What was the “SOUL” of Ancient Egypt?
... The Middle Kingdom (2050-1653 B.C.) was characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
... The Middle Kingdom (2050-1653 B.C.) was characterized by a new concern of the pharaohs for the people. In the Old Kingdom, the pharaoh had been viewed as an inaccessible god-king. Now he was portrayed as the shepherd of his people. ...
Document
... • The Nile was the source of life and path to immortality • Egyptians lived on Eastern side but buried on Western side – River was symbol of passage of one life to next ...
... • The Nile was the source of life and path to immortality • Egyptians lived on Eastern side but buried on Western side – River was symbol of passage of one life to next ...
Ancient Egypt (The Old Kingdom) - History-13-14
... During the Old Kingdom, Ancient Egypt was ruled by a strong government for 500 years until priests and other government officials demanded more ...
... During the Old Kingdom, Ancient Egypt was ruled by a strong government for 500 years until priests and other government officials demanded more ...
Nile—Egypt
... --”Book of the Dead” – aided the dead in the afterlife; contains ideas borrowed from outsiders; details how Isis & Nephthys brought Osiris back to life after being killed by his brother Set --mummification --ka (life force); ba (soul/personality); ren (name); ib (heart); sheut (shadow) f. Bronze Age ...
... --”Book of the Dead” – aided the dead in the afterlife; contains ideas borrowed from outsiders; details how Isis & Nephthys brought Osiris back to life after being killed by his brother Set --mummification --ka (life force); ba (soul/personality); ren (name); ib (heart); sheut (shadow) f. Bronze Age ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... • Legend has it that Menes had a long and successful reign until he was carried off and killed by a hippopotamus ...
... • Legend has it that Menes had a long and successful reign until he was carried off and killed by a hippopotamus ...
First Age of Empires - mrs-saucedo
... pharaohs of the New Kingdom (about 1570 – 1075 B.C.) sought to strengthen Egypt by building an Empire. Egypt now entered its third period of glory in the New Kingdom. During this time Egypt became wealthier and more powerful than ever before. ...
... pharaohs of the New Kingdom (about 1570 – 1075 B.C.) sought to strengthen Egypt by building an Empire. Egypt now entered its third period of glory in the New Kingdom. During this time Egypt became wealthier and more powerful than ever before. ...
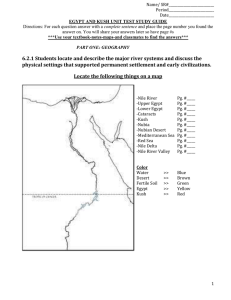
egypt and kush unit test study guide
... Kush: The kingdom to the south of Egypt, which shared a very complex relationship. They shared many cultural similarities and often were at peace and war. Pharaoh: the ruler of the Egyptian people, also thought to be a god. The pharaoh was in charge of keeping the Egyptians happy and safe. If things ...
... Kush: The kingdom to the south of Egypt, which shared a very complex relationship. They shared many cultural similarities and often were at peace and war. Pharaoh: the ruler of the Egyptian people, also thought to be a god. The pharaoh was in charge of keeping the Egyptians happy and safe. If things ...
Chapter 3 Ancient Egypt and Nubia
... 24. Why did Egypt go down hill at the end of the New Kingdom? ...
... 24. Why did Egypt go down hill at the end of the New Kingdom? ...
Egypt Common Assessment
... 7. What does this diagram tell about ancient Egyptian society? 8.4.9.C a. Artisans held a higher position in society over pharaohs. b. Peasant farmers made up the largest segment of society. c. Priests outnumbered slaves. d. Scribes held the highest positions in Egypt. ...
... 7. What does this diagram tell about ancient Egyptian society? 8.4.9.C a. Artisans held a higher position in society over pharaohs. b. Peasant farmers made up the largest segment of society. c. Priests outnumbered slaves. d. Scribes held the highest positions in Egypt. ...
Chapter 3 Egypt
... • Two periods when pharaohs were weak – 2200-2100 BCE: First Intermediate Period – 1650-1570 BCE: Hyksos Invasion ...
... • Two periods when pharaohs were weak – 2200-2100 BCE: First Intermediate Period – 1650-1570 BCE: Hyksos Invasion ...
Egypt - Pentecostal Evangel
... also has ancient temples, Greek and Roman monuments, and the capital city of Cairo — the largest city in Africa. Even though Egyptian children live around these historical sites, they have a lot in common with American children. They go to school, enjoy popular foods, watch television, listen to Wes ...
... also has ancient temples, Greek and Roman monuments, and the capital city of Cairo — the largest city in Africa. Even though Egyptian children live around these historical sites, they have a lot in common with American children. They go to school, enjoy popular foods, watch television, listen to Wes ...
Lesson 2 - Society
... Pharaohs were considered to be gods – the people called them god-kings. After they died, they were the gods of the dead ...
... Pharaohs were considered to be gods – the people called them god-kings. After they died, they were the gods of the dead ...
World History
... a. Egypt and Nubia had frequent wars between them. The Nubians created a great military force and around 2500 B.C.E., united upper and lower Nubia. This became known as the great kingdom of Kush. Though not as powerful as Egypt, Kush was very wealthy and often threatened Southern Egypt. D. Turmoil a ...
... a. Egypt and Nubia had frequent wars between them. The Nubians created a great military force and around 2500 B.C.E., united upper and lower Nubia. This became known as the great kingdom of Kush. Though not as powerful as Egypt, Kush was very wealthy and often threatened Southern Egypt. D. Turmoil a ...
History, cover page
... nine time periods. Namely, the Early Dynastic Kingdom, the Old Kingdom, the 1st intermediate Period, the Middle Kingdom, the 2nd Intermediate Period, the New Kingdom, the Late Dynastic Period and the Greek- Roman Period. The Early Dynastic Period, 3000 BC2575 BC, was the beginning of Ancient Egyptia ...
... nine time periods. Namely, the Early Dynastic Kingdom, the Old Kingdom, the 1st intermediate Period, the Middle Kingdom, the 2nd Intermediate Period, the New Kingdom, the Late Dynastic Period and the Greek- Roman Period. The Early Dynastic Period, 3000 BC2575 BC, was the beginning of Ancient Egyptia ...
Ancient Egypt
... • She remained in power for twenty years (1479 - 1457 BC) and during this time the Egyptian economy flourished, she expanded trading relations and built magnificent temples as well as restoring many others. • Eventually her nephew grew into a man and took his rightful place as pharaoh. ...
... • She remained in power for twenty years (1479 - 1457 BC) and during this time the Egyptian economy flourished, she expanded trading relations and built magnificent temples as well as restoring many others. • Eventually her nephew grew into a man and took his rightful place as pharaoh. ...
The Rise of Civilization in Egypt
... 2. While most people consider floods a disaster, the ancient Egyptians considered flooding beneficial or good. Why? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Egyp ...
... 2. While most people consider floods a disaster, the ancient Egyptians considered flooding beneficial or good. Why? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Egyp ...
Egyptian Civilization
... and the compound bow. Eventually the Egyptians used these new weapons to overthrow the Hyskos. ...
... and the compound bow. Eventually the Egyptians used these new weapons to overthrow the Hyskos. ...
File - Mr. Belter`s World History Virtual Classroom
... restored Egypt’s worship of traditional gods and brought the capital back to Thebes. Egypt enjoyed peace until around 1250 BC, when the Hittites from Mesopotamia invaded. Pharaoh Ramses II, also called Ramses the Great, eventually agreed to a truce. Ramses’ long reign of 60-plus years brought many p ...
... restored Egypt’s worship of traditional gods and brought the capital back to Thebes. Egypt enjoyed peace until around 1250 BC, when the Hittites from Mesopotamia invaded. Pharaoh Ramses II, also called Ramses the Great, eventually agreed to a truce. Ramses’ long reign of 60-plus years brought many p ...
Untitled 3
... title used by the rulers of Egypt. The title pharaoh means “great house.” Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Menes built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile Delta. The city was later named Memphis. For centuries, Memphis was the pol ...
... title used by the rulers of Egypt. The title pharaoh means “great house.” Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Menes built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile Delta. The city was later named Memphis. For centuries, Memphis was the pol ...
Chapter 5 study Guide
... 12. Describe the relationship between Egypt and Nubia. Lecture Outline A. The Gift of the Nile a. Annual floods created a fertile river valley b. Home of one of the most enduring and powerful civilizations in the ancient world B. The Pharaohs a. Power over the people and land virtually absolute b. M ...
... 12. Describe the relationship between Egypt and Nubia. Lecture Outline A. The Gift of the Nile a. Annual floods created a fertile river valley b. Home of one of the most enduring and powerful civilizations in the ancient world B. The Pharaohs a. Power over the people and land virtually absolute b. M ...
Egypt group notes 2016
... • Egypt's great pharaohs were powerful figures who shaped its history • Hatshepsut was one of the few women rulers of Egypt, her rule was peaceful • Hatshepsut was the daughter of one pharaoh and the wife of another • Hatshepsut carried out all the rituals expected of a king to gain support (she eve ...
... • Egypt's great pharaohs were powerful figures who shaped its history • Hatshepsut was one of the few women rulers of Egypt, her rule was peaceful • Hatshepsut was the daughter of one pharaoh and the wife of another • Hatshepsut carried out all the rituals expected of a king to gain support (she eve ...
Egypt GRAPES Pt 2
... Came to power c. 1473 BCE Was supposed to help her nephew rule but just made herself pharaoh ...
... Came to power c. 1473 BCE Was supposed to help her nephew rule but just made herself pharaoh ...
Egypt - Cobb Learning
... • Both the Egyptian empire and the Hittites were attacked by invaders referred to as the “Sea Peoples” that caused great destruction. • The Sahara to the west no longer protected Egypt and it was repeated raided by Libyans. ...
... • Both the Egyptian empire and the Hittites were attacked by invaders referred to as the “Sea Peoples” that caused great destruction. • The Sahara to the west no longer protected Egypt and it was repeated raided by Libyans. ...
WHICh2EGYPTSec1-notes-2014 - Alabama School of Fine Arts
... Toward the end of the Old Kingdom Period, the strength of the central government began to decline. Pepi II, last ruler of the Old Kingdom, just lived too long. He became weaker, and the local nobles grew more powerful and rebelled. For about 100 years, the central government there were civil wars as ...
... Toward the end of the Old Kingdom Period, the strength of the central government began to decline. Pepi II, last ruler of the Old Kingdom, just lived too long. He became weaker, and the local nobles grew more powerful and rebelled. For about 100 years, the central government there were civil wars as ...