The Benefits of the Nile Valley Papyrus
... Hyskos were finally driven from Egypt through the military genius of Ahmose, who named himself Pharaoh of all Egypt and established the 18th Dynasty. This gave rise to the New Kingdom. The New Kingdom (1550-1100 BCE) marks the apex of Egyptian power. Determined never to be invaded again, Egypt began ...
... Hyskos were finally driven from Egypt through the military genius of Ahmose, who named himself Pharaoh of all Egypt and established the 18th Dynasty. This gave rise to the New Kingdom. The New Kingdom (1550-1100 BCE) marks the apex of Egyptian power. Determined never to be invaded again, Egypt began ...
Egypt NAPLAN Test 1A
... 4. Egypt could maintain a massive population due to the inendation of the Nile River once a year. ...
... 4. Egypt could maintain a massive population due to the inendation of the Nile River once a year. ...
1 - inetTeacher
... 18. Sesostris III super forts can or cannot be visited? 19. Egyptian obelisks were moved by roads or during the yearly floods of the Nile? 20. How did ancient Egyptians move obelisks? We don’t know for sure or ...
... 18. Sesostris III super forts can or cannot be visited? 19. Egyptian obelisks were moved by roads or during the yearly floods of the Nile? 20. How did ancient Egyptians move obelisks? We don’t know for sure or ...
Ancient Egypt - cabarrus.k12.nc.us
... other worldly provisions told us that the Ancient Egyptians expected their dead to need these things in the "next life". ...
... other worldly provisions told us that the Ancient Egyptians expected their dead to need these things in the "next life". ...
DELTA RED LAND BLACK LAND MEDITERRANEAN SEA RED
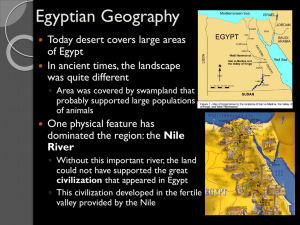
... 5. Egypt is divided into "Upper Egypt" or Southern Egypt and "Lower Egypt" or Northern Egypt. These two areas get their names based on elevation. *Remember that ALL rivers flow from higher elevations to lower elevations! 6. The Nile River floods its banks and leaves silt or rich fertile soil on its ...
... 5. Egypt is divided into "Upper Egypt" or Southern Egypt and "Lower Egypt" or Northern Egypt. These two areas get their names based on elevation. *Remember that ALL rivers flow from higher elevations to lower elevations! 6. The Nile River floods its banks and leaves silt or rich fertile soil on its ...
Egyptians had many ways of using transportation. One way was by
... a hard time walking. Another way were the ferries. Racing up the Nile rivers, trying to deliver their goods and supplies. People from the south had some difficulty reaching the north of Egypt because of the cataracts. In litters people, like the royal family’s, would sit in a royal chair and other p ...
... a hard time walking. Another way were the ferries. Racing up the Nile rivers, trying to deliver their goods and supplies. People from the south had some difficulty reaching the north of Egypt because of the cataracts. In litters people, like the royal family’s, would sit in a royal chair and other p ...
Ancient Egypt - Mrs. Hilton`s Class
... and were considered gods. Egyptians built pyramids at Giza. Power struggles, crop failures, and cost of pyramids contributed to the collapse of the Old Kingdom. ...
... and were considered gods. Egyptians built pyramids at Giza. Power struggles, crop failures, and cost of pyramids contributed to the collapse of the Old Kingdom. ...
APAH: Egyptian Art
... Cyclical flooding Irrigation/fertile soil ‘Rediscovery’ of Egypt by 19th century Europe Napoleon Hieroglyphics Rosetta Stone (1,799 AD Napoleon’s invasion) Hieroglyphics/demotic (common) Egyptian/Greek Sudden cultural development c. 3,500 BC Kingdom of two lands: Upper/Lower Nile ...
... Cyclical flooding Irrigation/fertile soil ‘Rediscovery’ of Egypt by 19th century Europe Napoleon Hieroglyphics Rosetta Stone (1,799 AD Napoleon’s invasion) Hieroglyphics/demotic (common) Egyptian/Greek Sudden cultural development c. 3,500 BC Kingdom of two lands: Upper/Lower Nile ...
Notes: Ancient Egypt
... • built fortresses • Protected gold, copper, granite resources in Sinai • Encouraged cultural development • Supervised construction of buildings • created elaborate improvements to existing shrines & temples • Jubilee Chapel at Karnak • Craftwork & literature ...
... • built fortresses • Protected gold, copper, granite resources in Sinai • Encouraged cultural development • Supervised construction of buildings • created elaborate improvements to existing shrines & temples • Jubilee Chapel at Karnak • Craftwork & literature ...
Study Guide The Geography of the
... • A kingdom is a period of time. • There were three main kingdoms: o Old Kingdom (Age of Pyramids) o Middle Kingdom o New Kingdom (Age of Empire) • The dates of the kingdoms are not important. • The intermediate periods were the times between the kingdoms. These were unstable times for Egypt. ...
... • A kingdom is a period of time. • There were three main kingdoms: o Old Kingdom (Age of Pyramids) o Middle Kingdom o New Kingdom (Age of Empire) • The dates of the kingdoms are not important. • The intermediate periods were the times between the kingdoms. These were unstable times for Egypt. ...
Ancient Egypt
... After Ramses II, pharaohs had trouble keeping neighboring countries under control. Egypt was attacked by groups from the eastern Mediterranean who had strong iron weapons. Egypt had iron weapons too, but they were very costly because Egypt had no iron ore. Finally the Kush took over and rule ...
... After Ramses II, pharaohs had trouble keeping neighboring countries under control. Egypt was attacked by groups from the eastern Mediterranean who had strong iron weapons. Egypt had iron weapons too, but they were very costly because Egypt had no iron ore. Finally the Kush took over and rule ...
Nile River Valley Civilization
... They were the kings or Queens of Egypt. They were the head of the government and high priest of every temple. The pharaoh owned all of Egypt. He or she decided what was right or wrong and their word was law. The people of Egypt considered the pharaoh to be a half-human and halfgod. ...
... They were the kings or Queens of Egypt. They were the head of the government and high priest of every temple. The pharaoh owned all of Egypt. He or she decided what was right or wrong and their word was law. The people of Egypt considered the pharaoh to be a half-human and halfgod. ...
The Dawn of Civilization
... •The reign of Ramses marked the end of Egypt’s greatness •Challenges came in the form of foreign powers •first of the major invasions was the Sea Peoples •No one is sure who the Sea People were, but their invasions did bring an end to the Hittite Empire and Egypt ...
... •The reign of Ramses marked the end of Egypt’s greatness •Challenges came in the form of foreign powers •first of the major invasions was the Sea Peoples •No one is sure who the Sea People were, but their invasions did bring an end to the Hittite Empire and Egypt ...
Egyptian Test
... d. The chance to use trial and error to test out new methods of curing the sick 9. Which statement best explains why Ancient Egypt was ruled by 31 different dynasties? a. Most Ancient Egyptian rulers did not live very long b. The Egyptian people treated pharaohs like gods c. There was frequent warfa ...
... d. The chance to use trial and error to test out new methods of curing the sick 9. Which statement best explains why Ancient Egypt was ruled by 31 different dynasties? a. Most Ancient Egyptian rulers did not live very long b. The Egyptian people treated pharaohs like gods c. There was frequent warfa ...
Egypt
... Then, Egypt was invaded by Hyksos, roughly translated as “Rulers of Foreign Lands”, a mixed horde originating in West Asia. This invasion ended the rule of the Middle Kingdom and begun another intermediate period characterized by chaos. It was not until Egypt defeated the Hyksos in 1560 BCE that ord ...
... Then, Egypt was invaded by Hyksos, roughly translated as “Rulers of Foreign Lands”, a mixed horde originating in West Asia. This invasion ended the rule of the Middle Kingdom and begun another intermediate period characterized by chaos. It was not until Egypt defeated the Hyksos in 1560 BCE that ord ...
Egyptian Geography
... for the Egyptians, marked by stability and prosperity Nobles and priests again began to weaken the power of the pharaoh By 1780 BC the Middle Kingdom was becoming unstable ...
... for the Egyptians, marked by stability and prosperity Nobles and priests again began to weaken the power of the pharaoh By 1780 BC the Middle Kingdom was becoming unstable ...
Before Civilization Introduction The first pre
... governors exercised political authority for nearly two hundred years. Temple priesthoods and religious foundations devoted to cults of the dead began to receive greater and greater amounts of land and wealth to support their devotion to the departed spirits. Eventually, the practice of creating shri ...
... governors exercised political authority for nearly two hundred years. Temple priesthoods and religious foundations devoted to cults of the dead began to receive greater and greater amounts of land and wealth to support their devotion to the departed spirits. Eventually, the practice of creating shri ...
Learning Period 3 Quiz
... D. Thought of himself as a great ruler. He battled with the Hittites and eventually reached peace with them by marrying the king’s daughter. ...
... D. Thought of himself as a great ruler. He battled with the Hittites and eventually reached peace with them by marrying the king’s daughter. ...
Social, Political, and Military History of Ancient Egypt
... organize all this activity. Bright boys from all classes were sent to schools where the one rule was, “a youngster’s ear is on his back—he listens when he is beaten.” The only other way to rise in Egyptian society was in the army, and that not until the New Kingdom when a professional army was permi ...
... organize all this activity. Bright boys from all classes were sent to schools where the one rule was, “a youngster’s ear is on his back—he listens when he is beaten.” The only other way to rise in Egyptian society was in the army, and that not until the New Kingdom when a professional army was permi ...
World History: Connections to Today
... ► Each state had distinct social hierarchy, or system of ranks. ► Most people were peasant farmers. ► Women had legal rights; some engaged in trade and owned property. ...
... ► Each state had distinct social hierarchy, or system of ranks. ► Most people were peasant farmers. ► Women had legal rights; some engaged in trade and owned property. ...
Ancient Egypt Society Map—Semenza Galbo Government and Laws
... 3100 B.C. They overthrew the king of Lower Egypt, and to show his victory, Menes made a new crown. The new crown was pieces from both crown, to show the unification of Egypt. *What are two meanings of the word "pharaoh" (p. 89)? The word Pharaoh refers to “great palace” but now is given to every rul ...
... 3100 B.C. They overthrew the king of Lower Egypt, and to show his victory, Menes made a new crown. The new crown was pieces from both crown, to show the unification of Egypt. *What are two meanings of the word "pharaoh" (p. 89)? The word Pharaoh refers to “great palace” but now is given to every rul ...