Egyptian Study Guide
... 12. Read the story of Isis and Osiris and then summarize it. (206-209) 13. Describe the location and geography of the Nubian Kingdom of Kush. ( pg.210 to 211) 14. Why (what) did Egypt want from the Nubians? (pg.211) 15. How and when was the Nubian/Kushite ruler Kashta able to conquer Egypt? (pg. 212 ...
... 12. Read the story of Isis and Osiris and then summarize it. (206-209) 13. Describe the location and geography of the Nubian Kingdom of Kush. ( pg.210 to 211) 14. Why (what) did Egypt want from the Nubians? (pg.211) 15. How and when was the Nubian/Kushite ruler Kashta able to conquer Egypt? (pg. 212 ...
The Old Kingdom
... • A household was made up of the owner’s family, servants, and artisans • Artisans were hired to make things for the family like boats and weave linen cloth • Most were farmers who lived in villages within the estates ...
... • A household was made up of the owner’s family, servants, and artisans • Artisans were hired to make things for the family like boats and weave linen cloth • Most were farmers who lived in villages within the estates ...
The Old Kingdom
... • A household was made up of the owner’s family, servants, and artisans • Artisans were hired to make things for the family like boats and weave linen cloth • Most were farmers who lived in villages within the estates ...
... • A household was made up of the owner’s family, servants, and artisans • Artisans were hired to make things for the family like boats and weave linen cloth • Most were farmers who lived in villages within the estates ...
Ancient Egypt Notes
... resin for glue. Magical amulets and other treasures were buried with the body. ...
... resin for glue. Magical amulets and other treasures were buried with the body. ...
Egypt Review Slideshow
... • Black, stone tablet which had writing in three different forms • Tablet used to “decode” the hieroglyphics ...
... • Black, stone tablet which had writing in three different forms • Tablet used to “decode” the hieroglyphics ...
Unit 1 EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION (OLD, MIDDLE, AND NEW
... - 3000 BC unification under King Narmer, first Egyptian dynasty centered at Memphis where Upper and lower Egypt meet. - Egyptian Civilization was united under one leader called a pharaoh = _______________________________ - pharaohs had absolute power and owned all land; however, they were expected t ...
... - 3000 BC unification under King Narmer, first Egyptian dynasty centered at Memphis where Upper and lower Egypt meet. - Egyptian Civilization was united under one leader called a pharaoh = _______________________________ - pharaohs had absolute power and owned all land; however, they were expected t ...
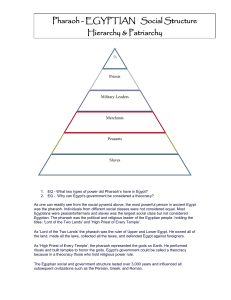
r EQ - What two types of power did Pharaoh`s have in Egypt? EQ
... the land, made all the laws, collected all the taxes, and defended Egypt against foreigners. As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honor the gods. Egypt’s government could be called a theocracy because in a theocracy th ...
... the land, made all the laws, collected all the taxes, and defended Egypt against foreigners. As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honor the gods. Egypt’s government could be called a theocracy because in a theocracy th ...
egypt - TriciaWood
... • Had no word for religion, the ideas were inseparable part of the world order • Egyptians were polytheistic, had many important gods and goddesses – Key god was the god of the sun = Re or Amon-Re • Father of the pharaohs – Anubis = protector of the dead – Osiris = introduced civilization into Egypt ...
... • Had no word for religion, the ideas were inseparable part of the world order • Egyptians were polytheistic, had many important gods and goddesses – Key god was the god of the sun = Re or Amon-Re • Father of the pharaohs – Anubis = protector of the dead – Osiris = introduced civilization into Egypt ...
egypt - murphysclass
... • Had no word for religion, the ideas were inseparable part of the world order • Egyptians were polytheistic, had many important gods and goddesses – Key god was the god of the sun = Re or Amon-Re • Father of the pharaohs – Anubis = protector of the dead – Osiris = introduced civilization into Egypt ...
... • Had no word for religion, the ideas were inseparable part of the world order • Egyptians were polytheistic, had many important gods and goddesses – Key god was the god of the sun = Re or Amon-Re • Father of the pharaohs – Anubis = protector of the dead – Osiris = introduced civilization into Egypt ...
The Kingdoms of Egypt - White Plains Public Schools
... 20. Why were the pyramids important sources of information about ancient Egypt? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 21. The three largest and best preserved pyramids are at __________________ near the city of _ ...
... 20. Why were the pyramids important sources of information about ancient Egypt? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 21. The three largest and best preserved pyramids are at __________________ near the city of _ ...
Egypt Test 2
... 19. The Nile is the second longest river in the world behind the Mississippi. _________ 20. Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife.________ 21. Menes is credited with unifying upper and lower Egypt. _____________ 22. The Nile has two main branches the White Nile and the Blue Nile. _____________ ...
... 19. The Nile is the second longest river in the world behind the Mississippi. _________ 20. Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife.________ 21. Menes is credited with unifying upper and lower Egypt. _____________ 22. The Nile has two main branches the White Nile and the Blue Nile. _____________ ...
The Middle Kingdom - Mr. Scott`s Cyberdesk
... They still controlled mining and trade, but the priests refused to give up the power they had gained during the decline of the Old Kingdom and the new pharaohs didn't have a large enough army to force the issue. The priests still recognized the pharaoh as their leader, though, because a leading figu ...
... They still controlled mining and trade, but the priests refused to give up the power they had gained during the decline of the Old Kingdom and the new pharaohs didn't have a large enough army to force the issue. The priests still recognized the pharaoh as their leader, though, because a leading figu ...
ancient river valley civilizations
... Egyptians were polytheistic, and worshiped many gods. Egyptian gods took the forms of humans, animals, and natural forces. Eventually the sun god came to be dominant, but initially there was little order to the pantheon. o Egyptians developed writing not long after Sumerians, and apparently independ ...
... Egyptians were polytheistic, and worshiped many gods. Egyptian gods took the forms of humans, animals, and natural forces. Eventually the sun god came to be dominant, but initially there was little order to the pantheon. o Egyptians developed writing not long after Sumerians, and apparently independ ...
The Nile Valley
... the activity below will help you learn more about Egypt’s Old Kingdom. Use your textbook to decide if a statement is true or false. Write T or F in the blank, and if a statement is false, rewrite it correctly on the line. 1. The period of Egyptian history known as the Old Kingdom began around 2300 B ...
... the activity below will help you learn more about Egypt’s Old Kingdom. Use your textbook to decide if a statement is true or false. Write T or F in the blank, and if a statement is false, rewrite it correctly on the line. 1. The period of Egyptian history known as the Old Kingdom began around 2300 B ...
The History Ancient Egypt
... used this land for growing their crops. This was the only land in ancient Egypt that ...
... used this land for growing their crops. This was the only land in ancient Egypt that ...
Early Civilizations Chapter 2
... ◦ Kings in Memphis lost power ◦ New united dynasty formed in the South at Thebes ◦ Became stronger, capturing Nubia (part of current Sudan) ◦ Canal constructed between Nile and Red Sea, improving trade ...
... ◦ Kings in Memphis lost power ◦ New united dynasty formed in the South at Thebes ◦ Became stronger, capturing Nubia (part of current Sudan) ◦ Canal constructed between Nile and Red Sea, improving trade ...
Ancient Egyptians
... dried mud and painted white. Houses had small windows to keep out the hot sun. Some people had a pool in their garden where they kept fish to eat. Start again ...
... dried mud and painted white. Houses had small windows to keep out the hot sun. Some people had a pool in their garden where they kept fish to eat. Start again ...
WHPP Unit 1 Section 3 Ancient Egypt
... resin for glue. Magical amulets and other treasures were buried with the body. ...
... resin for glue. Magical amulets and other treasures were buried with the body. ...
Egypt Fall 2014
... - Pharaoh Amenhotep in the New Kingdom tried to switch the religion to monotheism (belief in one god; in this case the sun god), but as soon as he died Egypt returned to polytheism. B) Priests performed rituals to please the gods in their temples. C) Because the Nile floods were usually predictable, ...
... - Pharaoh Amenhotep in the New Kingdom tried to switch the religion to monotheism (belief in one god; in this case the sun god), but as soon as he died Egypt returned to polytheism. B) Priests performed rituals to please the gods in their temples. C) Because the Nile floods were usually predictable, ...
Ancient Egypt - WordPress.com
... A group of people called the Hyksos (pronounced “Hik-sos”) came with chariots from the Middle East. Assimilated into Egyptian culture. ...
... A group of people called the Hyksos (pronounced “Hik-sos”) came with chariots from the Middle East. Assimilated into Egyptian culture. ...
The Ancient Egyptians - Sire`s Ancient History
... Old Kingdom: Age of the Pharaohs 2700-2200 B.C • Pharaohs: (Great House) Egyptian rulers who were the religious and political leaders of united ancient Egypt (King of the Two Lands) considered to be gods in human form. ...
... Old Kingdom: Age of the Pharaohs 2700-2200 B.C • Pharaohs: (Great House) Egyptian rulers who were the religious and political leaders of united ancient Egypt (King of the Two Lands) considered to be gods in human form. ...
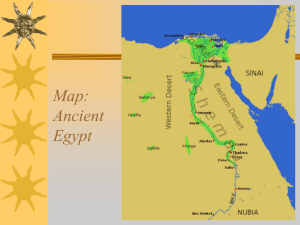
I. Geography of Ancient Egypt - New Paltz Central School District
... III. The Old Kingdom or Pyramid Age Pharaohs, Builders of the Pyramids E. Pharaohs: The Builders of the Pyramids – Lasting Contribution ...
... III. The Old Kingdom or Pyramid Age Pharaohs, Builders of the Pyramids E. Pharaohs: The Builders of the Pyramids – Lasting Contribution ...
Ancient Egypt Jeopardy
... The Ancient Egyptians developed this discipline in order to build the pyramids. ...
... The Ancient Egyptians developed this discipline in order to build the pyramids. ...