learning-and-intro-to-attachment-2017
... the psychodynamic approach had emphasis on the invisible and untestable unconscious, and lacked the scientific rigor of physics and chemistry at the start of the ...
... the psychodynamic approach had emphasis on the invisible and untestable unconscious, and lacked the scientific rigor of physics and chemistry at the start of the ...
Classical and Operant Conditioning
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
Learning Perspective
... Describe the Historical and Cultural influences of the Learning Perspective. Evaluate the Basic Assumptions on which the Learning Perspective is based. Explain how classical conditioning can be used to explain the effectiveness of some types of advertising. Explain the strengths and weaknesses of Cl ...
... Describe the Historical and Cultural influences of the Learning Perspective. Evaluate the Basic Assumptions on which the Learning Perspective is based. Explain how classical conditioning can be used to explain the effectiveness of some types of advertising. Explain the strengths and weaknesses of Cl ...
classical conditioning
... behaviors of various organisms could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. (cognition in rats and dogs does not play a role) Rescorla and Wagner (1972) disagreed Experimented ...
... behaviors of various organisms could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. (cognition in rats and dogs does not play a role) Rescorla and Wagner (1972) disagreed Experimented ...
Classical Cond powerpoint
... behaviors of various organisms could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. (cognition in rats and dogs does not play a role) Rescorla and Wagner (1972) disagreed Experimented ...
... behaviors of various organisms could be reduced to mindless mechanisms. (cognition in rats and dogs does not play a role) Rescorla and Wagner (1972) disagreed Experimented ...
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
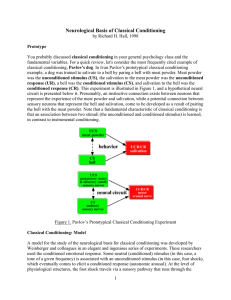
... Figure 1. Pavlov’s Prototypical Classical Conditioning Experiment Classical Conditioning: Model A model for the study of the neurological basis for classical conditioning was developed by Weinberger and colleagues in an elegant and ingenious series of experiments. These researchers used the conditio ...
... Figure 1. Pavlov’s Prototypical Classical Conditioning Experiment Classical Conditioning: Model A model for the study of the neurological basis for classical conditioning was developed by Weinberger and colleagues in an elegant and ingenious series of experiments. These researchers used the conditio ...
missing slide slide 7
... conditioned response (CR) that often resembles the unconditioned response (UCR) Stimuli that are similar to CS also elicit the CR to some extent , although such generalization can be curbed by discrimination training . These phenomena occur in organisms as flatworm and humans. ...
... conditioned response (CR) that often resembles the unconditioned response (UCR) Stimuli that are similar to CS also elicit the CR to some extent , although such generalization can be curbed by discrimination training . These phenomena occur in organisms as flatworm and humans. ...
LEARNING
... conditioned response (CR) that often resembles the unconditioned response (UCR) Stimuli that are similar to CS also elicit the CR to some extent , although such generalization can be curbed by discrimination training . These phenomena occur in organisms as flatworm and humans. ...
... conditioned response (CR) that often resembles the unconditioned response (UCR) Stimuli that are similar to CS also elicit the CR to some extent , although such generalization can be curbed by discrimination training . These phenomena occur in organisms as flatworm and humans. ...
Slide 1
... of each joint along the trajectory and also contextrelated information. Inputs encoding the error are sent (upper downward arrow) through the inferior olive (IO). Cerebellar outputs are provided by the deep-cerebellar-nuclei cells (DCN) (lower downward arrow). The DCN collects activity from the moss ...
... of each joint along the trajectory and also contextrelated information. Inputs encoding the error are sent (upper downward arrow) through the inferior olive (IO). Cerebellar outputs are provided by the deep-cerebellar-nuclei cells (DCN) (lower downward arrow). The DCN collects activity from the moss ...
Learning Learning
... • Learning to link two stimuli in a way that helps us anticipate an event to which we have a reaction ...
... • Learning to link two stimuli in a way that helps us anticipate an event to which we have a reaction ...
Neural coding in the primary olfactory cortex
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
Learning/Behavior Quizzo - Knob
... Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Classical Conditioning ...
... Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Classical Conditioning ...
Motor disorders
... stimulus (e.g. a tone) followed by an unconditioned stimulus (e.g. small shock to the eye, causing it to blink). Initially, animals blink with the stimulus. However, with repeated exposure, animals start to blink when the tone sounds (this is the conditioned response). In the cerebellar cortex, mos ...
... stimulus (e.g. a tone) followed by an unconditioned stimulus (e.g. small shock to the eye, causing it to blink). Initially, animals blink with the stimulus. However, with repeated exposure, animals start to blink when the tone sounds (this is the conditioned response). In the cerebellar cortex, mos ...
Learning about Learning - by Directly Driving Networks of Neurons
... New behaviors require new patterns of neural activity among the population of neurons that control behavior. How can the brain find a pattern of activity appropriate for the desired behavior? Why does that learning process take time? To tackle questions like these, we reverse the normal order of ope ...
... New behaviors require new patterns of neural activity among the population of neurons that control behavior. How can the brain find a pattern of activity appropriate for the desired behavior? Why does that learning process take time? To tackle questions like these, we reverse the normal order of ope ...
U7 AP PSYCH Classical conditioning 2014
... A man goes to a nice restaurant & gets his favorite dish – shrimp. After eating at the restaurant, he gets food poisoning & is violently ill. After the food poisoning, he never wants to eat shrimp again and gags a little when he smells it. ...
... A man goes to a nice restaurant & gets his favorite dish – shrimp. After eating at the restaurant, he gets food poisoning & is violently ill. After the food poisoning, he never wants to eat shrimp again and gags a little when he smells it. ...
Classical Conditioning
... Ring tuning fork (NS) No response from dog Food (UCS) Dog salivates automatically (UCR) ...
... Ring tuning fork (NS) No response from dog Food (UCS) Dog salivates automatically (UCR) ...
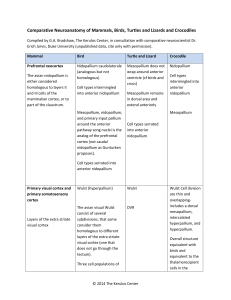
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... overlappingincludes a dorsal mesopallium, intercalated hyperpallium, and hyperpallium. Overall structure equivalent with birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
... overlappingincludes a dorsal mesopallium, intercalated hyperpallium, and hyperpallium. Overall structure equivalent with birds and equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the ...
An Overview to the Behavioral Perspective
... behavioral view. Researchers who affiliate with this position do not generally look with favor on the term "behavior potential" (i.e., may be capable of performing but did not for some reason such as illness, situation, etc.) that was included in a definition accepted by those with a cognitive or hu ...
... behavioral view. Researchers who affiliate with this position do not generally look with favor on the term "behavior potential" (i.e., may be capable of performing but did not for some reason such as illness, situation, etc.) that was included in a definition accepted by those with a cognitive or hu ...
Option A.4 pt 2 - Peoria Public Schools
... due to signals such as a ringing of a bell, flashing light, etc 1. These are conditioned stimuli and conditioned responses. ...
... due to signals such as a ringing of a bell, flashing light, etc 1. These are conditioned stimuli and conditioned responses. ...
We are investigating the use of novel stimulus
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
cerebellum
... There are two kinds of synaptic inputs: • Mossy fibers: – Arise from numerous regions – Ascend through cerebellar WM to form excitatory synapses onto dendrites of granule cells – Granule cells send axons into the molecular layer, which bifurcate, forming parallel fibers that run parallel to the fol ...
... There are two kinds of synaptic inputs: • Mossy fibers: – Arise from numerous regions – Ascend through cerebellar WM to form excitatory synapses onto dendrites of granule cells – Granule cells send axons into the molecular layer, which bifurcate, forming parallel fibers that run parallel to the fol ...
Chapter 4 practice
... Chapter 4 1. Farsightedness due to aging is referred to as a. hyperopia. b. myopia. c. presbyopia. d. astigmatism. 2. As you move from the bright colorful movie theater lobby into the darkened theater your eye transitions from using its __________ to its ______________. a. cones, rods b. photo recep ...
... Chapter 4 1. Farsightedness due to aging is referred to as a. hyperopia. b. myopia. c. presbyopia. d. astigmatism. 2. As you move from the bright colorful movie theater lobby into the darkened theater your eye transitions from using its __________ to its ______________. a. cones, rods b. photo recep ...
5 Behavioural - WordPress.com
... • For most behaviourists, the structural unit of personality is the response. • Each response is a behaviour, which is emitted to satisfy a specific need. • the core tendency that organises behaviour is the reduction of ...
... • For most behaviourists, the structural unit of personality is the response. • Each response is a behaviour, which is emitted to satisfy a specific need. • the core tendency that organises behaviour is the reduction of ...
Anatomy of the Cerebellum
... ganglia (through the subthalamic nucleus, STN) and limbic areas are relayed to the cerebellum through the anterior pontine nuclei (APN). The cerebellum in turn sends its output through the deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN), red nucleus (RN), and anterior thalamic nucleus (ATN) to various telencephalic ar ...
... ganglia (through the subthalamic nucleus, STN) and limbic areas are relayed to the cerebellum through the anterior pontine nuclei (APN). The cerebellum in turn sends its output through the deep cerebellar nuclei (DCN), red nucleus (RN), and anterior thalamic nucleus (ATN) to various telencephalic ar ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 26
... Following a rest, however, the CR reappears in response to the CS. This phenomenon is called ______________ _______________. (1 pt) ...
... Following a rest, however, the CR reappears in response to the CS. This phenomenon is called ______________ _______________. (1 pt) ...