Chapter 3 Section 2
... A. King Tutankhamen-became ruler of Egypt as a child (age 8) and ruled until age 18 when he died. (tomb shows wealth of Egypt) B. Hatshepsut-ruled for 15 years a. originally ruled as regent for her stepson-would not give up power when he was old enough to rule b. time of peace and economic success c ...
... A. King Tutankhamen-became ruler of Egypt as a child (age 8) and ruled until age 18 when he died. (tomb shows wealth of Egypt) B. Hatshepsut-ruled for 15 years a. originally ruled as regent for her stepson-would not give up power when he was old enough to rule b. time of peace and economic success c ...
Ch. 3 Reading Questions
... occasionally worried Egypt. The relationship with Egypt was always full of tension, but many explorers still traveled between the two. Many Nubians looked for an improved fortune in Egypt, and many Egyptians looked to Nubia for trade. 5. How did the invasion of the Hyksos influence the later develop ...
... occasionally worried Egypt. The relationship with Egypt was always full of tension, but many explorers still traveled between the two. Many Nubians looked for an improved fortune in Egypt, and many Egyptians looked to Nubia for trade. 5. How did the invasion of the Hyksos influence the later develop ...
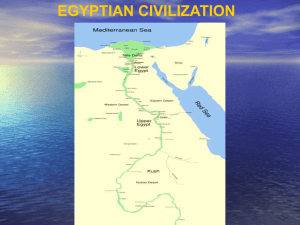
Geography and Early Egypt
... issued at Memphis in 196 BCE on behalf of King Ptolemy V. The decree appears in three scripts: the upper text is Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, the middle portion Demotic script, and the lowest Ancient Greek. Because it presents essentially the same text in all three scripts (with some minor differen ...
... issued at Memphis in 196 BCE on behalf of King Ptolemy V. The decree appears in three scripts: the upper text is Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, the middle portion Demotic script, and the lowest Ancient Greek. Because it presents essentially the same text in all three scripts (with some minor differen ...
Notes 12-15-15 - Hewlett
... the people prospered. It was considered a golden age of stability because a new dynasty came to power after 200 years of confusion and battles among the nobles. This new dynasty moved the capital to Thebes from the old capital of Memphis. The Middle Kingdom lasted from about 2050 BCE to 1670 BCE. ...
... the people prospered. It was considered a golden age of stability because a new dynasty came to power after 200 years of confusion and battles among the nobles. This new dynasty moved the capital to Thebes from the old capital of Memphis. The Middle Kingdom lasted from about 2050 BCE to 1670 BCE. ...
Ancient Egypt
... Not completely sure, but Egypt might have been unified by a king named Scorpion…or maybe it was Narmer A new capital was created at Memphis, where the kingdoms met…was the first of 31 dynasties for 2,600 years Egyptians pharaohs (god kings) were worshiped as real gods ...
... Not completely sure, but Egypt might have been unified by a king named Scorpion…or maybe it was Narmer A new capital was created at Memphis, where the kingdoms met…was the first of 31 dynasties for 2,600 years Egyptians pharaohs (god kings) were worshiped as real gods ...
No Slide Title
... Pharaohs organized a strong central state, were absolute rulers, and were considered gods. ...
... Pharaohs organized a strong central state, were absolute rulers, and were considered gods. ...
The Egyptian Empire
... The Drive for More Land • During the Middle Kingdom, Egypt took control of new lands • Conquered peoples sent tribute to the Egyptian pharaoh enriching the kingdom. – forced payments ...
... The Drive for More Land • During the Middle Kingdom, Egypt took control of new lands • Conquered peoples sent tribute to the Egyptian pharaoh enriching the kingdom. – forced payments ...
File
... Who were the leaders during the Middle Kingdom? The pharaohs. When does the New Kingdom occur? From 1550 – 1050 BC How did the Egyptians build an empire? (Where and who did they conquer?) After battling the Hyksos, Egypt’s leaders feared future invasions. To prevent such invasions from occurring, th ...
... Who were the leaders during the Middle Kingdom? The pharaohs. When does the New Kingdom occur? From 1550 – 1050 BC How did the Egyptians build an empire? (Where and who did they conquer?) After battling the Hyksos, Egypt’s leaders feared future invasions. To prevent such invasions from occurring, th ...
Study Guide Chapter 3 Test Social Studies
... Manetho was a priest and scribe who first started to report information about Egyptian rulers. Hatshepsut was a powerful female pharaoh who wore a fake beard. Nubian written language is called Meroitic. The geography (land forms) of Nubia and Egypt were very different Kings were called Pharaohs in t ...
... Manetho was a priest and scribe who first started to report information about Egyptian rulers. Hatshepsut was a powerful female pharaoh who wore a fake beard. Nubian written language is called Meroitic. The geography (land forms) of Nubia and Egypt were very different Kings were called Pharaohs in t ...
What is Papyrus and why was it important to the Egyptians?
... The invention helped make the Egyptian’s central government possible. Papyrus kept important written records for their society. ...
... The invention helped make the Egyptian’s central government possible. Papyrus kept important written records for their society. ...
Ancient Egypt
... – Caused sun to rise, Nile to flood, crops to grow, as well as promote truth and justice ...
... – Caused sun to rise, Nile to flood, crops to grow, as well as promote truth and justice ...
Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death
... During the Old Kingdom, only the pharaohs had expected to live forever. During the Middle Kingdom, Egyptians came to believe that ordinary people had eternal souls as well. Above: Coffin of a Middle Kingdom Official ...
... During the Old Kingdom, only the pharaohs had expected to live forever. During the Middle Kingdom, Egyptians came to believe that ordinary people had eternal souls as well. Above: Coffin of a Middle Kingdom Official ...
File - Dameron`s World History
... • King in Lower Egypt had a red crown • King in Upper Egypt had a white crown • When two become one…a new crown! • The two were united by king Narmer • A new capital was created at Memphis, where the kingdoms met…was the first of 31 dynasties for 2,600 years • Egyptians pharaohs (god kings) were wor ...
... • King in Lower Egypt had a red crown • King in Upper Egypt had a white crown • When two become one…a new crown! • The two were united by king Narmer • A new capital was created at Memphis, where the kingdoms met…was the first of 31 dynasties for 2,600 years • Egyptians pharaohs (god kings) were wor ...
File - Teacher Anthoney
... In the New Kingdom, Egypt reached the height of its power Akhenaton tried to change Egypt's religion, while Tutankhamen is famous for his tomb Under Ramses II, Egypt built great temples, but the empire fell by 1150 B.C. ...
... In the New Kingdom, Egypt reached the height of its power Akhenaton tried to change Egypt's religion, while Tutankhamen is famous for his tomb Under Ramses II, Egypt built great temples, but the empire fell by 1150 B.C. ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Egypt Multiple Choice – This section will be
... 11. This is the capital of Egypt’s Old Kingdom and is located on the Nile River. Memphis 12. This city became the capital of Egypt’s New Kingdom. Thebes 13. The world’s longest river, which flows northward through East Africa into the Mediterranean Sea is called the Nile River. 14. The Valley of the ...
... 11. This is the capital of Egypt’s Old Kingdom and is located on the Nile River. Memphis 12. This city became the capital of Egypt’s New Kingdom. Thebes 13. The world’s longest river, which flows northward through East Africa into the Mediterranean Sea is called the Nile River. 14. The Valley of the ...
Impact of Geography
... 46. The pharaoh _____________________________ _____ introduced the worship of _______________, god of the sun disk, as the _______________ god. 47. Amenhotep changed his own name to Akhenaton and closed the temples of other gods. 48. Akhenton’s changes were soon undone after his death by the boy-pha ...
... 46. The pharaoh _____________________________ _____ introduced the worship of _______________, god of the sun disk, as the _______________ god. 47. Amenhotep changed his own name to Akhenaton and closed the temples of other gods. 48. Akhenton’s changes were soon undone after his death by the boy-pha ...
African Canadian Studies Early African Civilizations: Egypt
... Egyptians used brushes and ink to write on these reed strips Egyptian system of writing Egyptians dug a canal to connect the Nile River to this body of water Built huge stone pyramids for their burials Line of hereditary rulers Collection of stories and traditions ...
... Egyptians used brushes and ink to write on these reed strips Egyptian system of writing Egyptians dug a canal to connect the Nile River to this body of water Built huge stone pyramids for their burials Line of hereditary rulers Collection of stories and traditions ...
Egyptian & Nubian Empires
... • Both the Egyptian empire and the Hittites were attacked by invaders referred to as the “Sea Peoples” that caused great destruction. • The Sahara to the west no longer protected Egypt and it was repeated raided by Libyans. ...
... • Both the Egyptian empire and the Hittites were attacked by invaders referred to as the “Sea Peoples” that caused great destruction. • The Sahara to the west no longer protected Egypt and it was repeated raided by Libyans. ...
King who first united upper and lower Egypt. Ancient Egyptian
... King who first united upper and lower Egypt. Ancient Egyptian system of writing. Name for an archaeologist who studies only ancient Egypt. ...
... King who first united upper and lower Egypt. Ancient Egyptian system of writing. Name for an archaeologist who studies only ancient Egypt. ...
Ancient Egypt Study Guide
... _____ 7. Famous pharaoh of the Old Kingdom; responsible for building the Great Pyramid _____ 8. Goods traded that are sent out to other regions _____ 9. Located in southern Egypt; called this because it was uphill _____ 10. A series of rulers from the same family _____ 11. Goods traded that are brou ...
... _____ 7. Famous pharaoh of the Old Kingdom; responsible for building the Great Pyramid _____ 8. Goods traded that are sent out to other regions _____ 9. Located in southern Egypt; called this because it was uphill _____ 10. A series of rulers from the same family _____ 11. Goods traded that are brou ...
Ancient Egypt Study Guide
... a. The Nile River brought fertility and life to the region. 2. Why did the Egyptians blame the pharaoh if the crops did not grow or if disease struck? a. He was considered both ruler and god 3. What was the purpose of the pyramids? a. They were tombs for the pharaohs so they could be happy in the af ...
... a. The Nile River brought fertility and life to the region. 2. Why did the Egyptians blame the pharaoh if the crops did not grow or if disease struck? a. He was considered both ruler and god 3. What was the purpose of the pyramids? a. They were tombs for the pharaohs so they could be happy in the af ...
Ancient Egypt
... • Egyptians believed that humans possessed a ka, or life-force, which left the body at the point of death. In life, the ka received its sustenance from food and drink. Each person also had a ba, the set of spiritual characteristics unique to each individual.[30] Unlike the ka, the ba remained attach ...
... • Egyptians believed that humans possessed a ka, or life-force, which left the body at the point of death. In life, the ka received its sustenance from food and drink. Each person also had a ba, the set of spiritual characteristics unique to each individual.[30] Unlike the ka, the ba remained attach ...
File
... http://www.history.com/topics/ancienthistory/videos#massive-stones-moved-tobuild-monuments ...
... http://www.history.com/topics/ancienthistory/videos#massive-stones-moved-tobuild-monuments ...