Egypt ppt. 2014
... – Not able to build a conquering army – No massive public works projects (lack of funds) – Capital moved to Thebes for new temple, it was never completed. ...
... – Not able to build a conquering army – No massive public works projects (lack of funds) – Capital moved to Thebes for new temple, it was never completed. ...
Chapter 3 Egypt
... • Decisively unified about 3100 BCE under a pharaoh • Foundation period (3100200 BCE) – greatest triumphs, cultural achievements ...
... • Decisively unified about 3100 BCE under a pharaoh • Foundation period (3100200 BCE) – greatest triumphs, cultural achievements ...
Chapter 2 section 1 and 2 Test Review (with answers) (Section 1
... What was their system of writing known as? Cuneiform How many laws did Hammurabi have in his code? 282 (Chapter 2 Section 2 material) Delta: land formed by silt deposits at mouth of a river Narmer: Egyptian king that united Upper and Lower Egypt. Pharaoh: Kings of Egypt, considered to be gods by Egy ...
... What was their system of writing known as? Cuneiform How many laws did Hammurabi have in his code? 282 (Chapter 2 Section 2 material) Delta: land formed by silt deposits at mouth of a river Narmer: Egyptian king that united Upper and Lower Egypt. Pharaoh: Kings of Egypt, considered to be gods by Egy ...
Ancient Egyptian Civilization
... Hatshepsut was one of only a few female pharaohs and was the first wife of Thutmose II. After Thutmose's death, his son, Thutmose III, (by a minor wife) was named as the heir. Because the boy was so young, Hatshepsut ruled with him until she declared herself as the pharaoh. Dressed not as a lady, bu ...
... Hatshepsut was one of only a few female pharaohs and was the first wife of Thutmose II. After Thutmose's death, his son, Thutmose III, (by a minor wife) was named as the heir. Because the boy was so young, Hatshepsut ruled with him until she declared herself as the pharaoh. Dressed not as a lady, bu ...
Passport to Egypt - Goshen Local School District
... What Are We Going to See? • Today, our class will be visiting ancient sites of pharaohs in Ancient Egypt • What is a Pharaoh?? • A pharaoh is a king of ancient Egypt who had complete control over their people • Temples were built in the pharaoh’s honor ...
... What Are We Going to See? • Today, our class will be visiting ancient sites of pharaohs in Ancient Egypt • What is a Pharaoh?? • A pharaoh is a king of ancient Egypt who had complete control over their people • Temples were built in the pharaoh’s honor ...
02ancientegypt
... • End of civil wars, farming and trade return • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
... • End of civil wars, farming and trade return • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
EGYPT
... Spoke different dialects and had different customs Dynasty = a series of rulers from the same family There were a total of 31 dynasties ...
... Spoke different dialects and had different customs Dynasty = a series of rulers from the same family There were a total of 31 dynasties ...
File - Mrs. King`s World History Website
... Learned scribes played a central role in Egyptian society. Some kept records of ceremonies, taxes, and gifts. Others served government officials or the pharaoh. Scribes also acquired skills in mathematics, medicine, and engineering. With skill and luck, a scribe from a poor family might become rich ...
... Learned scribes played a central role in Egyptian society. Some kept records of ceremonies, taxes, and gifts. Others served government officials or the pharaoh. Scribes also acquired skills in mathematics, medicine, and engineering. With skill and luck, a scribe from a poor family might become rich ...
Notes- Daily Life in Egypt Name Period ______ Daily Life in Ancient
... While Egypt becomes a ______________empire, ordinary people continued to work in much the same ways as they had for thousands of years. Enslaved Syrians and Nubians became key workers in Egypt’s empire. They worked alongside ______________ and craft workers to produce needed crops and goods. M ...
... While Egypt becomes a ______________empire, ordinary people continued to work in much the same ways as they had for thousands of years. Enslaved Syrians and Nubians became key workers in Egypt’s empire. They worked alongside ______________ and craft workers to produce needed crops and goods. M ...
Pharaoh
... •Osiris was the god of the Underworld and resurrection. •It is from the story of his death and resurrection, that Egyptians got their belief in the importance of mummification. ...
... •Osiris was the god of the Underworld and resurrection. •It is from the story of his death and resurrection, that Egyptians got their belief in the importance of mummification. ...
File
... •Osiris was the god of the Underworld and resurrection. •It is from the story of his death and resurrection, that Egyptians got their belief in the importance of mummification. ...
... •Osiris was the god of the Underworld and resurrection. •It is from the story of his death and resurrection, that Egyptians got their belief in the importance of mummification. ...
Egypt - Issaquah Connect
... Ruled by pharaohs – generational – family member Pharaohs in charge of trade Theocracy – ruled by one Three kingdoms (time periods) – Old, middle ,new Controlled both upper and lower Egypt Pharaoh’s thought of as a god – like a dictator Appointed bureaucrats and political leaders to carry out his or ...
... Ruled by pharaohs – generational – family member Pharaohs in charge of trade Theocracy – ruled by one Three kingdoms (time periods) – Old, middle ,new Controlled both upper and lower Egypt Pharaoh’s thought of as a god – like a dictator Appointed bureaucrats and political leaders to carry out his or ...
Egypt - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 3. Which leader did God use to deliver Israel out of Egyptian bondage? a) Joseph b) Moses c) Jacob d) Solomon 4. This 18th Dynasty hot-shot was able to re-establish control over Syria AND Nubia. Historians often call him “The Napoleon of Ancient Egypt.” a) Tuthmosis III b) Akhenaten c) Amenhotep III ...
... 3. Which leader did God use to deliver Israel out of Egyptian bondage? a) Joseph b) Moses c) Jacob d) Solomon 4. This 18th Dynasty hot-shot was able to re-establish control over Syria AND Nubia. Historians often call him “The Napoleon of Ancient Egypt.” a) Tuthmosis III b) Akhenaten c) Amenhotep III ...
Chpt. 2 prentice hall world history
... as a demonstration of the strength and wealth of their society. ...
... as a demonstration of the strength and wealth of their society. ...
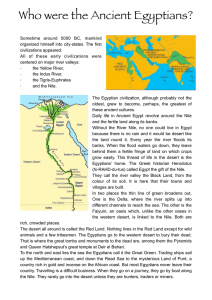
Who were the Ancient Egyptians?
... under the pharaoh. They were the most powerful groups in Egypt. Government officials carried out the orders of the pharaoh. Most of them came from noble families. They were powerful and wealthy, and they enjoyed a high quality of life. Priests were also a powerful group, because religion touched eve ...
... under the pharaoh. They were the most powerful groups in Egypt. Government officials carried out the orders of the pharaoh. Most of them came from noble families. They were powerful and wealthy, and they enjoyed a high quality of life. Priests were also a powerful group, because religion touched eve ...
Name________________________ Ms. Trout
... MM. What led to the end of the Middle Kingdom? Egypt was invaded by the Hyksos, a people from western Asia. NN. How did the Hyksos conquer Egypt? 1. The Hyksos had chariots and weapons made of bronze and iron. 2. The Egyptians fought on foot with weapons of copper and stone, which led to their defea ...
... MM. What led to the end of the Middle Kingdom? Egypt was invaded by the Hyksos, a people from western Asia. NN. How did the Hyksos conquer Egypt? 1. The Hyksos had chariots and weapons made of bronze and iron. 2. The Egyptians fought on foot with weapons of copper and stone, which led to their defea ...
Jeopardy (powerpoint
... Mummification focused on Egyptian belief of the importance of preserving the body Afterlife would be spent enjoying best of life experiences Body covered with natron and dried for up to 70 days Body wrapped in linen coated with resins and oils Middle Kingdom became customary to place a mask over the ...
... Mummification focused on Egyptian belief of the importance of preserving the body Afterlife would be spent enjoying best of life experiences Body covered with natron and dried for up to 70 days Body wrapped in linen coated with resins and oils Middle Kingdom became customary to place a mask over the ...
Egyptian Civilization Fact Sheet
... fought constantly over control of the government. c. By 1000 BCE, iron replaced bronze as the chief metal for weapons and tools (the Iron Age). Egypt fell behind other kingdoms in the production of iron. ...
... fought constantly over control of the government. c. By 1000 BCE, iron replaced bronze as the chief metal for weapons and tools (the Iron Age). Egypt fell behind other kingdoms in the production of iron. ...
Ancient Egypt and Kush
... - Because so many pharaohs built _____________, the Old Kingdom _______________ - The ____________ of the pharaoh was taken away - _____________ disrupted life in Egypt - Invaders, called the ________________, conquered Lower Egypt - Eventually, ______________ defeated the Hyksos and _______________ ...
... - Because so many pharaohs built _____________, the Old Kingdom _______________ - The ____________ of the pharaoh was taken away - _____________ disrupted life in Egypt - Invaders, called the ________________, conquered Lower Egypt - Eventually, ______________ defeated the Hyksos and _______________ ...