Pharaohs/Gods/Places - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Osiris – god of death & rebirth, afterlife (1st god to die and live again) Anubis – jackal headed god of embalmers; performs the “weighing of the heart” when the soul is judged Aten - god of sun (Akhenaton tried to make him the only god) Horus – falcon headed god of sky and kings(protector of pharao ...
... Osiris – god of death & rebirth, afterlife (1st god to die and live again) Anubis – jackal headed god of embalmers; performs the “weighing of the heart” when the soul is judged Aten - god of sun (Akhenaton tried to make him the only god) Horus – falcon headed god of sky and kings(protector of pharao ...
Describe how the Nile River influenced Egyptian
... western Asia. These invaders made great use of horse-drawn chariots and used weapons made of bronze and iron. The Egyptians only had weapons of copper and stone. What was the name of these invaders? ...
... western Asia. These invaders made great use of horse-drawn chariots and used weapons made of bronze and iron. The Egyptians only had weapons of copper and stone. What was the name of these invaders? ...
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
... of craft workers began working at the age of 5. At about the age of 12 girls studied to become weavers. Sons of government leaders became assistants to their fathers. ...
... of craft workers began working at the age of 5. At about the age of 12 girls studied to become weavers. Sons of government leaders became assistants to their fathers. ...
Section 3 Reading
... The Old Kingdom ended with the pharaohs in debt. Nobles serving in government positions took power from the pharaohs and ruled Egypt for nearly 160 years. Finally, a powerful pharaoh regained control of Egypt around 2050 BC and started a peaceful period of rule. This era was called the Middle Kingdo ...
... The Old Kingdom ended with the pharaohs in debt. Nobles serving in government positions took power from the pharaohs and ruled Egypt for nearly 160 years. Finally, a powerful pharaoh regained control of Egypt around 2050 BC and started a peaceful period of rule. This era was called the Middle Kingdo ...
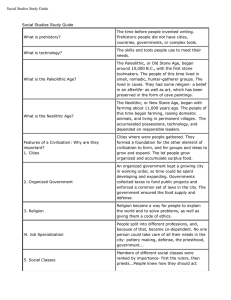
2.1 Why was Ancient Egypt such a successful civilization?
... Geographic Setting One of the earliest civilizations arose in Egypt about 5,000 years ago around the mighty Nile River. Ancient Egypt could not have existed without its great river. It hardly ever rains in Egypt, but the Nile River waters the land and gives it life. Without the river, the entire cou ...
... Geographic Setting One of the earliest civilizations arose in Egypt about 5,000 years ago around the mighty Nile River. Ancient Egypt could not have existed without its great river. It hardly ever rains in Egypt, but the Nile River waters the land and gives it life. Without the river, the entire cou ...
Chapter 4 – Ancient Egypt
... The Middle Kingdom was a period of stable government between periods of disorder Following a period of competition for power between the nobles and the pharaohs, the Middle Kingdom began. The Old Kingdom declined due to the cost of building pyramids pharaoh’s could not collect enough taxes to keep ...
... The Middle Kingdom was a period of stable government between periods of disorder Following a period of competition for power between the nobles and the pharaohs, the Middle Kingdom began. The Old Kingdom declined due to the cost of building pyramids pharaoh’s could not collect enough taxes to keep ...
Chapter 4 notes
... The Egyptian pharaohs wanted people to remember just how rich and powerful they were. Some had huge statues of themselves made. They also had their people build great teams for them. When the pharaohs died their bodies were placed in the tombs. Jewelry, food, clothing – all of the pharaoh’s favorite ...
... The Egyptian pharaohs wanted people to remember just how rich and powerful they were. Some had huge statues of themselves made. They also had their people build great teams for them. When the pharaohs died their bodies were placed in the tombs. Jewelry, food, clothing – all of the pharaoh’s favorite ...
Prehistory - Study Guides
... in an afterlife- as well as art, which has been preserved in the form of cave paintings. ...
... in an afterlife- as well as art, which has been preserved in the form of cave paintings. ...
Unit Test on Ancient Egypt Study Guide Answers
... • When his tomb was discovered his mummy and artifacts were still intact, giving archaeologists a lot of information about life during ancient Egypt ...
... • When his tomb was discovered his mummy and artifacts were still intact, giving archaeologists a lot of information about life during ancient Egypt ...
{}LOVE{}
... It is believed to have been built as a tomb for Fourth dynasty Egyptian pharaoh Khufu and constructed over a 20 year period concluding around 2560 BC. The tallest man-made structure in the world for over 3,800 years, it is sometimes called Khufu's Pyramid or the Pyramid of Khufu. ...
... It is believed to have been built as a tomb for Fourth dynasty Egyptian pharaoh Khufu and constructed over a 20 year period concluding around 2560 BC. The tallest man-made structure in the world for over 3,800 years, it is sometimes called Khufu's Pyramid or the Pyramid of Khufu. ...
Chapter 4, Section 1: Geography and Ancient Egypt
... The water, fertile soils, and protected setting of the Nile Valley allowed a great civilization to arise in Egypt around 3200 BC. Main Ideas • Egypt was called the gift of the Nile because the Nile River gave life to the desert. • Civilization developed along the Nile after people began farming in t ...
... The water, fertile soils, and protected setting of the Nile Valley allowed a great civilization to arise in Egypt around 3200 BC. Main Ideas • Egypt was called the gift of the Nile because the Nile River gave life to the desert. • Civilization developed along the Nile after people began farming in t ...
Chapter 4, Section 1: Geography and Ancient Egypt
... The water, fertile soils, and protected setting of the Nile Valley allowed a great civilization to arise in Egypt around 3200 BC. Main Ideas • Egypt was called the gift of the Nile because the Nile River gave life to the desert. • Civilization developed along the Nile after people began farming in t ...
... The water, fertile soils, and protected setting of the Nile Valley allowed a great civilization to arise in Egypt around 3200 BC. Main Ideas • Egypt was called the gift of the Nile because the Nile River gave life to the desert. • Civilization developed along the Nile after people began farming in t ...
Egypt Test 1
... 35.. Without the annual ______________________________ , people never could have settled in Egypt. 36. in Egypt________________________ grew wheat, barley, fruits, and vegetables, as well as raised cattle and sheep. 37. Around 3100 BC, a leader named_____________________________ rose to power in Upp ...
... 35.. Without the annual ______________________________ , people never could have settled in Egypt. 36. in Egypt________________________ grew wheat, barley, fruits, and vegetables, as well as raised cattle and sheep. 37. Around 3100 BC, a leader named_____________________________ rose to power in Upp ...
Ancient Egypt
... The civilization of Ancient Egypt was one of the earliest in world history. It is usually held to have come to existence in around 3000 BC in the Nile River Valley. As well as being one of the earliest, the Ancient Egyptians had one of the longest lasting civilizations in world history. The great da ...
... The civilization of Ancient Egypt was one of the earliest in world history. It is usually held to have come to existence in around 3000 BC in the Nile River Valley. As well as being one of the earliest, the Ancient Egyptians had one of the longest lasting civilizations in world history. The great da ...
Ancient Civilizations Mr. Hanover Egypt Student Study Guide Egypt
... 41) Where did the Nubians live? 42) What is another name for Nubians? 43) What were the Nubians known for? 44) Define a dynasty. 45) What is a mace? 46) Who was King Narmer? 47) What was important about Memphis? 48) What is a nome? 49) What were the “two lands” of Egypt? 50) Why did Egyptian kings w ...
... 41) Where did the Nubians live? 42) What is another name for Nubians? 43) What were the Nubians known for? 44) Define a dynasty. 45) What is a mace? 46) Who was King Narmer? 47) What was important about Memphis? 48) What is a nome? 49) What were the “two lands” of Egypt? 50) Why did Egyptian kings w ...
Ancient Egypt
... most of their attention and efforts to the Great Pyramid. Bottom line premise: it is too large a monument to have been built without aid of sophisticated machinery or that the stones were too heavy to be moved with the technology available to the ancient Egyptians. ...
... most of their attention and efforts to the Great Pyramid. Bottom line premise: it is too large a monument to have been built without aid of sophisticated machinery or that the stones were too heavy to be moved with the technology available to the ancient Egyptians. ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... Kingdom of Axum • Aksum (also spelled Axum) is the name of a powerful, urban Iron Age Kingdom in Ethiopia • The modern city of Aksum is located in the northeastern portion of what is now Ethiopia, on the horn of Africa. • An early text shows that trade on the Red Sea coast was active as early as 1s ...
... Kingdom of Axum • Aksum (also spelled Axum) is the name of a powerful, urban Iron Age Kingdom in Ethiopia • The modern city of Aksum is located in the northeastern portion of what is now Ethiopia, on the horn of Africa. • An early text shows that trade on the Red Sea coast was active as early as 1s ...
Class Lesson Plan
... 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? ______________________________________________________________ 23. What five things did the priest ...
... 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? ______________________________________________________________ 23. What five things did the priest ...
Section 3: The Middle and the New Kingdoms
... The Middle Kingdom was a period of stable government between times of disorder. The New Kingdom was when Egypt’s trade and military power reached its peak. Work and daily life were different for each social class. Facts to Know: Old Kingdom fall due to lack of farming, huge building projects, nobles ...
... The Middle Kingdom was a period of stable government between times of disorder. The New Kingdom was when Egypt’s trade and military power reached its peak. Work and daily life were different for each social class. Facts to Know: Old Kingdom fall due to lack of farming, huge building projects, nobles ...
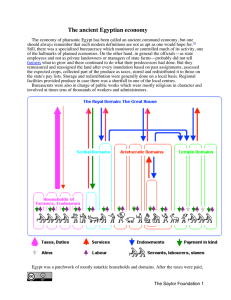
The Ancient Egyptian Economy
... Scribes recording the amount of grain harvested Source: Lionel Casson, Ancient Egypt - Time-Life Books ... they think that all the diseases which exist are produced in men by the food on which they live: for the Egyptians are from other causes also the most healthy of all men next after the Libyans ...
... Scribes recording the amount of grain harvested Source: Lionel Casson, Ancient Egypt - Time-Life Books ... they think that all the diseases which exist are produced in men by the food on which they live: for the Egyptians are from other causes also the most healthy of all men next after the Libyans ...
Location and Physical Features
... Another Geographical Advantage • Nile has desert extending for miles on either side • Provided a natural barrier against invaders • By 3,200 B.C. villages had banded together to develop into two kingdoms • Lower Egypt, capital Pe, red crown • Upper Egypt, capital Nekhen, white crown ...
... Another Geographical Advantage • Nile has desert extending for miles on either side • Provided a natural barrier against invaders • By 3,200 B.C. villages had banded together to develop into two kingdoms • Lower Egypt, capital Pe, red crown • Upper Egypt, capital Nekhen, white crown ...
Egypt
... “Gift of the Nile” The Ancient Egyptian Civilization was located along the Nile River in northern Africa. Egypt was known as the “Gift of the Nile.” The Nile River is the main reason that a civilization started here. Without the Nile Egypt would be an empty desert. The Nile River Valley is the only ...
... “Gift of the Nile” The Ancient Egyptian Civilization was located along the Nile River in northern Africa. Egypt was known as the “Gift of the Nile.” The Nile River is the main reason that a civilization started here. Without the Nile Egypt would be an empty desert. The Nile River Valley is the only ...
Egyptian History 101
... The early rulers of the Middle Kingdom restored peace and order. They spent the nation's wealth on public works instead of on wars. They built a lot of temples and pyramids. They funded irrigation projects. Under their rule, the economy boomed. Arts flourished. Things were looking up again. Unfortun ...
... The early rulers of the Middle Kingdom restored peace and order. They spent the nation's wealth on public works instead of on wars. They built a lot of temples and pyramids. They funded irrigation projects. Under their rule, the economy boomed. Arts flourished. Things were looking up again. Unfortun ...