Ancient Egypt
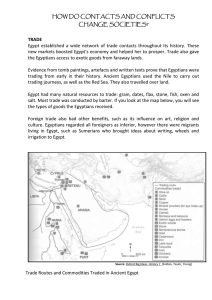
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirely on ...
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirely on ...
Ancient Egypt - Polk School District
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirely on ...
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirely on ...
Egypt, Kush, and Axum - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Hyksos warriors destroyed temples, and burned cities. ...
... Hyksos warriors destroyed temples, and burned cities. ...
The Art of Ancient Egypt
... how to regulate and divert the flow of water through dams and irrigation upstream as well. Coming north from Ethiopia, the Nile falls over several cataracts and then creates a long narrow valley before spreading out into the delta. The cataracts marked the southernmost natural boundary of Egypt (the ...
... how to regulate and divert the flow of water through dams and irrigation upstream as well. Coming north from Ethiopia, the Nile falls over several cataracts and then creates a long narrow valley before spreading out into the delta. The cataracts marked the southernmost natural boundary of Egypt (the ...
Issue 11. June 2002
... event raised over £2500. This surpassed our wildest hopes and the fund is still growing daily! The Fun Day was opened by Emma Nehemiah, Out of School Learning Development Worker for New Opportunities Funding and Eve Lawton, Trustee and Outreach Officer for the Sunshine Project ...
... event raised over £2500. This surpassed our wildest hopes and the fund is still growing daily! The Fun Day was opened by Emma Nehemiah, Out of School Learning Development Worker for New Opportunities Funding and Eve Lawton, Trustee and Outreach Officer for the Sunshine Project ...
Egypt is the Gift of the Nile
... 3. The Hyksos people invaded Egypt and so the Egyptians set out to capture their lands over the eastern frontier to prevent the Hyksos from ever invading them again. 4. Once the Egyptians had fought on foot, but the Hyksos brought a revolutionary new weapon to Egypt—the horse and chariot. 5. Based o ...
... 3. The Hyksos people invaded Egypt and so the Egyptians set out to capture their lands over the eastern frontier to prevent the Hyksos from ever invading them again. 4. Once the Egyptians had fought on foot, but the Hyksos brought a revolutionary new weapon to Egypt—the horse and chariot. 5. Based o ...
The doctor in Ancient Egypt
... In the fifth century B.C. Herodotus remarked on the degree of specialisation he found in Egypt. Most of the known specialist medical titles were carried by a certain Iren-akhty discussed below. Dentists carried the separate title ibeh. Three of the five known dentists of the Old Kingdom also carried ...
... In the fifth century B.C. Herodotus remarked on the degree of specialisation he found in Egypt. Most of the known specialist medical titles were carried by a certain Iren-akhty discussed below. Dentists carried the separate title ibeh. Three of the five known dentists of the Old Kingdom also carried ...
Unit 2 Social Studies Review
... 4). Discuss at least 3 ways that the Ancient Egyptians influenced the Kush. A). When being lead by Egypt, Kushites wore Egyptian clothes and make-up like a regular Egyptian citizen. In sum, they became Egyptianized. B). Kush children were educated by Egyptian teachers during Egypt's rein over Kush. ...
... 4). Discuss at least 3 ways that the Ancient Egyptians influenced the Kush. A). When being lead by Egypt, Kushites wore Egyptian clothes and make-up like a regular Egyptian citizen. In sum, they became Egyptianized. B). Kush children were educated by Egyptian teachers during Egypt's rein over Kush. ...
The Pyramid Builders
... Sometimes they also stole the mummies. Egyptians believed that if a tomb was robbed, the person buried there could not have a happy afterlife. During the New Kingdom, pharaohs began building more secret tombs in an area called the Valley of the Kings. The burial chambers were hidden in mountains nea ...
... Sometimes they also stole the mummies. Egyptians believed that if a tomb was robbed, the person buried there could not have a happy afterlife. During the New Kingdom, pharaohs began building more secret tombs in an area called the Valley of the Kings. The burial chambers were hidden in mountains nea ...
NAME
... Explain: THROUGH SERVICE TO THE PHARAOH 3. List the 3 social classes and the people who inhabited them. a. SMALL UPPER CLASS: PRIESTS, PHARAOH’S COURT, NOBLES b. MIDDLE CLASS: MERCHANTS, SKILLED WORKERS c. LOWEST CLASS: PEASANTS 4. For who was a separate class made? SLAVES 5. What did peasants do fo ...
... Explain: THROUGH SERVICE TO THE PHARAOH 3. List the 3 social classes and the people who inhabited them. a. SMALL UPPER CLASS: PRIESTS, PHARAOH’S COURT, NOBLES b. MIDDLE CLASS: MERCHANTS, SKILLED WORKERS c. LOWEST CLASS: PEASANTS 4. For who was a separate class made? SLAVES 5. What did peasants do fo ...
Ancient Egypt Test
... 38. Why was ancient Egypt called the “gift of the Nile” by the historian Herodotus? a. Because of the fertile soil left by the flooding of the Nile, Egyptians farmed land that is surrounded by desert and has a hot and dry climate b. The Egyptians lived in the Sahara, a huge desert in North Africa, a ...
... 38. Why was ancient Egypt called the “gift of the Nile” by the historian Herodotus? a. Because of the fertile soil left by the flooding of the Nile, Egyptians farmed land that is surrounded by desert and has a hot and dry climate b. The Egyptians lived in the Sahara, a huge desert in North Africa, a ...
Ancient Egypt - FLYPARSONS.org
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirel ...
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirel ...
Farming - Grade4-BCA
... lettuce, lentils, cabbages, radishes, turnips, grapes, figs, plums and melons. The Egyptians had plenty of food with great variety! Since Egypt didn’t get much rain, they had to find a way of watering the crops once all of the flood water receded (went away). The Egyptians solved this problem by dig ...
... lettuce, lentils, cabbages, radishes, turnips, grapes, figs, plums and melons. The Egyptians had plenty of food with great variety! Since Egypt didn’t get much rain, they had to find a way of watering the crops once all of the flood water receded (went away). The Egyptians solved this problem by dig ...
PPT - FLYPARSONS.org
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirely on ...
... • Simple economy based on food production and minerals from desert • access to the Mediterranean their routes extended trade as far as Northern Europe, subtropical Africa and the Near East • Trading was done by bartering goods (grain, oil, wheat) • Taxes, salaries and loans were all paid entirely on ...
H British Museum Online Part 1
... On the left-hand side of the page, select Story Read the story and answer the following questions: ...
... On the left-hand side of the page, select Story Read the story and answer the following questions: ...
Male Pharaohs
... Major Male Pharaohs • There were several Pharaohs of Egypt. However, we will focus on the main male Pharaohs: ...
... Major Male Pharaohs • There were several Pharaohs of Egypt. However, we will focus on the main male Pharaohs: ...
Chapter 3
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
Chapter 3
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
... Kingdoms: Old Kingdom (2686-2181 B.C.), Middle Kingdom (1991-1786 B.C.), New Kingdom (1567-1085 B.C.) • Remember the kingdoms are NOT places but time periods. • The gaps between Kingdoms were times of trouble or war, invasions, or weak rulers. These periods were rare. ...
Name: Cohort: ______ Date: Before you start the Do Now complete
... Directions: Highlight the passage as you read, use your highlights to help you complete the outline on the back. You WILL be checked for accurate highlighting. Who were the pharaohs? Ancient Egyptian government was dominated by a single person, the pharaoh. The people believed that the pharaoh was m ...
... Directions: Highlight the passage as you read, use your highlights to help you complete the outline on the back. You WILL be checked for accurate highlighting. Who were the pharaohs? Ancient Egyptian government was dominated by a single person, the pharaoh. The people believed that the pharaoh was m ...
EGYPT
... • Kingship was a divine institution and pharaohs had absolute power – Belief that the pharaoh was a god in human form – Egypt was a theocracy, a state ruled by a religious figure • Surrounded by a well-established bureaucracy – Bureaucracy = a highly structured organization, often governmental, mana ...
... • Kingship was a divine institution and pharaohs had absolute power – Belief that the pharaoh was a god in human form – Egypt was a theocracy, a state ruled by a religious figure • Surrounded by a well-established bureaucracy – Bureaucracy = a highly structured organization, often governmental, mana ...
Ancient Egypt by Jason
... coast of Africa. It’s beside the Nile river where they get all their water. If it wasn’t for the Nile river, there would be no such thing as Egypt. Their transport was camels and bare foot. The camels were sometimes only used to carry luggage. ...
... coast of Africa. It’s beside the Nile river where they get all their water. If it wasn’t for the Nile river, there would be no such thing as Egypt. Their transport was camels and bare foot. The camels were sometimes only used to carry luggage. ...
Chapter 5: Ancient Egypt
... - The pharaoh ruled from capital city of _______________________________ • Egyptians believed pharaoh was a god, blamed him for hard times - in such times, a rival might replace pharaoh, start new dynasty • Since pharaoh seen as god, government and religion not separate - priests had much power, wer ...
... - The pharaoh ruled from capital city of _______________________________ • Egyptians believed pharaoh was a god, blamed him for hard times - in such times, a rival might replace pharaoh, start new dynasty • Since pharaoh seen as god, government and religion not separate - priests had much power, wer ...
Egypt
... • Amon-Re, hieroglyphs, Lower Egypt, Memphis, mummification, Nile River, pharaoh, pyramids, Queen Hatshepsut, Thebes, Upper Egypt ...
... • Amon-Re, hieroglyphs, Lower Egypt, Memphis, mummification, Nile River, pharaoh, pyramids, Queen Hatshepsut, Thebes, Upper Egypt ...