Major Time Periods of Egypt
... Women oversaw the running of the households and gave the servants instructions for daily menus and child care. Children were allowed much playtime. Girls practiced singing and dancing. Boys wrestled and played army. Women and girls wore straight dresses of beautiful lined and a lot of jewelry. ...
... Women oversaw the running of the households and gave the servants instructions for daily menus and child care. Children were allowed much playtime. Girls practiced singing and dancing. Boys wrestled and played army. Women and girls wore straight dresses of beautiful lined and a lot of jewelry. ...
Social Studies Question Of the Day (QOD)
... 46. What is a material prepared in ancient Egypt from the pithy stem of a water plant, used in sheets throughout the ancient Mediterranean world for writing or painting on? – papyrus 47. The main Egyptian god was the sun god Re or Ra. 48. What king took control of Lower Egypt and unified the two kin ...
... 46. What is a material prepared in ancient Egypt from the pithy stem of a water plant, used in sheets throughout the ancient Mediterranean world for writing or painting on? – papyrus 47. The main Egyptian god was the sun god Re or Ra. 48. What king took control of Lower Egypt and unified the two kin ...
Old Kingdom
... III. Work and daily life were different among Egypt’s social classes. 1. The complex society required people to take on many different kinds of jobs. 2. Family life was very important in Egyptian society, and most Egyptians lived in their own homes. ...
... III. Work and daily life were different among Egypt’s social classes. 1. The complex society required people to take on many different kinds of jobs. 2. Family life was very important in Egyptian society, and most Egyptians lived in their own homes. ...
River Valley Civilizations
... 2. Worshipped thousands of gods – 5 main ones 1. Re (Ra): The sun-god; represented as falconheaded - seem as the father of the gods 2. Isis: Isis is known as the divine mother - wife of Osiris and mother of Horus 3. Osiris: The god of the underworld, king of the dead - seen as the great judge of the ...
... 2. Worshipped thousands of gods – 5 main ones 1. Re (Ra): The sun-god; represented as falconheaded - seem as the father of the gods 2. Isis: Isis is known as the divine mother - wife of Osiris and mother of Horus 3. Osiris: The god of the underworld, king of the dead - seen as the great judge of the ...
Egypt – Nile River Valley River Valley Project Cornell notes
... were also given to help the deceased “live forever” by giving them instructions they would need on the way to god for their eternal life. The Egyptian religion had over 2,000 gods and goddesses with chief gods being Amon-Ra and Osiris. Amon-Ra was the sun god and the lord of the universe and Osiris ...
... were also given to help the deceased “live forever” by giving them instructions they would need on the way to god for their eternal life. The Egyptian religion had over 2,000 gods and goddesses with chief gods being Amon-Ra and Osiris. Amon-Ra was the sun god and the lord of the universe and Osiris ...
1) Pharoahs and Pyramids
... real people or kings who ruled the ancient Egypt and were considered as deities, but not the gods like in a myth. 16) Seth, Hathor, Isis, Horus, Re, Aton, Osiris: In the Jewish and Christian Bible, Seth is explained as meaning "foundation." According to this tradition, Seth was perceived as the "Fou ...
... real people or kings who ruled the ancient Egypt and were considered as deities, but not the gods like in a myth. 16) Seth, Hathor, Isis, Horus, Re, Aton, Osiris: In the Jewish and Christian Bible, Seth is explained as meaning "foundation." According to this tradition, Seth was perceived as the "Fou ...
I. The Egyptians - Eldred Central School
... in early autumn, and left a deposit of mud that created an area of rich soil. ...
... in early autumn, and left a deposit of mud that created an area of rich soil. ...
pharaohs
... believed their kings were also gods. Modern people refer to ancient Egyptian rulers as pharaohs, but pharaoh originally referred to the palace where the king lived. Pharaoh was not used as a title for the Egyptian ruler until the later part of ancient Egyptian history, but today we use the term to d ...
... believed their kings were also gods. Modern people refer to ancient Egyptian rulers as pharaohs, but pharaoh originally referred to the palace where the king lived. Pharaoh was not used as a title for the Egyptian ruler until the later part of ancient Egyptian history, but today we use the term to d ...
Chapter 2:
... (Egyptian rulers) were believed to be gods. – Viziers- chief ministers • Viziers also collected taxes, farming, etc. ...
... (Egyptian rulers) were believed to be gods. – Viziers- chief ministers • Viziers also collected taxes, farming, etc. ...
Syllabus for "The Nile River Valley" Unit
... B) Describe their religion and how it related to the construction of pyramids. C) How was their society organized? D) List and briefly explain 3 other forms of technology from ancient Egypt. 5. Define in your notebook: incense and envoy. DUE : _________ 6. Read "Egypt's Empire" on pages 120 - 127. A ...
... B) Describe their religion and how it related to the construction of pyramids. C) How was their society organized? D) List and briefly explain 3 other forms of technology from ancient Egypt. 5. Define in your notebook: incense and envoy. DUE : _________ 6. Read "Egypt's Empire" on pages 120 - 127. A ...
Egypt and the Kingdom of Kush
... 1. During most of the Third Intermediate Period and the Late Period, Egypt survived as a divided country with a Pharaoh in the north at Tanis and another in the south at Thebes. 2. Order was restored for a time when the southern kingdom of Kush in Nubia invaded Egypt at the invitation of the souther ...
... 1. During most of the Third Intermediate Period and the Late Period, Egypt survived as a divided country with a Pharaoh in the north at Tanis and another in the south at Thebes. 2. Order was restored for a time when the southern kingdom of Kush in Nubia invaded Egypt at the invitation of the souther ...
Ancient Egypt - Northside Middle School
... • The Nile forms branches near the Mediterranean Sea. These branches fan out over an area of fertile soil called a delta. ...
... • The Nile forms branches near the Mediterranean Sea. These branches fan out over an area of fertile soil called a delta. ...
File - world history
... __esert in horse-drawn ________________ and used weapons made of __ronze and __ron. Egyptians had always fought on ___________ with __opper and __tone weapons. They were ____ match for the invaders. The Hyksos ruled Egypt for about ______________ years. Then, around 1550 BCE, an Egyptian prince name ...
... __esert in horse-drawn ________________ and used weapons made of __ronze and __ron. Egyptians had always fought on ___________ with __opper and __tone weapons. They were ____ match for the invaders. The Hyksos ruled Egypt for about ______________ years. Then, around 1550 BCE, an Egyptian prince name ...
Egypt – An Ancient Civilisation
... Memphis in the north and Thebes in the south became the most important centres. The first great period was that of the Old Kingdom (ca 2700 to 2200 BC). In that age the pharaohs built huge tombs for themselves, the pyramids. After a time of wars among rival kings a second ...
... Memphis in the north and Thebes in the south became the most important centres. The first great period was that of the Old Kingdom (ca 2700 to 2200 BC). In that age the pharaohs built huge tombs for themselves, the pyramids. After a time of wars among rival kings a second ...
Ancient Egypt
... children. But one has to keep in mind that the death rate among babies was very high. Most children never went to any kind of school. Sons learned from their fathers and mothers taught their daughters how to organise the home. As noted earlier, people had a high opinion of scribes. So fathers tried ...
... children. But one has to keep in mind that the death rate among babies was very high. Most children never went to any kind of school. Sons learned from their fathers and mothers taught their daughters how to organise the home. As noted earlier, people had a high opinion of scribes. So fathers tried ...
Book of the Dead
... Farming communities formed along the Nile during the Neolithic period - before 7000 B.C. ...
... Farming communities formed along the Nile during the Neolithic period - before 7000 B.C. ...
Ancient Egypt
... • was the Capital City of the first unified Egyptian state since the days of Pharaoh King Narmer". Giza's most famous archaeological site, the Giza Plateau, holds some of the most astonishing monuments in Egyptian history. Once thriving with the Nile that flowed right into the Giza Plateau, the Pyra ...
... • was the Capital City of the first unified Egyptian state since the days of Pharaoh King Narmer". Giza's most famous archaeological site, the Giza Plateau, holds some of the most astonishing monuments in Egyptian history. Once thriving with the Nile that flowed right into the Giza Plateau, the Pyra ...
Copy of Egypt2
... The Middle Kingdom (2050-1653 B.C.) was characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
... The Middle Kingdom (2050-1653 B.C.) was characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
Ancient Egypt power point
... The Middle Kingdom (2050-1653 B.C.) was characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
... The Middle Kingdom (2050-1653 B.C.) was characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
Egypt`s Powerful Kings and Queens
... The rulers of Egypt held the respected title of pharaoh (FAIR oh). The pharaohs were allpowerful. Whatever the ...
... The rulers of Egypt held the respected title of pharaoh (FAIR oh). The pharaohs were allpowerful. Whatever the ...
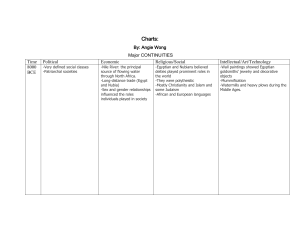
PERSIAN Charts: Definitions and Guiding Questions
... Menes- A ruler who brought unified rule to Egypt in 3,100 B.C.E, which combined Upper and Lower Egypt. He founded the city of Memphis, which served as Menes’ capital. He was sometimes identified with an early Egyptian ruler called Narmer. He was a minor official who rose to power and extended his au ...
... Menes- A ruler who brought unified rule to Egypt in 3,100 B.C.E, which combined Upper and Lower Egypt. He founded the city of Memphis, which served as Menes’ capital. He was sometimes identified with an early Egyptian ruler called Narmer. He was a minor official who rose to power and extended his au ...
Pyramids on the Nile - mrs
... • To Egyptians, Kings were gods and became known as pharaohs • Pharaoh stood at center of religion, government, and army • Theocracy- ruler is a divine figure • Believed pharaoh responsible for kingdom’s well being, sun rising, the Nile to flood and crops to grow ...
... • To Egyptians, Kings were gods and became known as pharaohs • Pharaoh stood at center of religion, government, and army • Theocracy- ruler is a divine figure • Believed pharaoh responsible for kingdom’s well being, sun rising, the Nile to flood and crops to grow ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... • To Egyptians, Kings were gods and became known as pharaohs • Pharaoh stood at center of religion, government, and army • Theocracy- ruler is a divine figure • Believed pharaoh responsible for kingdom’s well being, sun rising, the Nile to flood and crops to grow ...
... • To Egyptians, Kings were gods and became known as pharaohs • Pharaoh stood at center of religion, government, and army • Theocracy- ruler is a divine figure • Believed pharaoh responsible for kingdom’s well being, sun rising, the Nile to flood and crops to grow ...
Ancient egypt social classes
... The ancient Egyptians were fascinating people, and thanks to the movies, are often misunderstood. The ancient Egyptians were not in love with death, but with. Women in ancient Egypt had a status that significantly contrasts the status of many modern women because they occupied power in ways that wom ...
... The ancient Egyptians were fascinating people, and thanks to the movies, are often misunderstood. The ancient Egyptians were not in love with death, but with. Women in ancient Egypt had a status that significantly contrasts the status of many modern women because they occupied power in ways that wom ...