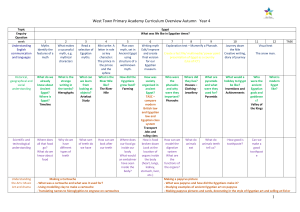
Ancient Egypt Society Map—Semenza Galbo Government and Laws
... 3100 B.C. They overthrew the king of Lower Egypt, and to show his victory, Menes made a new crown. The new crown was pieces from both crown, to show the unification of Egypt. *What are two meanings of the word "pharaoh" (p. 89)? The word Pharaoh refers to “great palace” but now is given to every rul ...
... 3100 B.C. They overthrew the king of Lower Egypt, and to show his victory, Menes made a new crown. The new crown was pieces from both crown, to show the unification of Egypt. *What are two meanings of the word "pharaoh" (p. 89)? The word Pharaoh refers to “great palace” but now is given to every rul ...
Ch 4 Notes
... Following a period of _________________ for power between the nobles and the pharaohs, the Middle Kingdom began. Egypt fell into disorder around 1750 BC. A group called the ___________ invaded and ruled the region for 200 years. The Egyptians fought back, and _____________ of Thebes declared h ...
... Following a period of _________________ for power between the nobles and the pharaohs, the Middle Kingdom began. Egypt fell into disorder around 1750 BC. A group called the ___________ invaded and ruled the region for 200 years. The Egyptians fought back, and _____________ of Thebes declared h ...
Floodplain Civilizations Overview
... • The concept of the afterlife became fully developed during the Middle Kingdom • Amon became god of the living and Osiris god of the dead ...
... • The concept of the afterlife became fully developed during the Middle Kingdom • Amon became god of the living and Osiris god of the dead ...
PPT - FLYPARSONS.org
... • The concept of the afterlife became fully developed during the Middle Kingdom • Amon became god of the living and Osiris god of the dead ...
... • The concept of the afterlife became fully developed during the Middle Kingdom • Amon became god of the living and Osiris god of the dead ...
Egyptian Culture
... authority on the Nile through the use of bronze, which the Egyptians later adapted into their military culture. Iron production (which was also prominent in Anotolia—Hittites—remember?) arose independently from local experimentation in Africa at around 900 b.c.e. ...
... authority on the Nile through the use of bronze, which the Egyptians later adapted into their military culture. Iron production (which was also prominent in Anotolia—Hittites—remember?) arose independently from local experimentation in Africa at around 900 b.c.e. ...
5-4 Notes: The New Kingdom
... 1279 BCE – 44 years after Tutankhamen died, Ramses II took power – he ruled for 66 years (longest in Egyptian history!) Ramses expanded Egypt’s territory south into Nubia, an African kingdom, and to the eastern rim of the Mediterranean Sea where it bordered the Hittite empire Ramses II and the Hitti ...
... 1279 BCE – 44 years after Tutankhamen died, Ramses II took power – he ruled for 66 years (longest in Egyptian history!) Ramses expanded Egypt’s territory south into Nubia, an African kingdom, and to the eastern rim of the Mediterranean Sea where it bordered the Hittite empire Ramses II and the Hitti ...
The Egyptian Empire
... 2. Thutmose III, otherwise known as the Napoleon of Egypt, expands Egypt’s army. 3. Amenhotep IV promotes the artists of Egypt and leads to flourish of realism. 4. The Hittites extend their influence to Egypt and become a major political power. Nineteenth Dynasty1. Ramesses II recovers territories i ...
... 2. Thutmose III, otherwise known as the Napoleon of Egypt, expands Egypt’s army. 3. Amenhotep IV promotes the artists of Egypt and leads to flourish of realism. 4. The Hittites extend their influence to Egypt and become a major political power. Nineteenth Dynasty1. Ramesses II recovers territories i ...
Ancient Egypt Overview
... • End of civil wars, farming and trade return • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
... • End of civil wars, farming and trade return • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
Ancient Egypt - FLYPARSONS.org
... • End of civil wars, farming and trade return • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
... • End of civil wars, farming and trade return • move capital south to Upper Egypt (Thebes) • public improvements – drain swamps, canal to Red Sea ...
The Old Kingdom
... 2 Directions: On your own sheet of paper, answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. What were the two regions that made up ancient Egypt? 2. Why was the Nile Delta well suited for settlement? ...
... 2 Directions: On your own sheet of paper, answer the following questions in complete sentences. 1. What were the two regions that made up ancient Egypt? 2. Why was the Nile Delta well suited for settlement? ...
Module 2 - Travel Biz Monitor
... Egypt, the cradle of civilization, is host to the last remaining wonder of the ancient world, and is considered by many to be the place from which modern civilisation arose. So, to understand why the world admires this civilization, we have to return back to the beginning of the story and read caref ...
... Egypt, the cradle of civilization, is host to the last remaining wonder of the ancient world, and is considered by many to be the place from which modern civilisation arose. So, to understand why the world admires this civilization, we have to return back to the beginning of the story and read caref ...
Research Methodologies
... drain swamps. This made even more land available for farming. They also built a canal connecting the Nile River with trade routes near the Red Sea. This improved trade during the Middle Kingdom. Egyptians were able to get various kinds of woods from areas in Southwest Asia. This wood was used to b ...
... drain swamps. This made even more land available for farming. They also built a canal connecting the Nile River with trade routes near the Red Sea. This improved trade during the Middle Kingdom. Egyptians were able to get various kinds of woods from areas in Southwest Asia. This wood was used to b ...
Chapter 3 Ancient Egypt Lesson 1
... • A pharaoh is born into power • Mummified • Honored as a god ...
... • A pharaoh is born into power • Mummified • Honored as a god ...
Egypt is the gift of the Nile
... Slavery was a reality of life for a large part of ancient Egypt's population. Even common people who were nominally free could be conscripted by the king for construction projects during the annual floods, when agricultural work could not be performed. These slaves are being punished for misdeeds. ...
... Slavery was a reality of life for a large part of ancient Egypt's population. Even common people who were nominally free could be conscripted by the king for construction projects during the annual floods, when agricultural work could not be performed. These slaves are being punished for misdeeds. ...
The Rulers of Egypt - Manasquan Public Schools
... of its pharaohs. Men were usually appointed as Pharaoh. Women have made their appearance on the throne Hatshepsut is an example of a powerful woman Pharaoh. ...
... of its pharaohs. Men were usually appointed as Pharaoh. Women have made their appearance on the throne Hatshepsut is an example of a powerful woman Pharaoh. ...
5-3 Notes: The Pyramid Builders
... growing/preparing food, caring for animals, and building boats) Robbers stole the treasures from almost every tomb, with the exception of one secret tomb from a New Kingdom pharaoh ...
... growing/preparing food, caring for animals, and building boats) Robbers stole the treasures from almost every tomb, with the exception of one secret tomb from a New Kingdom pharaoh ...
Ancient Egypt - WordPress.com
... built at Saqqara for the pharaoh Djoser. It was made by building several 'steps' or layers of stone on top of each other. ...
... built at Saqqara for the pharaoh Djoser. It was made by building several 'steps' or layers of stone on top of each other. ...
HW/ Social Studies Chapter Four/ Section One – Egypt Under the
... 8. What region does the Nile Delta form? Why is this area so fertile? ...
... 8. What region does the Nile Delta form? Why is this area so fertile? ...
global project qtr 4
... Sumer was founded in the area now known as the Middle East. At that time it was called Mesopotamia, which means “between the rivers” in Greek. It was also called the Fertile Crescent because it is a very fertile piece of land. It is between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. The rivers frequently floo ...
... Sumer was founded in the area now known as the Middle East. At that time it was called Mesopotamia, which means “between the rivers” in Greek. It was also called the Fertile Crescent because it is a very fertile piece of land. It is between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. The rivers frequently floo ...
Untitled
... expected to make trade profitable and prevent war. To manage these duties, he appointed government officials, mostly from his family. Social classes developed, with the pharaoh at the top and nobles from rich and powerful families making up the upper class. The middle class ...
... expected to make trade profitable and prevent war. To manage these duties, he appointed government officials, mostly from his family. Social classes developed, with the pharaoh at the top and nobles from rich and powerful families making up the upper class. The middle class ...
Ancient Egypt Unit Test: Study Guide Use your notes and the
... There was a terrible drought that lasted for almost 100 years. Many people starved. The Egyptians were conquered by a people called the Hyksos, and were ruled for about 100 years before finally reclaiming their land. During this time, the age of pyramid building came to an end. ...
... There was a terrible drought that lasted for almost 100 years. Many people starved. The Egyptians were conquered by a people called the Hyksos, and were ruled for about 100 years before finally reclaiming their land. During this time, the age of pyramid building came to an end. ...