ways did the ancient Egyptians utilize the Nile River? The Ancient Egy ...