AP Study Guide for Chapter 7- Learning
... Know the definitions of the following: Learning (relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience.) Associative learning (A type of learning principle based on the assumption that ideas and experiences reinforce one another and can be linked to enhance the learning process- Pavlov.) Acquisi ...
... Know the definitions of the following: Learning (relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience.) Associative learning (A type of learning principle based on the assumption that ideas and experiences reinforce one another and can be linked to enhance the learning process- Pavlov.) Acquisi ...
AP Study Guide for Chapter 7- Learning
... Know the definitions of the following: Learning (relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience.) Associative learning (A type of learning principle based on the assumption that ideas and experiences reinforce one another and can be linked to enhance the learning process- Pavlov.) Acquisi ...
... Know the definitions of the following: Learning (relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience.) Associative learning (A type of learning principle based on the assumption that ideas and experiences reinforce one another and can be linked to enhance the learning process- Pavlov.) Acquisi ...
PSY100-learning10sum
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
Cerebellar Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Physiology
... binds, charged ions pass through a channel in the receptor center. Both basket and stellate cells in the molecular layer express presynaptic AMPA receptors, to which overflow glutamate from climbing fibers can bind.6 The metabotropic glutamate receptors, which are G-protein–coupled receptors acting ...
... binds, charged ions pass through a channel in the receptor center. Both basket and stellate cells in the molecular layer express presynaptic AMPA receptors, to which overflow glutamate from climbing fibers can bind.6 The metabotropic glutamate receptors, which are G-protein–coupled receptors acting ...
learning - Angelfire
... UCS (food) ------------------- UCR (salivation) AFTER CONDITIONING CS (light) --------------------- UCS (salivation) Critical Periods: a. ACQUISITION – trails during which the subject is learning the association between the two stimuli b. TRIAL – stage wherein there is a paired presentation of the ...
... UCS (food) ------------------- UCR (salivation) AFTER CONDITIONING CS (light) --------------------- UCS (salivation) Critical Periods: a. ACQUISITION – trails during which the subject is learning the association between the two stimuli b. TRIAL – stage wherein there is a paired presentation of the ...
The role of the basal ganglia in habit formation
... 22. Is the information represented by activity in hippocampal place cells being compared to activity in BG goal representation cells? ...
... 22. Is the information represented by activity in hippocampal place cells being compared to activity in BG goal representation cells? ...
Psych 1 Chapter-5 Review Quiz 1. Learning that occurs but is not
... a. Her son must always model the behavior immediately. b. Her son must be motivated to learn how to do the laundry. c. Her son must be able to complete other tasks while watching her. d. Cheryl must show her son how to do the laundry while she is making dinner. ...
... a. Her son must always model the behavior immediately. b. Her son must be motivated to learn how to do the laundry. c. Her son must be able to complete other tasks while watching her. d. Cheryl must show her son how to do the laundry while she is making dinner. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
classical conditiong ppt
... 2. (UCS) does not depend on the learners response 3. The learner responds to the environment In contrast, OPERANT CONDITIONING is a process by which the consequences of a response affect the likelihood that the response will occur again. This is what we will study next ...
... 2. (UCS) does not depend on the learners response 3. The learner responds to the environment In contrast, OPERANT CONDITIONING is a process by which the consequences of a response affect the likelihood that the response will occur again. This is what we will study next ...
Medial Longitudinal Fissure
... Receives afferents from sensory modalities and relay via Thalamus ...
... Receives afferents from sensory modalities and relay via Thalamus ...
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COEPLETION 1. Primary
... (B) eliminate direct synaptic input to the amygdala from entorhinal cortex (C) produce retrograde degeneration of neurons in orbital cortex (D) eliminate direct synaptic projections from amygdala to the dorsal medial thalamus (E) eliminate some synaptic input to the contralateral amygdala 16. Declar ...
... (B) eliminate direct synaptic input to the amygdala from entorhinal cortex (C) produce retrograde degeneration of neurons in orbital cortex (D) eliminate direct synaptic projections from amygdala to the dorsal medial thalamus (E) eliminate some synaptic input to the contralateral amygdala 16. Declar ...
cb2-12
... Consumer Learning - A process by which individuals acquire the purchase and consumption knowledge and experience that they apply to future related behavior. ...
... Consumer Learning - A process by which individuals acquire the purchase and consumption knowledge and experience that they apply to future related behavior. ...
Thank you for helping the effort to translate Psychology Tools
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
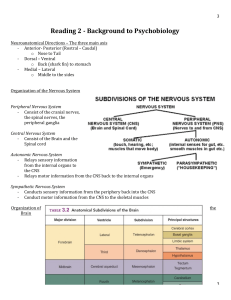
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Corpus Callosum – Principal commissure connecting the left and right hemisphere together - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matte ...
... - Corpus Callosum – Principal commissure connecting the left and right hemisphere together - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matte ...
Ch. 9: Learning / Conditioning
... Unconditioned Response (UR) -automatic reaction (ex: drooling from meat) Conditioned Response (CR) -learned reaction to a neutral stimulus (ex: drooling at bell) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) -causes CR (ex: the bell) ...
... Unconditioned Response (UR) -automatic reaction (ex: drooling from meat) Conditioned Response (CR) -learned reaction to a neutral stimulus (ex: drooling at bell) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) -causes CR (ex: the bell) ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Neuronal Circuit of the Functional Unit a. Purkinje fibers and deep nuclear cells fire continuously under normal resting conditions b. Balance between excitation and inhibition at the deep cerebellar nuclei ...
... • Neuronal Circuit of the Functional Unit a. Purkinje fibers and deep nuclear cells fire continuously under normal resting conditions b. Balance between excitation and inhibition at the deep cerebellar nuclei ...
Exam - (canvas.brown.edu).
... matching number in the photocopied figures at the back of the exam. Original versions of the photocopies with somewhat better reproductions are available for viewing at the front of the room. You should try to be quite specific, but we are not looking for extraordinary detail. As a hypothetical exam ...
... matching number in the photocopied figures at the back of the exam. Original versions of the photocopies with somewhat better reproductions are available for viewing at the front of the room. You should try to be quite specific, but we are not looking for extraordinary detail. As a hypothetical exam ...
Thank you for helping the effort to translate PsychologyTools
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
... the CS and the US becomes weaker. This process is known as extinction. With time the CS stops leading to the CR and the CR is said to be extinguished. Why is classical conditioning important to therapists? Often neutral stimuli become associated with fearful situations and cause difficulties in peop ...
Classical & Operant Conditiong
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
Chapter 13
... Many studies of STM involve a delayed matching-to-sample task (a task that requires the subject to indicate which stimulus has just been perceived) ...
... Many studies of STM involve a delayed matching-to-sample task (a task that requires the subject to indicate which stimulus has just been perceived) ...