HW/ Social Studies Chapter Four/ Section One – Egypt Under the
... 8. What region does the Nile Delta form? Why is this area so fertile? ...
... 8. What region does the Nile Delta form? Why is this area so fertile? ...
The Art of Ancient Egypt - Pleasant Valley High School
... and common method of mummification dates back to the 18th Dynasty. The first step was to remove the internal organs and liquid so that the body would not decay. The embalmers took out the brain by inserting a sharp object in the nostril, breaking through it into the brain and then liquefying it. The ...
... and common method of mummification dates back to the 18th Dynasty. The first step was to remove the internal organs and liquid so that the body would not decay. The embalmers took out the brain by inserting a sharp object in the nostril, breaking through it into the brain and then liquefying it. The ...
Religion, Writing and Daily Life The Egyptians were very religious
... The daily lives of the Egyptians were full of hard work, but they worked together and also found time to enjoy themselves. Egyptian social structure is shaped like a pyramid. The pharaoh was at the top with his government officials, viziers and priests. The middle class was made up of soldiers, merc ...
... The daily lives of the Egyptians were full of hard work, but they worked together and also found time to enjoy themselves. Egyptian social structure is shaped like a pyramid. The pharaoh was at the top with his government officials, viziers and priests. The middle class was made up of soldiers, merc ...
File - Mr. Bowling`s Social Studies Class
... soaked in scented oil so that they would regain the shape they had in life. Cover with necklaces, rings and bracelets made of gold and gems. ...
... soaked in scented oil so that they would regain the shape they had in life. Cover with necklaces, rings and bracelets made of gold and gems. ...
Document
... • Ancient Egypt included two regions, a southern and a northern region, that were given their names by their relation to the Nile. • At several points, the rough terrain caused cataracts, or rapids, to form. ...
... • Ancient Egypt included two regions, a southern and a northern region, that were given their names by their relation to the Nile. • At several points, the rough terrain caused cataracts, or rapids, to form. ...
Ancient Egypt Quiz
... workers and advanced technology: A. “They owned many slaves.” B. “One pyramid was 755 feet high and took twenty years to build.” C. “…those who lived evil lives would meet up with a wicked beast called the “Devourer of Souls.” D. “The officials lived in large homes made of brick and wood, with elabo ...
... workers and advanced technology: A. “They owned many slaves.” B. “One pyramid was 755 feet high and took twenty years to build.” C. “…those who lived evil lives would meet up with a wicked beast called the “Devourer of Souls.” D. “The officials lived in large homes made of brick and wood, with elabo ...
Standard 6.2.3 Understand the relationship between religion and
... the gods they were expected to take care of the people and were blamed for famines, floods and droughts. Pharaohs were religious leaders and were expected to participate in religious ceremonies. When they died, pharaohs went to the afterlife. 2. The pharaohs usually inherited their power from family ...
... the gods they were expected to take care of the people and were blamed for famines, floods and droughts. Pharaohs were religious leaders and were expected to participate in religious ceremonies. When they died, pharaohs went to the afterlife. 2. The pharaohs usually inherited their power from family ...
Standard 6.2.3 Understand the relationship between religion and
... the gods they were expected to take care of the people and were blamed for famines, floods and droughts. Pharaohs were religious leaders and were expected to participate in religious ceremonies. When they died, pharaohs went to the afterlife. 2. The pharaohs usually inherited their power from family ...
... the gods they were expected to take care of the people and were blamed for famines, floods and droughts. Pharaohs were religious leaders and were expected to participate in religious ceremonies. When they died, pharaohs went to the afterlife. 2. The pharaohs usually inherited their power from family ...
Do you know anything about Egypt
... pharaoh Mentuhotep united Egypt and moved the capital city to Thebes. The dominant king reclaimed power. Art and literature begin to develop in the capital city Thebes, and the first known schools were set up. Egypt successfully conquered Southern Nubia under Senwosret I and III during this time. ...
... pharaoh Mentuhotep united Egypt and moved the capital city to Thebes. The dominant king reclaimed power. Art and literature begin to develop in the capital city Thebes, and the first known schools were set up. Egypt successfully conquered Southern Nubia under Senwosret I and III during this time. ...
Ancient Egypt €€€€€€€€The giant pyramids, temples, an
... The people of ancient Egypt took great care in preparing for life after death. They denied that death ended the existence of a person who had led a good life. They believed that the next world w ould be like Egypt in its richest and most enjoyable form. They built stone tombs and filled them w ith c ...
... The people of ancient Egypt took great care in preparing for life after death. They denied that death ended the existence of a person who had led a good life. They believed that the next world w ould be like Egypt in its richest and most enjoyable form. They built stone tombs and filled them w ith c ...
ETERNAL EGYPT, Smithsonian, June 2001
... avoids the term "artifacts" as subtly demeaning to works of art, wants visitors to "Eternal Egypt" to come away with an appreciation for the sheer visual appeal of these objects and the mastery with which they were fashioned. The classic conventions of Egyptian art were literally set in stone during ...
... avoids the term "artifacts" as subtly demeaning to works of art, wants visitors to "Eternal Egypt" to come away with an appreciation for the sheer visual appeal of these objects and the mastery with which they were fashioned. The classic conventions of Egyptian art were literally set in stone during ...
EGYPTIAN CHRONOLOGY
... regained control, but Esarhaddon's son Ashurbanipal attacked and recaptured Memphis. Taharqa's successor, Tanutamun, managed to regain control of the country, but eventually Ashurbanipal returned with a vengeance and moved to Thebes where the temples were raided of their treasures. Nubia would never ...
... regained control, but Esarhaddon's son Ashurbanipal attacked and recaptured Memphis. Taharqa's successor, Tanutamun, managed to regain control of the country, but eventually Ashurbanipal returned with a vengeance and moved to Thebes where the temples were raided of their treasures. Nubia would never ...
Ancient Egypt
... – High priest of all – Overlord of all citizens – Thought to be chosen by the gods – Had four crowns to wear – Had as much as 900 children ...
... – High priest of all – Overlord of all citizens – Thought to be chosen by the gods – Had four crowns to wear – Had as much as 900 children ...
Ancient Egypt . Crystal Wang Period.3 9/6/12 • The Predynastic and
... achievement – this was the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the highest points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley (the others being Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom ). ...
... achievement – this was the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the highest points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley (the others being Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom ). ...
The Old Kingdom - Mr. Scott`s Cyberdesk
... There were many gods dealing with death and the afterlife. Chief among the gods of death and the afterlife was Osiris (lower right). The Egyptians believed that once, long ago, Osiris had been a king of Lower Egypt who was loved by everyone except his jealous brother, Seth. Seth decided to murder Os ...
... There were many gods dealing with death and the afterlife. Chief among the gods of death and the afterlife was Osiris (lower right). The Egyptians believed that once, long ago, Osiris had been a king of Lower Egypt who was loved by everyone except his jealous brother, Seth. Seth decided to murder Os ...
Ancient Egypt - K12LessonPlans
... Government officials gave themselves all kinds of titles. But in ancient Egypt, the only title that mattered besides the title of Pharaoh was that of Vizier. The Vizier was Pharaoh's right hand man. Everyone reported to the official above them. The top officials reported to the Vizier. The Vizier re ...
... Government officials gave themselves all kinds of titles. But in ancient Egypt, the only title that mattered besides the title of Pharaoh was that of Vizier. The Vizier was Pharaoh's right hand man. Everyone reported to the official above them. The top officials reported to the Vizier. The Vizier re ...
Notes for Ancient Egypt Interactive Notebook Pages
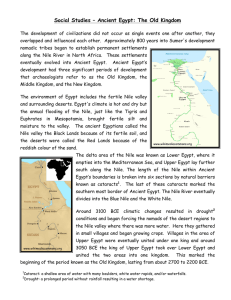
... The Old Kingdom – What were the significant events that occurred in the Old Kingdom? ANSWER: Egypt had their first dynasty; Memphis was made the capital of the kingdom; they build their famous pyramids. Lasted from 2700 to 2200 BCE; strong central government set up; Known as the “Age of the Pyramids ...
... The Old Kingdom – What were the significant events that occurred in the Old Kingdom? ANSWER: Egypt had their first dynasty; Memphis was made the capital of the kingdom; they build their famous pyramids. Lasted from 2700 to 2200 BCE; strong central government set up; Known as the “Age of the Pyramids ...
Name - Quia
... Egypt’s resources, there was a lot of jealousy that often led to violence, just like in the New Stone Age. Archaeologists have uncovered ruins of walls around early towns and paintings of bloody battle scenes that suggest that there were many wars between villages. People began to fear for their saf ...
... Egypt’s resources, there was a lot of jealousy that often led to violence, just like in the New Stone Age. Archaeologists have uncovered ruins of walls around early towns and paintings of bloody battle scenes that suggest that there were many wars between villages. People began to fear for their saf ...
Mummies and Pyramids - Campbell County Schools
... The pharaoh was the king of Egypt. He had all the power and owned all the land. He had many government officials and priests who did the work of running the country for him. (Pharaohs were usually men, but a few were women!) Generally the pharaoh’s son became king after the pharaoh died. The royal f ...
... The pharaoh was the king of Egypt. He had all the power and owned all the land. He had many government officials and priests who did the work of running the country for him. (Pharaohs were usually men, but a few were women!) Generally the pharaoh’s son became king after the pharaoh died. The royal f ...
The Old Kingdom - White Plains Public Schools
... The Old Kingdom In this lesson, students will identify characteristics of the Old Kingdom of ancient Egyptian history. Students will be able to define and/or identify the following terms: Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Dynasty Pharaoh Pyramid E. Napp ...
... The Old Kingdom In this lesson, students will identify characteristics of the Old Kingdom of ancient Egyptian history. Students will be able to define and/or identify the following terms: Lower Egypt Upper Egypt Dynasty Pharaoh Pyramid E. Napp ...
Ancient Egypt - Maples Elementary School
... 4. List the 6 things necessary to have a civilization. ...
... 4. List the 6 things necessary to have a civilization. ...
Egypt By Jack T
... was a weed called papyrus. This weed grew wildly along the shores of the Nile River. • The ancient Egyptians used papyrus to make many things, such as baskets, sandals, mats, rope, and paper! ...
... was a weed called papyrus. This weed grew wildly along the shores of the Nile River. • The ancient Egyptians used papyrus to make many things, such as baskets, sandals, mats, rope, and paper! ...
EGYPT 2012
... • Had no word for religion, the ideas were inseparable part of the world order • Egyptians were polytheistic, had many important gods and goddesses – Key god was the god of the sun = Re or Amon-Re (father of the pharaohs) – Anubis = protector of the dead ...
... • Had no word for religion, the ideas were inseparable part of the world order • Egyptians were polytheistic, had many important gods and goddesses – Key god was the god of the sun = Re or Amon-Re (father of the pharaohs) – Anubis = protector of the dead ...