Egypt and the Nile
... characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
... characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
AnEgypt - River Grove School
... characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
... characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
The Pharaoh
... The most powerful person in ancient Egypt was the pharaoh. The pharaoh was the political and religious leader of the Egyptian people, holding the titles: 'Lord of the Two Lands' and 'High Priest of Every Temple'. As 'Lord of the Two Lands' the pharaoh was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned ...
... The most powerful person in ancient Egypt was the pharaoh. The pharaoh was the political and religious leader of the Egyptian people, holding the titles: 'Lord of the Two Lands' and 'High Priest of Every Temple'. As 'Lord of the Two Lands' the pharaoh was the ruler of Upper and Lower Egypt. He owned ...
Review sheet 2017
... and unity under the rule of pharaohs. These periods were the Old Kingdom (Age of the Pyramids) from about 2700 to 2200 B.C.E.; the Middle Kingdom, (Period of Reunification) from about 2000 to 1800 B.C.E.; and the New Kingdom, (Golden Age) from about 1600 to 1100 B.C.E. Powers of Pharaoh: Absolute po ...
... and unity under the rule of pharaohs. These periods were the Old Kingdom (Age of the Pyramids) from about 2700 to 2200 B.C.E.; the Middle Kingdom, (Period of Reunification) from about 2000 to 1800 B.C.E.; and the New Kingdom, (Golden Age) from about 1600 to 1100 B.C.E. Powers of Pharaoh: Absolute po ...
Study sheet for Egypt summative with answers
... married the Princess of Lower Egypt to symbolize this). Eventually, pharaohs began spending large amounts of money on different projects (pyramids, temples, and the sphinx). The pharaoh became broke, and rich nobles were able to take power away from the pharaoh (by paying people the pharaoh couldn’t ...
... married the Princess of Lower Egypt to symbolize this). Eventually, pharaohs began spending large amounts of money on different projects (pyramids, temples, and the sphinx). The pharaoh became broke, and rich nobles were able to take power away from the pharaoh (by paying people the pharaoh couldn’t ...
Egypt Study Guide 1. Be able to locate the following on a map and
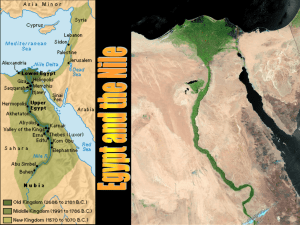
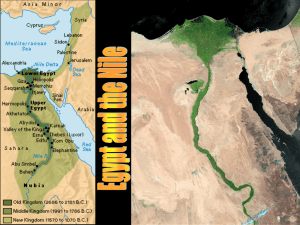
... q. Silt r. Slavery s. Unification 3. How was ancient Egypt influenced by its physical environment? a. How did the Nile Effect Egypt? b. What was the difference between Upper and Lower Egypt? c. What agricultural techniques did Egyptians use to survive the desert and floods? i. Irrigation ii. ...
... q. Silt r. Slavery s. Unification 3. How was ancient Egypt influenced by its physical environment? a. How did the Nile Effect Egypt? b. What was the difference between Upper and Lower Egypt? c. What agricultural techniques did Egyptians use to survive the desert and floods? i. Irrigation ii. ...
From ABC-CLIO`s World History: Ancient and Medieval Eras website
... Wealthier Egyptians might also enjoy a variety of meats, pastries, and wine. Typical clothing was linen dresses for women and kilts for men. Women and men alike outlined their eyes with makeup, both for fashion and to protect the eyes from diseases, the sun's glare, and evil spirits. Religion and Py ...
... Wealthier Egyptians might also enjoy a variety of meats, pastries, and wine. Typical clothing was linen dresses for women and kilts for men. Women and men alike outlined their eyes with makeup, both for fashion and to protect the eyes from diseases, the sun's glare, and evil spirits. Religion and Py ...
Egyptian Civ Final
... A time of territorial expansion to Mesopotamia and other places in Africa. Most powerful state in Africa. Outside forces attacked Egypt- Kush, Assyrians, Persians and Alexander the Great. ...
... A time of territorial expansion to Mesopotamia and other places in Africa. Most powerful state in Africa. Outside forces attacked Egypt- Kush, Assyrians, Persians and Alexander the Great. ...
Blue Nile and White Nile 2) How
... 12) What are the three time periods, or kingdoms, into which these dynasties are divided? The Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. 13) If you looked at a timeline of the dynasties in Ancient Egypt and saw gaps or breaks between the kingdoms, what would this tell you? Gaps meant ther ...
... 12) What are the three time periods, or kingdoms, into which these dynasties are divided? The Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. 13) If you looked at a timeline of the dynasties in Ancient Egypt and saw gaps or breaks between the kingdoms, what would this tell you? Gaps meant ther ...
Document
... • Around 2050 BC, a powerful pharaoh defeated his rivals, and once again all of Egypt was united. • This marked the beginning of the Middle Kingdom, which was a period of order and stability that lasted to about 1750 BCE. ...
... • Around 2050 BC, a powerful pharaoh defeated his rivals, and once again all of Egypt was united. • This marked the beginning of the Middle Kingdom, which was a period of order and stability that lasted to about 1750 BCE. ...
Chapter 4 Egypt Outline - Methacton School District
... Around 2300 BC, government officials took control of Egypt 200 years of confusion followed finally new pharaohs brought peace and a new period pharaohs had less power, buried in cliffs in hillsides, began trading with other countries 1786 BC the Hyksos from western Asia invaded crossed t ...
... Around 2300 BC, government officials took control of Egypt 200 years of confusion followed finally new pharaohs brought peace and a new period pharaohs had less power, buried in cliffs in hillsides, began trading with other countries 1786 BC the Hyksos from western Asia invaded crossed t ...
Egypt and the Nile River Valley
... d. Middle Kingdom (11th to 14th Dynasties) (1975 to 1640 BC) i. Egyptian state _________________ under strong pharaohs ii. Egypt conquered ________________ => iii. Classical period of … e. Second Intermediate Period (15th to 17th Dynasties) (1630 to 1520 BC) i. Hyksos (______________________________ ...
... d. Middle Kingdom (11th to 14th Dynasties) (1975 to 1640 BC) i. Egyptian state _________________ under strong pharaohs ii. Egypt conquered ________________ => iii. Classical period of … e. Second Intermediate Period (15th to 17th Dynasties) (1630 to 1520 BC) i. Hyksos (______________________________ ...
Notes - Question and Answer - Manzanita Elementary School District
... 4-1 p. 96 1. What major river is at the heart of Egypt? 2. Describe the Nile River. 3. How did the cataracts affect the people of ancient Egypt? 4. What parts of Egypt are Upper and Lower Egypt? 5. What caused the actual formation of Lower Egypt? 6. What happens during the Nile’s yearly flooding? 7. ...
... 4-1 p. 96 1. What major river is at the heart of Egypt? 2. Describe the Nile River. 3. How did the cataracts affect the people of ancient Egypt? 4. What parts of Egypt are Upper and Lower Egypt? 5. What caused the actual formation of Lower Egypt? 6. What happens during the Nile’s yearly flooding? 7. ...
Notes for the Wed. October 3 quiz on ch. 2-2
... Thoth (god of writing and scribes) weighed the heart... if the deceased had been found to not have followed the concept of ma'at during his life (if he had lied or cheated or killed or done anything against ma'at) his heart was devoured by a demon (she was called Ammut - Devouress of the Dead) and h ...
... Thoth (god of writing and scribes) weighed the heart... if the deceased had been found to not have followed the concept of ma'at during his life (if he had lied or cheated or killed or done anything against ma'at) his heart was devoured by a demon (she was called Ammut - Devouress of the Dead) and h ...
Chapter 4 - Egypt - Blanchard Middle School
... - ______ Egypt (southern part of Nile) - Lower Egypt (north ________) * Narmer (Menes) = _____________________________ - 3100 BC led his armies from the valley and conquered Lower Egypt. - He __________ the two kingdoms. - He set up a new capital at ________________. * 2600 BV = Old Kingdom that las ...
... - ______ Egypt (southern part of Nile) - Lower Egypt (north ________) * Narmer (Menes) = _____________________________ - 3100 BC led his armies from the valley and conquered Lower Egypt. - He __________ the two kingdoms. - He set up a new capital at ________________. * 2600 BV = Old Kingdom that las ...
the Ch 4 Sec 1 Notes if you missed them.
... Thutmose III, Hatshepsut’s stepson, expands Egypt’s empire ...
... Thutmose III, Hatshepsut’s stepson, expands Egypt’s empire ...
File
... Instead of building pyramids, Pharaohs had their ________________________________________. This area is known as _______________________________. ...
... Instead of building pyramids, Pharaohs had their ________________________________________. This area is known as _______________________________. ...
Egypt Badarian By 5000 BC simple farming based on cattle herding
... coincided with poor flood years and rapid successions of ineffective pharaohs. Egyptian society as a pyramid: balance between flatter and steeper. Archaic Egypt and Creation of the Great Culture (2920-2575 BC) Four broad periods: Archaic Egypt and the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, the New Kingdom ...
... coincided with poor flood years and rapid successions of ineffective pharaohs. Egyptian society as a pyramid: balance between flatter and steeper. Archaic Egypt and Creation of the Great Culture (2920-2575 BC) Four broad periods: Archaic Egypt and the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, the New Kingdom ...
Ancient Egypt - Allenwood BNS
... This how the Ancient Egyptians got there water, the basket would be loured down and the water would flow in to the basket and the farmer would lift it up and bring it back to the village ...
... This how the Ancient Egyptians got there water, the basket would be loured down and the water would flow in to the basket and the farmer would lift it up and bring it back to the village ...
Chapter 4
... Children shaved their heads also- but left one ___________________ of hair hanging down by their ear People worked as farmers, soldiers, ______________________, artisans, _______________________, priests, government jobs such as viziers, palace _________________, fan bearers, and scribes Ancie ...
... Children shaved their heads also- but left one ___________________ of hair hanging down by their ear People worked as farmers, soldiers, ______________________, artisans, _______________________, priests, government jobs such as viziers, palace _________________, fan bearers, and scribes Ancie ...
The Egyptian and Nubian Empires
... • Invades Palestine, Syria, and Nubia— region around the upper Nile River. • Egypt is most powerful and wealthy during reign of the New Kingdom pharaohs. ...
... • Invades Palestine, Syria, and Nubia— region around the upper Nile River. • Egypt is most powerful and wealthy during reign of the New Kingdom pharaohs. ...
The Egyptian and Nubian Empires
... • Invades Palestine, Syria, and Nubia— region around the upper Nile River. • Egypt is most powerful and wealthy during reign of the New Kingdom pharaohs. ...
... • Invades Palestine, Syria, and Nubia— region around the upper Nile River. • Egypt is most powerful and wealthy during reign of the New Kingdom pharaohs. ...
The Story of Egypt - Bildungsverlag Lemberger
... pharaohs – one in the north and one in the south. This was the end of the Old Kingdom. The Middle Kingdom When a new family from Thebes finally brought the country together, this was called the Middle Kingdom which lasted for 250 years. This was the height3 of the Egyptian culture – writing, art and ...
... pharaohs – one in the north and one in the south. This was the end of the Old Kingdom. The Middle Kingdom When a new family from Thebes finally brought the country together, this was called the Middle Kingdom which lasted for 250 years. This was the height3 of the Egyptian culture – writing, art and ...
Ancient Mediterranean Culture- Egypt
... suggesting that the first pharaoh was in fact named Narmer. Most historians agree that the evidence is inconclusive. The Early Dynastic period was followed by the Old Kingdom, which lasted from 2630-2151 BC. This period is also known as the Golden Age of ancient Egypt. It was during this time that t ...
... suggesting that the first pharaoh was in fact named Narmer. Most historians agree that the evidence is inconclusive. The Early Dynastic period was followed by the Old Kingdom, which lasted from 2630-2151 BC. This period is also known as the Golden Age of ancient Egypt. It was during this time that t ...
File
... Essential Question(s): How did Egyptians put their advances to use in building powerful societies during the Old and Middle Kingdoms? Chapter Quote: What they built of gates and chapels now are fallen, their soul-priests and their gardeners are gone, their headstones undiscovered in the dirt, their ...
... Essential Question(s): How did Egyptians put their advances to use in building powerful societies during the Old and Middle Kingdoms? Chapter Quote: What they built of gates and chapels now are fallen, their soul-priests and their gardeners are gone, their headstones undiscovered in the dirt, their ...