* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download learning-and-intro-to-attachment-2017
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
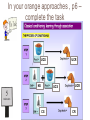
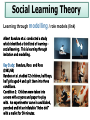
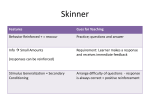
Learning approach and intro to Attachment Learning Objectives • Briefly outline the leaning approach – no more than 50 words • Consider what attachment is – discuss then outline • Identify 4 key behaviours that indicate that an attachment has been formed • Define the key terms reciprocity, care-giver interactions and Interactional synchrony Use your orange approaches pack alongside this PP – the packs are full of info and key words. Highlight the key words as we go through – make notes next to the text – I have covered as much as possible in the packs Learning approach The assumption that we learn our behaviour through the environment Behaviourism Social Learning theory Behaviourism - Behaviourism came out of the dissatisfaction with the - - - psychodynamic approach to psychology. the psychodynamic approach had emphasis on the invisible and untestable unconscious, and lacked the scientific rigor of physics and chemistry at the start of the 20th Century. John B. Watson said the methods used by Freud and Wundt were unscientific In 1913 Watson published ‘Psychology as the Behaviourist Views It’ Watson said we should observe and measure behaviour instead of mental states – too much emphasis on instincts, but he didn’t deny that these existed Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning: association between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus to produce a response Key Study: Ivan Pavlov (1927) - When Pavlov presented the dogs with food they began to salivate – an unconditioned response. - Pavlov presented a neutral stimulus to dogs (a bell or buzzer) and it produced no response. - Pavlov presented the two together several times, and eventually the sound of the bell alone made the dogs salivate – a conditioned response. Pavlov was awarded a Nobel Prize for his work in 1904. In your orange approaches , p6 – complete the task UCS NS UCR UCS CS UCR CR Now, pg 7 Draw your own conditioning process. Condition the dog to associate a new neutral stimulus with a stimulus that would naturally create a response. Use the correct terminology - Watson and his colleague Rayner also carried out an experiment investigating classical conditioning using an infant ‘Little Albert’ - Albert was 10 months old and showed little fear, the only thing that frightened him and made him cry was loud noises. - Watson conditioned Albert to be afraid of his pet rat by pairing it with a loud noise. - After a while, Albert would cry whenever he saw the rat. Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning: learning through consequences such as reward and punishment Key Study: Skinner (1953) - Skinner created a box (Skinner box) in which a hungry animal could be put inside and which contained a button that could be pressed to release food. - A rat was placed inside the box and allowed to roam freely (so its actions were operant – not reflexive) - Eventually it would press the lever and receive food - The rat learned that pressing the button gave it the reward (positive reinforcement) of food and thus the lever was pressed more often. - Skinner also changed the lever to make it stop an unpleasant stimulus, (negative reinforcement) which also led https://ww to a increase in leverw.youtube. pressing, and made the lever deliver com/watch a punishment, which led to a decrease. ?v=teLoNY vOf90 Pg 8 in orange pack Parents often use positive reinforcement to encourage good behaviour. For example, if a parent wants a child to tidy their bedroom, they might offer money, ‘If you tidy your room, I will give your £2’. Can you see any implications of using positive reinforcement in this way? Discuss with peer then make some notes Social Learning Theory Learning through modelling / role models (link) Albert Bandura et al. conducted a study which identified a third kind of learning – social learning. This is learning through imitation and modelling. Key Study: Bandura, Ross and Ross (1961/63) Bandura et al. studied 72 children, half boys, half girls aged 4 and split them into three conditions. Condition 1: Children were taken into a room with crayons and paper to play with. An experimenter came in and kicked, punched and hit an inflatable “Bobo doll” with a mallet for 10 minutes. Condition 2: The experimenter just played with other toys and did not show aggression towards the doll. Condition 3: A control group, no experimenter came in. The children were then taken to a room with attractive toys and were told they couldn’t play with them. They were then taken to a third room with ordinary toys and a Bobo doll. They were filmed for 20 minutes. When analysing the film, Bandura et al. found that the children in condition 1, who had seen the adult model be violent towards the doll, showed higher levels of aggressive behaviour than any other children. Pg 12 In pairs read the extract on pg 12 and answer the questions If you want to know more about the case of Jamie Bulger have a look at this website: http://crimeandinvestigation.co.uk/crime-files/james-bulger What has the learning approach provided us with? •Classical conditioning can help explain phobias, and can also help treat them using systematic desensitisation •Systematic desensitisation is a method used to treat phobias based on counter-conditioning – the phobia is paired with something relaxing •Siegel (1984) found that drug addicts are much more likely to die of an overdose in an unfamiliar environment. This is because your body does not associate that environment with drugs, and therefore does not prepare. •Social learning theory is used to explain many things such as food preferences, eating disorders, addictions, and gender roles. Also helps us understand Attachment!