Three Kingdoms of Egypt
... texts. They did not have to pay taxes and many became wealthy. 2. Why did pharaohs value talented architects? Architects designed the temples and royal tombs. They could rise to become high government officials. 3. What did the military offer citizens in Egypt? The military offered people a chance t ...
... texts. They did not have to pay taxes and many became wealthy. 2. Why did pharaohs value talented architects? Architects designed the temples and royal tombs. They could rise to become high government officials. 3. What did the military offer citizens in Egypt? The military offered people a chance t ...
Quiz on Egypt
... 1. What were pyramids? tombs built by pharaohs 2. Who were pharaohs? rulers/leaders of Egyptian society 3. What is a theocracy?government run by a religious authority 4. What river did Egyptians live by, and WHY did they live by it? Nile River, for transportation, flooding and irrigation 5. What hap ...
... 1. What were pyramids? tombs built by pharaohs 2. Who were pharaohs? rulers/leaders of Egyptian society 3. What is a theocracy?government run by a religious authority 4. What river did Egyptians live by, and WHY did they live by it? Nile River, for transportation, flooding and irrigation 5. What hap ...
AncientEgypt-general 1
... A governor, or nomarch, was at the head of each nome and was responsible to the pharaoh. These governors tended to amass large holding of land and power within their nomes, creating a potential rivalry with the pharaohs. Of special importance to the administration of the state was a vast bureaucracy ...
... A governor, or nomarch, was at the head of each nome and was responsible to the pharaoh. These governors tended to amass large holding of land and power within their nomes, creating a potential rivalry with the pharaohs. Of special importance to the administration of the state was a vast bureaucracy ...
Egypt
... A.D. stands for Anno Domini, which is Latin for "year of our Lord," and it means the number of years since the birth of Jesus Christ. That was 2000 years ago, so the date 500 A.D. means 1500 years ago. Some people use C.E. instead. That stands for Common Era, and is used in order to avoid Christ ...
... A.D. stands for Anno Domini, which is Latin for "year of our Lord," and it means the number of years since the birth of Jesus Christ. That was 2000 years ago, so the date 500 A.D. means 1500 years ago. Some people use C.E. instead. That stands for Common Era, and is used in order to avoid Christ ...
File - Miss Cummings` Social Studies Homepage
... • Rose along the 4,100-mile Nile River on narrow strip of fertile land ...
... • Rose along the 4,100-mile Nile River on narrow strip of fertile land ...
Egypt Notes page Geography • Nile River – 4,100 miles long, flows
... Wealthy or middle class women could own and trade property Women could propose marriage or seek divorce Intellectual The earliest form of writing was pictographs, then developed a more flexible system called hieroglyphics developed papyrus, a paper-like substance made from reeds. developed cal ...
... Wealthy or middle class women could own and trade property Women could propose marriage or seek divorce Intellectual The earliest form of writing was pictographs, then developed a more flexible system called hieroglyphics developed papyrus, a paper-like substance made from reeds. developed cal ...
Ancient Egypt Vocabulary
... ◦ Pharaohs began the long, difficult process of building their tombs as soon as they came to power ◦ Pyramid- huge buildings with four sloping triangleshaped sides ◦ Giza- location of important pyramids ◦ Could take 20 years to build by slaves and other ...
... ◦ Pharaohs began the long, difficult process of building their tombs as soon as they came to power ◦ Pyramid- huge buildings with four sloping triangleshaped sides ◦ Giza- location of important pyramids ◦ Could take 20 years to build by slaves and other ...
ANCIENT EGYPT DAILY LIFE
... present-day Cairo, Egypt's current capital. Some historians think Menes, the first pharaoh of Egypt, built Memphis. During the New Kingdom, Egypt grew enormously rich by trading in gold and controlling Asian mines. The New Kingdom ended when, under weak rulers, one enemy after another attacked ...
... present-day Cairo, Egypt's current capital. Some historians think Menes, the first pharaoh of Egypt, built Memphis. During the New Kingdom, Egypt grew enormously rich by trading in gold and controlling Asian mines. The New Kingdom ended when, under weak rulers, one enemy after another attacked ...
Egypt and Babylon
... • Another Semitic group from eastern Syria, the Amorites, conquer the region • Conquered the Sumerian city-states to the south • Established capital at Babylon • Greatest expansion and growth under King ...
... • Another Semitic group from eastern Syria, the Amorites, conquer the region • Conquered the Sumerian city-states to the south • Established capital at Babylon • Greatest expansion and growth under King ...
Ancient_Egypt_PPT[1]
... Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
... Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
Ancient Egypt PPT
... Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
... Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
Egypt`s Powerful Kings and Queens
... pharaoh as a child • Because of his young age, a regent was appointed to watch over him until he is old enough to rule by ...
... pharaoh as a child • Because of his young age, a regent was appointed to watch over him until he is old enough to rule by ...
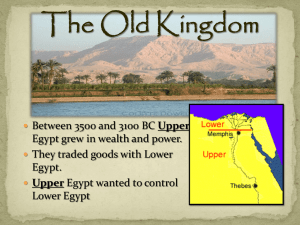
The Old Kingdom - Kingdom of Reese
... a region with a united people and a single government. King Narmer’s rule became known as the first dynasty A dynasty is a series of rulers from the same family About 31 dynasties ruled Egypt over a period of 3,000 ...
... a region with a united people and a single government. King Narmer’s rule became known as the first dynasty A dynasty is a series of rulers from the same family About 31 dynasties ruled Egypt over a period of 3,000 ...
File
... ◦ Pharaohs began the long, difficult process of building their tombs as soon as they came to power ◦ Pyramid- huge buildings with four sloping triangleshaped sides ◦ Giza- location of important pyramids ◦ Could take 20 years to build by slaves and other ...
... ◦ Pharaohs began the long, difficult process of building their tombs as soon as they came to power ◦ Pyramid- huge buildings with four sloping triangleshaped sides ◦ Giza- location of important pyramids ◦ Could take 20 years to build by slaves and other ...
Ahmose founded a new dynasty of pharaohs and
... Ahmose founded a new dynasty of pharaohs and began the period known as the New Kingdom. During this time, most pharaohs were no longer content to stay in the Nile Valley. After defeating and expelling the Hyksos, the pharaohs marched their armies into lands to the east. It was during this time that ...
... Ahmose founded a new dynasty of pharaohs and began the period known as the New Kingdom. During this time, most pharaohs were no longer content to stay in the Nile Valley. After defeating and expelling the Hyksos, the pharaohs marched their armies into lands to the east. It was during this time that ...
Chapter 7: Egypt and Kush Fill
... 5. Which Egyptian ruler do you think served the people better, Hatshepsut or Thutmose III? Why? ...
... 5. Which Egyptian ruler do you think served the people better, Hatshepsut or Thutmose III? Why? ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... days for holidays and feasts. It fell short of the true solar year by only 6 hours. Also, numbers were used, though there was no concept of zero. Their medicine was excellent for the time, with knowledge of how to take a pulse, splint broken limbs, and how to perform surgery. ...
... days for holidays and feasts. It fell short of the true solar year by only 6 hours. Also, numbers were used, though there was no concept of zero. Their medicine was excellent for the time, with knowledge of how to take a pulse, splint broken limbs, and how to perform surgery. ...
Egypt - Bonar Law Memorial
... • It was 60M high • It stands as a symbol of the ultimate power enjoyed by Egyptian Kings ...
... • It was 60M high • It stands as a symbol of the ultimate power enjoyed by Egyptian Kings ...
Class Lesson Plan
... 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? ______________________________________________________________ 23. What five things did the priest ...
... 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? ______________________________________________________________ 23. What five things did the priest ...
The Land of the Pharaohs
... This is known as the first Intermediate period and would last for 100 years. ...
... This is known as the first Intermediate period and would last for 100 years. ...
File
... each pyramid took around 2030 years to build construction workers, carpenters, water carriers and potters all worked on the pyramids they were mostly made of limestone and granite the pharaoh Khufu built the first and largest pyramid in Giza ...
... each pyramid took around 2030 years to build construction workers, carpenters, water carriers and potters all worked on the pyramids they were mostly made of limestone and granite the pharaoh Khufu built the first and largest pyramid in Giza ...
Ancient Egypt - Review Guide
... Describe a festival celebrated in Egypt. Describe the major Egyptian gods: Isis, Osiris, Horus, Anubis, Thoth, Maat, Seth, Ra/Amoun - ra, . What were their roles? Why were many Egyptian deities associated with animals or given animal characteristics? Why was the preservation of the body after death ...
... Describe a festival celebrated in Egypt. Describe the major Egyptian gods: Isis, Osiris, Horus, Anubis, Thoth, Maat, Seth, Ra/Amoun - ra, . What were their roles? Why were many Egyptian deities associated with animals or given animal characteristics? Why was the preservation of the body after death ...

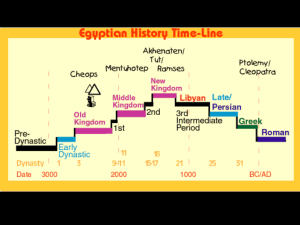







![Ancient_Egypt_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003961717_1-e60e333be34cd6eff9a295b52d154e89-300x300.png)