The Old Kingdom: Age of the pyramids
... • The Ka was a spiritual duplicate of the human. It was stored in the heart, and at death, it was separated from the body. The ka would inhabit the tomb of the individual to be near the body after death. The ka would need food, clothing, perfume and furniture in the afterlife. • The ba was a non-phy ...
... • The Ka was a spiritual duplicate of the human. It was stored in the heart, and at death, it was separated from the body. The ka would inhabit the tomb of the individual to be near the body after death. The ka would need food, clothing, perfume and furniture in the afterlife. • The ba was a non-phy ...
The Nile River Valley - NORTH MUSKEGON PUBLIC SCHOOLS Mr
... • Egypt grew richer and more powerful. • _______________was one of the few women rulers. • Trade grew during her rule. Beads, tools, wood, ivory and incense were traded. • _________________became pharaoh after Hatshepsut died. Egypt conquered more land and became even richer. • Slavery was very comm ...
... • Egypt grew richer and more powerful. • _______________was one of the few women rulers. • Trade grew during her rule. Beads, tools, wood, ivory and incense were traded. • _________________became pharaoh after Hatshepsut died. Egypt conquered more land and became even richer. • Slavery was very comm ...
gradenineegypt
... • History of Egypt is divided into periods called Kingdoms (Old, Middle, New) • Further divided into times when the same family ruled called Dynasties • Reign ended with the death of a Pharaoh and crowning of someone from the same family - to keep the blood “pure” ...
... • History of Egypt is divided into periods called Kingdoms (Old, Middle, New) • Further divided into times when the same family ruled called Dynasties • Reign ended with the death of a Pharaoh and crowning of someone from the same family - to keep the blood “pure” ...
Kingdoms of Egypt
... The first ritual was to remove all the organs. The first organ was the Brain which was removed from the nose. They believed the brain was not important. Then they took out the liver, intestines, lungs and stomach were placed in conopic jars. The heart was left in the body. The heads on the jars were ...
... The first ritual was to remove all the organs. The first organ was the Brain which was removed from the nose. They believed the brain was not important. Then they took out the liver, intestines, lungs and stomach were placed in conopic jars. The heart was left in the body. The heads on the jars were ...
Ancient Egypt - Deer Park ISD
... Egyptian Life and Culture • The Achievements of Ancient Egypt • Architecture and the Arts • Pyramids & Sphinx • There are still about 80 pyramids • Sculpture and paintings ...
... Egyptian Life and Culture • The Achievements of Ancient Egypt • Architecture and the Arts • Pyramids & Sphinx • There are still about 80 pyramids • Sculpture and paintings ...
Ancient Egypt Part 2 - Crest Ridge R-VII
... culture. But, they did not get along. They were always fighting. ...
... culture. But, they did not get along. They were always fighting. ...
ancient_egypt_def - James M. Hill High School
... All government administrators, ranging from personal staff to imperial officials, were subject to the approval of the pharaoh. Religion guided every aspect of Egyptian life. Egyptian religion was based on polytheism, or the worship of many deities, except for during the reign of Akenaton. The Egypt ...
... All government administrators, ranging from personal staff to imperial officials, were subject to the approval of the pharaoh. Religion guided every aspect of Egyptian life. Egyptian religion was based on polytheism, or the worship of many deities, except for during the reign of Akenaton. The Egypt ...
Answers - Schoolwires.net
... crops. The Egyptian lives and civilization revolved around the River. They created the Shaduf and Nilometer ...
... crops. The Egyptian lives and civilization revolved around the River. They created the Shaduf and Nilometer ...
Egypt - S14
... Immortality of the Pharaoh Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death. He had an eternal spirit, or ka, that continued to take part in the governing of Egypt. Egyptians also believed that the ka remained much like a living pharaoh in its needs and pleasures. Pharaoh’s Tomb nee ...
... Immortality of the Pharaoh Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death. He had an eternal spirit, or ka, that continued to take part in the governing of Egypt. Egyptians also believed that the ka remained much like a living pharaoh in its needs and pleasures. Pharaoh’s Tomb nee ...
Government in Ancient Egypt
... a•erwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unifica•on happened, it became the world’s first ever na•on-state. King Narmer was the first king of Egypt’s first dynasty, and there would be 30 more dynas•es a•er him. The king controlled all of Egypt, but assigned governors t ...
... a•erwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unifica•on happened, it became the world’s first ever na•on-state. King Narmer was the first king of Egypt’s first dynasty, and there would be 30 more dynas•es a•er him. The king controlled all of Egypt, but assigned governors t ...
3.1 Notes
... The Hyksos ruled Egypt for almost 100 years before the Egyptians rose up and drove them out. The army that defeated the Hyksos was led by nobles from Thebes. They became the new rulers of Egypt, and with this, the New Kingdom began. During the New Kingdom, Egyptians realized that a permanent army an ...
... The Hyksos ruled Egypt for almost 100 years before the Egyptians rose up and drove them out. The army that defeated the Hyksos was led by nobles from Thebes. They became the new rulers of Egypt, and with this, the New Kingdom began. During the New Kingdom, Egyptians realized that a permanent army an ...
Society in the Ancient Eastern Mediterranean 3500 BCE
... when Menes united the villages of Upper (southern) and Lower (northern) Egypt into a single kingdom and created the first dynasty. Dynasty - a family of rulers whose right to rule is passed on within the family. ...
... when Menes united the villages of Upper (southern) and Lower (northern) Egypt into a single kingdom and created the first dynasty. Dynasty - a family of rulers whose right to rule is passed on within the family. ...
Ancient River Valley Civilizations Powerpoint
... in into L.E.- river turns into rapids for stretch and it difficult to navigate ...
... in into L.E.- river turns into rapids for stretch and it difficult to navigate ...
Mummy - a body that has been embalmed and wrapped in linen
... Cataract steep rapids formed by cliffs and boulders in a river Delta - area of fertile soil at the mouth of a river ...
... Cataract steep rapids formed by cliffs and boulders in a river Delta - area of fertile soil at the mouth of a river ...
• Chapter 2 • Ancient Egypt • Without the Nile River, Egypt would be
... Ancient Egypt had two distinct regions: 1. Upper Egypt in the south 2. Lower Egypt in the north 3. Upper Egypt stretched from the Nile’s first waterfall to within 100 miles of the Mediterranean Sea, where it forms the Nile Delta (delta is a triangular area of marshland formed by deposits of silt at ...
... Ancient Egypt had two distinct regions: 1. Upper Egypt in the south 2. Lower Egypt in the north 3. Upper Egypt stretched from the Nile’s first waterfall to within 100 miles of the Mediterranean Sea, where it forms the Nile Delta (delta is a triangular area of marshland formed by deposits of silt at ...
Chapter 2
... united the 2 regions. • Menes founded Egypt’s first capital at Memphis, a site where the Nile empties into its delta. • Menes and his successors used the Nile as a highway linking the North and South. They could send officials or armies to towns along the river. Thus, the Nile River helped make Egyp ...
... united the 2 regions. • Menes founded Egypt’s first capital at Memphis, a site where the Nile empties into its delta. • Menes and his successors used the Nile as a highway linking the North and South. They could send officials or armies to towns along the river. Thus, the Nile River helped make Egyp ...
The First Civilizations powerpoint
... While wrapping the body, secret amulets were placed between the layers of wraps to protect the body during its journey to the afterlife. While the body was wrapped, a priest recited magic spells from the “Book of the Dead”, to keep away evil spirits. Then the arms and legs were tied together, and a ...
... While wrapping the body, secret amulets were placed between the layers of wraps to protect the body during its journey to the afterlife. While the body was wrapped, a priest recited magic spells from the “Book of the Dead”, to keep away evil spirits. Then the arms and legs were tied together, and a ...
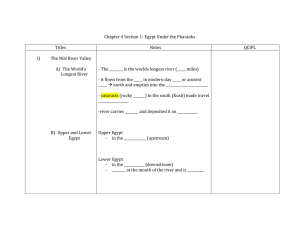
Early African Empires (Chapter 4, Sections 1-3)
... 0 Overthrew Libyan rulers in Egypt 751 B.C. 0 United entire Nile Valley from the delta in the north to ...
... 0 Overthrew Libyan rulers in Egypt 751 B.C. 0 United entire Nile Valley from the delta in the north to ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... United by King Narmer (King of Upper Egypt) King of Upper Egypt wore a white crown Lower Egypt wore a red crown Narmer Palette: both crowns as one Symbol of unification around 3000 BC ...
... United by King Narmer (King of Upper Egypt) King of Upper Egypt wore a white crown Lower Egypt wore a red crown Narmer Palette: both crowns as one Symbol of unification around 3000 BC ...
Kasha Korwek
... Egypt did have a civilization. These people knew what to do. Either from when the Nile would rise and they would use it for irrigation or building great pyramids at Giza. These Egyptians knew what to do, they were a civilization. Although their civilization isn’t like what it is today, they still di ...
... Egypt did have a civilization. These people knew what to do. Either from when the Nile would rise and they would use it for irrigation or building great pyramids at Giza. These Egyptians knew what to do, they were a civilization. Although their civilization isn’t like what it is today, they still di ...
Chapter 4 Section 1-‐ Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL
... -‐ wife of _________________ and step mother/aunt of _________________-‐ took over as pharaoh while her son’s regent -‐ represented herself as masculine (pharaoh’s beard and clothes) to ward off concern of ...
... -‐ wife of _________________ and step mother/aunt of _________________-‐ took over as pharaoh while her son’s regent -‐ represented herself as masculine (pharaoh’s beard and clothes) to ward off concern of ...
Mr. Hessel: Global History I: Ancient Egypt
... Pharoah (Great House) This period is also known as The Pyramid Age o Khufu (Cheops), Khafre, Menkaure expensive building projects o high taxes provincial Governors gained in power o challenged the authority of the Pharoah Egypt plunged into Civil War The First Intermediate Period (2280-200BC) "Mis ...
... Pharoah (Great House) This period is also known as The Pyramid Age o Khufu (Cheops), Khafre, Menkaure expensive building projects o high taxes provincial Governors gained in power o challenged the authority of the Pharoah Egypt plunged into Civil War The First Intermediate Period (2280-200BC) "Mis ...
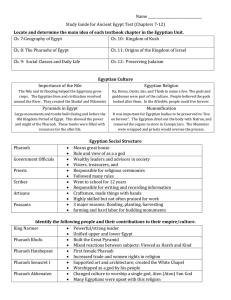
Study Guide: Ancient Egypt
... body and a human’s head 19. Dynasty – a group of people who ruled from the same family 20. Menes – Egypt’s first pharaoh 21. Khufu – made the first pyramids 22. Ahmose – drove out the Hyksos ...
... body and a human’s head 19. Dynasty – a group of people who ruled from the same family 20. Menes – Egypt’s first pharaoh 21. Khufu – made the first pyramids 22. Ahmose – drove out the Hyksos ...