First Age of Empires, Classical Greece, Ancient Rome
... in check with an alliance with the Nubian kingdom of Cush. Despite this, the southern Egyptian city of Thebes finally began a war of independence that culminated with the expulsion of the Hyksos by Ahmose I in 1567 BC. The rather peaceful dynasty was hereby ended (like the Egyptian dynasty) and the ...
... in check with an alliance with the Nubian kingdom of Cush. Despite this, the southern Egyptian city of Thebes finally began a war of independence that culminated with the expulsion of the Hyksos by Ahmose I in 1567 BC. The rather peaceful dynasty was hereby ended (like the Egyptian dynasty) and the ...
Chapter 2 Ancient Egypt
... some people became artisans instead of farmers. Artisans wove cloth, made pottery, carved statues, and crafted weapons and tools. Egyptians traded with each other and with others in Mesopotamia. ...
... some people became artisans instead of farmers. Artisans wove cloth, made pottery, carved statues, and crafted weapons and tools. Egyptians traded with each other and with others in Mesopotamia. ...
Presentation
... • The vast and forbidding deserts on either side of the Nile acted as natural barriers between Egypt and other lands. - They forced Egyptians to live on a very small portion of the land and reduced interaction with other peoples. - The deserts also shut out invaders and spared Egypt the constant war ...
... • The vast and forbidding deserts on either side of the Nile acted as natural barriers between Egypt and other lands. - They forced Egyptians to live on a very small portion of the land and reduced interaction with other peoples. - The deserts also shut out invaders and spared Egypt the constant war ...
File
... I. Geography of the Nile River - “Gift of the Nile” – without the Nile, Egypt would be swallowed up by desert - Nile flows from south to north- Yearly Floods - Rain in the spring at the source of the Nile in Central Africa caused a yearly flood of the Nile. - The yearly flood covered the land with s ...
... I. Geography of the Nile River - “Gift of the Nile” – without the Nile, Egypt would be swallowed up by desert - Nile flows from south to north- Yearly Floods - Rain in the spring at the source of the Nile in Central Africa caused a yearly flood of the Nile. - The yearly flood covered the land with s ...
Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
... Men supported the family and trained their sons to take on their line of work. Women raised the children. Upper class women had servants or slaves. – Egyptian women had more rights that in other societies. They could: ask for divorces, represent themselves in legal matters, upper and middle class wo ...
... Men supported the family and trained their sons to take on their line of work. Women raised the children. Upper class women had servants or slaves. – Egyptian women had more rights that in other societies. They could: ask for divorces, represent themselves in legal matters, upper and middle class wo ...
Chapter 5.1
... At first Upper and Lower Egypt were not united. Upper Egypt was symbolized by a white cone-shaped crown. Lower Egypt was symbolized by a red crown. Around 3100BC, Narmer (Menes) from Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt and married one of their princesses, uniting both kingdoms. ...
... At first Upper and Lower Egypt were not united. Upper Egypt was symbolized by a white cone-shaped crown. Lower Egypt was symbolized by a red crown. Around 3100BC, Narmer (Menes) from Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt and married one of their princesses, uniting both kingdoms. ...
Sandra - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Why do we learned about the Egyptian Civilization? • This civilization was one of the first and oldest civilization that we know of. • They were a group of people who lived in Egypt more than five thousand years ago. • They were able to start a civilization because they were able to grow and built ...
... Why do we learned about the Egyptian Civilization? • This civilization was one of the first and oldest civilization that we know of. • They were a group of people who lived in Egypt more than five thousand years ago. • They were able to start a civilization because they were able to grow and built ...
The Nile River Valley - Rutherford County Schools
... At first Upper and Lower Egypt were not united. Upper Egypt was symbolized by a white cone-shaped crown. Lower Egypt was symbolized by a red crown. Around 3100BC, Narmer (Menes) from Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt and married one of their princesses, uniting both kingdoms. ...
... At first Upper and Lower Egypt were not united. Upper Egypt was symbolized by a white cone-shaped crown. Lower Egypt was symbolized by a red crown. Around 3100BC, Narmer (Menes) from Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt and married one of their princesses, uniting both kingdoms. ...
The Nile River Valley
... At first Upper and Lower Egypt were not united. Upper Egypt was symbolized by a white cone-shaped crown. Lower Egypt was symbolized by a red crown. Around 3100BC, Narmer (Menes) from Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt and married one of their princesses, uniting both kingdoms. ...
... At first Upper and Lower Egypt were not united. Upper Egypt was symbolized by a white cone-shaped crown. Lower Egypt was symbolized by a red crown. Around 3100BC, Narmer (Menes) from Upper Egypt conquered Lower Egypt and married one of their princesses, uniting both kingdoms. ...
First Civilizations: Africa and Asia 3200BCE – 500BCE
... stretched to the Euphrates River - Hatshepsut was a woman who ruled as Pharaoh from 1583 BCE – 1482 BCE - Ramses II was the most powerful ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into dec ...
... stretched to the Euphrates River - Hatshepsut was a woman who ruled as Pharaoh from 1583 BCE – 1482 BCE - Ramses II was the most powerful ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into dec ...
First Civilizations: Africa and Asia 3200BCE – 500BCE
... stretched to the Euphrates River - Hatshepsut was a woman who ruled as Pharaoh from 1583 BCE – 1482 BCE - Ramses II was the most powerful ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into dec ...
... stretched to the Euphrates River - Hatshepsut was a woman who ruled as Pharaoh from 1583 BCE – 1482 BCE - Ramses II was the most powerful ruler of the New Kingdom and during his reign Egypt enjoyed great wealth and prosperity as well as military conquests. - After Ramses II died, Egypt went into dec ...
Food and Farming - The Fitzwilliam Museum
... water jars, another sieves lumps of bread into a vat where it will ferment with water to make beer. For baking, dough could be cooked on a flat stone over the fire, on the outer walls of a clay oven or in heated moulds, most of which were conical. Both leavened and unleavened breads were eaten. Leav ...
... water jars, another sieves lumps of bread into a vat where it will ferment with water to make beer. For baking, dough could be cooked on a flat stone over the fire, on the outer walls of a clay oven or in heated moulds, most of which were conical. Both leavened and unleavened breads were eaten. Leav ...
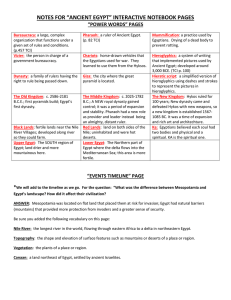
notes for “ancient egypt” interactive notebook pages
... Pharaoh: the ruler of Egypt: acted as a god. Viziers, Priests, Nobles: Highest officials worked under the pharaoh. Most powerful groups in Egypt under the pharaoh; Viziers – government officials (assisted pharaoh) that decided court cases. Noble: person of high birth. Scribes: MEN ONLY!! They were u ...
... Pharaoh: the ruler of Egypt: acted as a god. Viziers, Priests, Nobles: Highest officials worked under the pharaoh. Most powerful groups in Egypt under the pharaoh; Viziers – government officials (assisted pharaoh) that decided court cases. Noble: person of high birth. Scribes: MEN ONLY!! They were u ...
Ancient Egypt (3,150 B.C. – 30 B.C.)
... along the Nile River in the northeast of Africa. The civilization was formed when two kingdoms were united (Upper and Lower Egypt). The Nile was very important for the ancient Egyptians. The people built irrigation systems along the river and were able to grow lots of crops in the area. The river ga ...
... along the Nile River in the northeast of Africa. The civilization was formed when two kingdoms were united (Upper and Lower Egypt). The Nile was very important for the ancient Egyptians. The people built irrigation systems along the river and were able to grow lots of crops in the area. The river ga ...
File - 12 Ancient History
... Egyptian term ‘per-aa’ which means ‘great house’. It originally referred to the palace of the king rather than to the king himself. Like many ancient rulers, the Egyptian pharaoh enjoyed absolute power over his subjects. He was the embodiment both of earthly and divine authority, and was regarded as ...
... Egyptian term ‘per-aa’ which means ‘great house’. It originally referred to the palace of the king rather than to the king himself. Like many ancient rulers, the Egyptian pharaoh enjoyed absolute power over his subjects. He was the embodiment both of earthly and divine authority, and was regarded as ...
Characteristics of Ancient Egyptian Art
... for common, utilitarian purposes, though at times it might have been decorated or painted. Blue painted pottery was somewhat common during the New Kingdom (1,550-1,069 BC). Marl Clay – made from material found around Qena in Upper Egypt. This type of pottery was usually thought superior to the commo ...
... for common, utilitarian purposes, though at times it might have been decorated or painted. Blue painted pottery was somewhat common during the New Kingdom (1,550-1,069 BC). Marl Clay – made from material found around Qena in Upper Egypt. This type of pottery was usually thought superior to the commo ...
Introduction to Ancient Egypt Visit the links below (they all link off the
... Most of the painting of Ancient Egypt that has survived were found in tombs of the pharaohs or high governmental officials. The art is know as funerary art because it is in tombs and depicts scenes of the afterlife. Tomb paintings were of everyday life until the New Kingdom about 1550 BC to 1020 BC. ...
... Most of the painting of Ancient Egypt that has survived were found in tombs of the pharaohs or high governmental officials. The art is know as funerary art because it is in tombs and depicts scenes of the afterlife. Tomb paintings were of everyday life until the New Kingdom about 1550 BC to 1020 BC. ...
Chapter Two Egyptian Overview Powerpoint
... Egypt was divided into many different parts. First the north from the south, then the north was divided into the east and the west. But these were more what we consider “The maritimes” or “Out West” here in Canada. Egypt was divided into 42 smaller cities or regions with what were called nodes. ...
... Egypt was divided into many different parts. First the north from the south, then the north was divided into the east and the west. But these were more what we consider “The maritimes” or “Out West” here in Canada. Egypt was divided into 42 smaller cities or regions with what were called nodes. ...
African Literary Tradition
... Provided settlers with water During flood season, provided silt for growing crops. Transportation for trade ...
... Provided settlers with water During flood season, provided silt for growing crops. Transportation for trade ...
Western Asia and Egypt
... sister/wife Isis [the fertile soil of Egypt, the star Sirius 2. Seth [Disorder, the God of Foreign Places] and his ...
... sister/wife Isis [the fertile soil of Egypt, the star Sirius 2. Seth [Disorder, the God of Foreign Places] and his ...
Activity Guide - Virginia Museum of Fine Arts
... or protected, through mummification, a very long and expensive process that not everyone could afford. Mummies were wrapped and placed in coffins and buried in tombs or graves. Magic spells and special instructions were often written in hieroglyphs on coffins and in tombs to offer protection and war ...
... or protected, through mummification, a very long and expensive process that not everyone could afford. Mummies were wrapped and placed in coffins and buried in tombs or graves. Magic spells and special instructions were often written in hieroglyphs on coffins and in tombs to offer protection and war ...
Kingdoms in North Eastern Africa
... • Hyksos warriors destroyed temples, and burned cities. III. New Kingdom (Age of the Empire) • 1580-1090 B.C. • Egyptian pharaohs drove out Hyksos warriors • The Egyptians created a standing army of charioteers, bowman and foot soldiers • Hatshepsut: Was a powerful female pharaoh, who expanded trade ...
... • Hyksos warriors destroyed temples, and burned cities. III. New Kingdom (Age of the Empire) • 1580-1090 B.C. • Egyptian pharaohs drove out Hyksos warriors • The Egyptians created a standing army of charioteers, bowman and foot soldiers • Hatshepsut: Was a powerful female pharaoh, who expanded trade ...
Pharaoh
... Egyptians built mountain-like pyramids, entirely of stone, as tombs for the pharaohs They were the size of several city blocks and were meant to protect the dead bodies of pharaohs from: ...
... Egyptians built mountain-like pyramids, entirely of stone, as tombs for the pharaohs They were the size of several city blocks and were meant to protect the dead bodies of pharaohs from: ...