The Rise of Civilization in Egypt
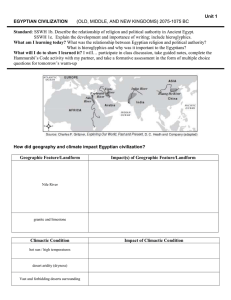
... Egypt is located in North Africa. Although most of Egypt is occupied by desert, the world’s longest river, the Nile runs through it. Historians call Egypt “the gift of the Nile” because the Nile River provides water for farming. Every spring, snows melt in the mountains of eastern Africa. Rain falls ...
... Egypt is located in North Africa. Although most of Egypt is occupied by desert, the world’s longest river, the Nile runs through it. Historians call Egypt “the gift of the Nile” because the Nile River provides water for farming. Every spring, snows melt in the mountains of eastern Africa. Rain falls ...
Student Information 8.2 Ancient Egypt and Its Rulers As in
... Built to celebrate Senusret’s 30th year as ruler of Egypt. Made of alabaster, a hard white stone. Some historians believe that it was covered with a thin layer of gold. Artwork and hieroglyphics decorated the chapel’s pillars (columns). The scenes showed Senusret with many gods. Once Senus ...
... Built to celebrate Senusret’s 30th year as ruler of Egypt. Made of alabaster, a hard white stone. Some historians believe that it was covered with a thin layer of gold. Artwork and hieroglyphics decorated the chapel’s pillars (columns). The scenes showed Senusret with many gods. Once Senus ...
ancient egypt
... “First they draw out the brains through the nostrils with an iron hook…then with a sharp stone they make an incision in the side, and take out all the bowels…then, having filled the belly with pure myrrh, cassia, and other perfumes, they sew it up again; and when they have done this they steep it in ...
... “First they draw out the brains through the nostrils with an iron hook…then with a sharp stone they make an incision in the side, and take out all the bowels…then, having filled the belly with pure myrrh, cassia, and other perfumes, they sew it up again; and when they have done this they steep it in ...
Egyptian Society - Cherry Creek Academy
... • The homes of the wealthy were larger and more luxurious. • SPACIOUS reception and living rooms opened onto a central garden court yard with a fish pond and flowering plants. • Each bedroom had a private bathroom, and the walls, columns and ceilings were painted with beautiful designs inspired by ...
... • The homes of the wealthy were larger and more luxurious. • SPACIOUS reception and living rooms opened onto a central garden court yard with a fish pond and flowering plants. • Each bedroom had a private bathroom, and the walls, columns and ceilings were painted with beautiful designs inspired by ...
Notes
... o stronger city-states controlled the larger areas o city-states began fighting each other to gain more farmland o City-states built strong armies and built walls around their cities for protection ...
... o stronger city-states controlled the larger areas o city-states began fighting each other to gain more farmland o City-states built strong armies and built walls around their cities for protection ...
Unit 1 - EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION
... - 3000 BC unification under King Narmer, first Egyptian dynasty centered at Memphis where Upper and lower Egypt meet. - Egyptian Civilization was united under one leader called a pharaoh = _______________________________ - pharaohs had absolute power and owned all land; however, they were expected t ...
... - 3000 BC unification under King Narmer, first Egyptian dynasty centered at Memphis where Upper and lower Egypt meet. - Egyptian Civilization was united under one leader called a pharaoh = _______________________________ - pharaohs had absolute power and owned all land; however, they were expected t ...
Ancient Egypt - sheehansocialstudies
... The Pharaoh was the ruler of the economy, which means he managed how money and resources were used. Egypt was able to thrive and be successful because farmers produced a lot of extra food that could be used for trade. The Pharaoh collected taxes from everyone, usually in the form of food and goods. ...
... The Pharaoh was the ruler of the economy, which means he managed how money and resources were used. Egypt was able to thrive and be successful because farmers produced a lot of extra food that could be used for trade. The Pharaoh collected taxes from everyone, usually in the form of food and goods. ...
YearsPeriods / DynastiesMain events and
... founds a new royal residence near Memphis Egypt conquers Lower Nubia under Senwosret I and III Classical period of art and literature xxxx 1630- 1520 BC2nd Intermediate Period (15th-17th Dynasties)Hyksos kings gets the white crownTheban 17th dynasty starts in the south xxxx 1539-1075 BCNew Kingdom ( ...
... founds a new royal residence near Memphis Egypt conquers Lower Nubia under Senwosret I and III Classical period of art and literature xxxx 1630- 1520 BC2nd Intermediate Period (15th-17th Dynasties)Hyksos kings gets the white crownTheban 17th dynasty starts in the south xxxx 1539-1075 BCNew Kingdom ( ...
First Age of Empires 1570 B.C.–200 B.C..
... develop warlike behavior in response to invasions – Assyrian kings built an empire with constant warfare ...
... develop warlike behavior in response to invasions – Assyrian kings built an empire with constant warfare ...
The Egyptian Empire The New Kingdom Expanding the Empire
... Unlike modern churches, temples, and mosques, Egyptian temples did not hold regular religious services. Instead, most Egyptians prayed at home. They considered the temples as houses for the gods and goddesses. Priests and priestesses, however, performed daily temple _______________, washing statu ...
... Unlike modern churches, temples, and mosques, Egyptian temples did not hold regular religious services. Instead, most Egyptians prayed at home. They considered the temples as houses for the gods and goddesses. Priests and priestesses, however, performed daily temple _______________, washing statu ...
Egypt - LaVergne Middle School
... • Monarchy/Theocracy- king (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). S ...
... • Monarchy/Theocracy- king (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). S ...
The Rise of Civilization
... from reddish brown clay. Pottery was often left undecorated, they had not painted them but they had made statues and sculptures out of the clay. They also carved designs into them using various tools. ● Hieroglyphics were found in many tombs and on many ancient scriptures. They were used to tell sto ...
... from reddish brown clay. Pottery was often left undecorated, they had not painted them but they had made statues and sculptures out of the clay. They also carved designs into them using various tools. ● Hieroglyphics were found in many tombs and on many ancient scriptures. They were used to tell sto ...
Ancient Egypt Review ppt.
... • He was the first of a dynasty which lasted many years • The time periods were divided in Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms • Pharaoh appointed bureaucrats to help govern • A government with the pharaoh as political and religious leader is a theocracy ...
... • He was the first of a dynasty which lasted many years • The time periods were divided in Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms • Pharaoh appointed bureaucrats to help govern • A government with the pharaoh as political and religious leader is a theocracy ...
Name___________________________________
... Achievements of the Egyptians The ancient Egyptians were skilled architects, sculptors, and engineers. But they excelled in other areas, too. For example, they created an accurate lunar calendar. The Babylonians had also invented a calendar based on the moon’s cycles, but the Egyptian calendar was m ...
... Achievements of the Egyptians The ancient Egyptians were skilled architects, sculptors, and engineers. But they excelled in other areas, too. For example, they created an accurate lunar calendar. The Babylonians had also invented a calendar based on the moon’s cycles, but the Egyptian calendar was m ...
Ch 2 section 1 and 2
... • The political basis of Egypt was a kingship in which the throne was passed on to the oldest son of the pharaoh. ...
... • The political basis of Egypt was a kingship in which the throne was passed on to the oldest son of the pharaoh. ...
Egypt GRAPES - LaVergne Middle School
... • Monarchy/Theocracy- king (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). S ...
... • Monarchy/Theocracy- king (pharaoh); political and religious leader • Dynasty- same family rules for many generations • Upper and Lower Egypt were once divided until Pharaoh Narmer (Menes) conquered lower Egypt, married a princess, and united them into 1 empire. Wore the double crown (red/white). S ...
Religious Beliefs CIVILIZATION IN EGYPT The Natural Environment
... The modem stereotype of an Ancient Egyptian is generally that of a person with dark, straight hair and clay-colored skin. In reality, even before the New Kingdom, Egyptians ranged from dark-skinned people related to the populations of Sub-Saharan Africa to lighter-skinned people related to inhabitan ...
... The modem stereotype of an Ancient Egyptian is generally that of a person with dark, straight hair and clay-colored skin. In reality, even before the New Kingdom, Egyptians ranged from dark-skinned people related to the populations of Sub-Saharan Africa to lighter-skinned people related to inhabitan ...
Station 1: Explain why Egyptian civilization began in the Nile River
... 1. wild rapids found on the Nile River. CATARACTS ...
... 1. wild rapids found on the Nile River. CATARACTS ...
Rivard Rivard While the societies of Ancient Egypt and the Ottoman
... While the societies of Ancient Egypt and the Ottoman Turks were similar in creating many new things such as building new inventions like the ramp or creating schools, they were different because their societies went in different ways like the Ottomans focused on expanding their empire and the Egypti ...
... While the societies of Ancient Egypt and the Ottoman Turks were similar in creating many new things such as building new inventions like the ramp or creating schools, they were different because their societies went in different ways like the Ottomans focused on expanding their empire and the Egypti ...
The royal titulary
... deity of Upper Egypt. Wadjet, the cobra goddess (c), represented Lower Egypt. The cobra or snake goddess was also closely linked with the Uraeus, the snake image of kingship. ...
... deity of Upper Egypt. Wadjet, the cobra goddess (c), represented Lower Egypt. The cobra or snake goddess was also closely linked with the Uraeus, the snake image of kingship. ...
Chapter 3
... Trade and Technology: 1. What made the Egyptian economy more prosperous? 2. How did the growth of trade in the Middle Kingdom affect Egypt’s economy? New Kingdom Pharaohs: 1. Why did Akhenaten’s advisors take control? 2. What was different about how some pharaohs ruled during the new Kingdom? Nubia ...
... Trade and Technology: 1. What made the Egyptian economy more prosperous? 2. How did the growth of trade in the Middle Kingdom affect Egypt’s economy? New Kingdom Pharaohs: 1. Why did Akhenaten’s advisors take control? 2. What was different about how some pharaohs ruled during the new Kingdom? Nubia ...
Egyptian Society
... • Ruled from 1279 BCE – 1213 BCE (60 years) • Considered to be one of the most famous pharaohs of Egypt • A neighboring group called the Hittites tried to take control of Egypt and Ramses led the Egyptian army to victory – Battle of Kadesh in 1274 BCE ...
... • Ruled from 1279 BCE – 1213 BCE (60 years) • Considered to be one of the most famous pharaohs of Egypt • A neighboring group called the Hittites tried to take control of Egypt and Ramses led the Egyptian army to victory – Battle of Kadesh in 1274 BCE ...
Geography of the Ancient Nile Valley
... the branch that deals with private rights and matters, such as business contracts, taxes, and property inheritance. ...
... the branch that deals with private rights and matters, such as business contracts, taxes, and property inheritance. ...
Egypt Notes
... • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
... • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...