Ancient Egypt 16
... •Unlike Mesopotamia, river serene and predictable •River was everything to Egyptians: life and communication ...
... •Unlike Mesopotamia, river serene and predictable •River was everything to Egyptians: life and communication ...
Egypt Test 2
... 19. The Nile is the second longest river in the world behind the Mississippi. _________ 20. Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife.________ 21. Menes is credited with unifying upper and lower Egypt. _____________ 22. The Nile has two main branches the White Nile and the Blue Nile. _____________ ...
... 19. The Nile is the second longest river in the world behind the Mississippi. _________ 20. Egyptian religion focused on the afterlife.________ 21. Menes is credited with unifying upper and lower Egypt. _____________ 22. The Nile has two main branches the White Nile and the Blue Nile. _____________ ...
Davidson
... Pharaohs had placed in tribute. Then the tide of conquest turns upon itself for a while, and sweeps up from the southward. The early kings of Kush, a state whose capital was at Napata (towards the region that had once been Irthet or Wawat for the great Imperial Pharaohs of an already distant past), ...
... Pharaohs had placed in tribute. Then the tide of conquest turns upon itself for a while, and sweeps up from the southward. The early kings of Kush, a state whose capital was at Napata (towards the region that had once been Irthet or Wawat for the great Imperial Pharaohs of an already distant past), ...
Ancient Egyptian Art Where is Egypt?
... geography of the region, Ancient Egyptian civilization developed beside the Nile River. ...
... geography of the region, Ancient Egyptian civilization developed beside the Nile River. ...
What we want to find out about egypt
... • 3.Thirdly they removed some of there inner parts of the body first. The organs were taken out and stored in special containers called canopic jars. • 4.The hart was left in the body however, so that it could be weighed in the after life. • 5.Then they rubbed the body with special ointments and wra ...
... • 3.Thirdly they removed some of there inner parts of the body first. The organs were taken out and stored in special containers called canopic jars. • 4.The hart was left in the body however, so that it could be weighed in the after life. • 5.Then they rubbed the body with special ointments and wra ...
Ancient Egyptian History
... related to our current form of the calendar. Our evidence of their order comes mostly from various "kings' lists, that almost exclusively were made during the New Kingdom. Another source is the Egyptian history written by Manetho, an Egyptian priest, but over the years, there have been modifications ...
... related to our current form of the calendar. Our evidence of their order comes mostly from various "kings' lists, that almost exclusively were made during the New Kingdom. Another source is the Egyptian history written by Manetho, an Egyptian priest, but over the years, there have been modifications ...
The Egyptians were masters of trade in the ancient world. Stimulated
... promoting friendship between civilizations. Gifts were given to show that one country wanted peace and/or alliance with another. Strangely, princesses were commonly given from one country (or ruler) to another! This may explain why Ramses II has over 100 wives! Sometimes, Egypt determined how much o ...
... promoting friendship between civilizations. Gifts were given to show that one country wanted peace and/or alliance with another. Strangely, princesses were commonly given from one country (or ruler) to another! This may explain why Ramses II has over 100 wives! Sometimes, Egypt determined how much o ...
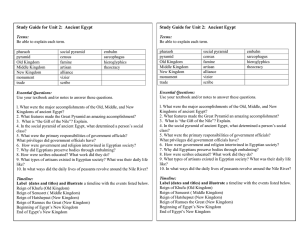
Study Guide for Unit 2: Ancient Egypt Study Guide for Unit 2
... 4. In the social pyramid of ancient Egypt, what determined a person’s social class? 5. What were the primary responsibilities of government officials? What privileges did government officials have? 6. How were government and religion intertwined in Egyptian society? 7. Why did Egyptians preserve bod ...
... 4. In the social pyramid of ancient Egypt, what determined a person’s social class? 5. What were the primary responsibilities of government officials? What privileges did government officials have? 6. How were government and religion intertwined in Egyptian society? 7. Why did Egyptians preserve bod ...
Ch. 5 Egypt: Lesson 1,2,3 Test Review Valley
... Created fractions, using them with whole numbers to add, subtract, and divide. Egypt’s Empire Around 2200 b.c., ruling pharaohs in Memphis began to weaken. Ambitious nobles fought for control. More than 200 years, disorder and violence swept through the region. A new dynasty of pharaohs came to powe ...
... Created fractions, using them with whole numbers to add, subtract, and divide. Egypt’s Empire Around 2200 b.c., ruling pharaohs in Memphis began to weaken. Ambitious nobles fought for control. More than 200 years, disorder and violence swept through the region. A new dynasty of pharaohs came to powe ...
Nubia and Ancient Egypt
... Christianity in the 6th cent. A.D. • Joined with the Christian kingdom of Ethiopia, it long resisted Muslim encroachment, but in the 14th cent. it finally collapsed. ...
... Christianity in the 6th cent. A.D. • Joined with the Christian kingdom of Ethiopia, it long resisted Muslim encroachment, but in the 14th cent. it finally collapsed. ...
File
... Christianity in the 6th cent. A.D. • Joined with the Christian kingdom of Ethiopia, it long resisted Muslim encroachment, but in the 14th cent. it finally collapsed. ...
... Christianity in the 6th cent. A.D. • Joined with the Christian kingdom of Ethiopia, it long resisted Muslim encroachment, but in the 14th cent. it finally collapsed. ...
8th World History Egypt Notes Sumerians The ________fertile
... o Ramses conquered Canaan and Syria in the Fertile Crescent and also attacked the ______persians_______________. Ramses lost and later made peace by agreeing on a border for the two civilizations. o During his reign he built more monuments than any other pharaoh. ...
... o Ramses conquered Canaan and Syria in the Fertile Crescent and also attacked the ______persians_______________. Ramses lost and later made peace by agreeing on a border for the two civilizations. o During his reign he built more monuments than any other pharaoh. ...
Egypt powerpoint
... Lower Egypt, and, thus, creating a united Egypt – he built a capital city at Memphis--located between both kingdoms ...
... Lower Egypt, and, thus, creating a united Egypt – he built a capital city at Memphis--located between both kingdoms ...
Chapter 2 Project (Global)
... • Egypt was divided into three main periods; Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom. (from about 2700 b.c.- 1100 b.c.) • In the Old kingdom, Egyptian rulers called Pharaohs organized a strong, centralized state. Egyptians believed the pharaoh was a God. Therefore pharaohs had absolute power, o ...
... • Egypt was divided into three main periods; Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom. (from about 2700 b.c.- 1100 b.c.) • In the Old kingdom, Egyptian rulers called Pharaohs organized a strong, centralized state. Egyptians believed the pharaoh was a God. Therefore pharaohs had absolute power, o ...
Chapter 2
... After a period of conquest and reconquest the Sumerian city-states fell to foreign invaders in the 2000s BC o The invaders were inspired by dreams of empire. Akkadians: The Akkadians, were Semites that had migrated from the Arabian Peninsula around 5000BC. They established a kingdom called Akkad ...
... After a period of conquest and reconquest the Sumerian city-states fell to foreign invaders in the 2000s BC o The invaders were inspired by dreams of empire. Akkadians: The Akkadians, were Semites that had migrated from the Arabian Peninsula around 5000BC. They established a kingdom called Akkad ...
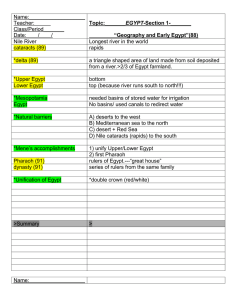
Topic:_______EGYPT-Section 1
... wealth/power of pharaohs declined (goes down) *Nobles begin to challenge pharaohs Nobles come to power>
... wealth/power of pharaohs declined (goes down) *Nobles begin to challenge pharaohs Nobles come to power>
chap 2_ sec 3 egyptian empire
... when the Egyptian prince Ahmose led a revolt to drive the Hykos out of Egypt. ...
... when the Egyptian prince Ahmose led a revolt to drive the Hykos out of Egypt. ...
Egypt Old Kingdom
... these flourishing settlements, which originally had little contact, began to establish strong links with each other. The newly formed bonds gave rise to the creation of two new kingdoms, that of Lower Egypt, in the Nile Delta, and that of Upper Egypt in the south. 1. What does the word nomadic mean? ...
... these flourishing settlements, which originally had little contact, began to establish strong links with each other. The newly formed bonds gave rise to the creation of two new kingdoms, that of Lower Egypt, in the Nile Delta, and that of Upper Egypt in the south. 1. What does the word nomadic mean? ...
Chapter 4 Sections 1 and 2
... • The household consisted on the owners family, servants, and artisans ...
... • The household consisted on the owners family, servants, and artisans ...
Life in the Old Kingdom
... 4. Most famous pharaoh of Old Kingdom: Khufu –cruel but people who served him were well fed. Many monuments built to him. (pyramids…) Society and Trade • Egypt’s population at end of Old Kingdom: 2 million • Social Classes in Egypt: the Egyptians believed that if their society was well-ordered it wo ...
... 4. Most famous pharaoh of Old Kingdom: Khufu –cruel but people who served him were well fed. Many monuments built to him. (pyramids…) Society and Trade • Egypt’s population at end of Old Kingdom: 2 million • Social Classes in Egypt: the Egyptians believed that if their society was well-ordered it wo ...
New Kingdom Egypt Grows Strong - Mr. Wisell`s Global History Web
... peace treaty, the first such document in history known to have survived. It declared that Egypt and the Hittites “shall be at peace and in brotherhood forever.” To the south of Egypt, Nubia developed along the Nile. For centuries, Egyptians traded or fought with their southern neighbor. From Nubia, ...
... peace treaty, the first such document in history known to have survived. It declared that Egypt and the Hittites “shall be at peace and in brotherhood forever.” To the south of Egypt, Nubia developed along the Nile. For centuries, Egyptians traded or fought with their southern neighbor. From Nubia, ...
File
... power during this period and continued massive construction projects. Eventually, the long reign of prosperity gave way to old problems: crop failures, economic woes, dynastic power struggles, and foreign invaders. ...
... power during this period and continued massive construction projects. Eventually, the long reign of prosperity gave way to old problems: crop failures, economic woes, dynastic power struggles, and foreign invaders. ...