cognitive psychology: part 2: learning
... Learning is a permanent change in the nervous system of an organism that changes the way it responds to its environment, usually as a result of an experience that the organism went through. (Note: By learning here we do not mean the acquisition of knowledge like in school but the acquisition of beha ...
... Learning is a permanent change in the nervous system of an organism that changes the way it responds to its environment, usually as a result of an experience that the organism went through. (Note: By learning here we do not mean the acquisition of knowledge like in school but the acquisition of beha ...
Abnormal Psychology - University of Toronto
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
PSY100-learning10
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
... – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-releasing neurons that projects into various higher brain centers origin ...
... sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-releasing neurons that projects into various higher brain centers origin ...
LEARNING
... Pavlov spent the rest of his life outlining his ideas. He came up with 5 critical terms that together make up classical conditioning. ...
... Pavlov spent the rest of his life outlining his ideas. He came up with 5 critical terms that together make up classical conditioning. ...
A1984SK79600002
... 1. Feldberg W & Vogt M. Acetylcholine synthesis in different regions of the central nervous system. J. Physiology 107:372-81, 1948. (Cited 265 times since 1955.) 2. Carisson A. The occurrence, distribution and physiological role of catecholamines in the nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 11:490-3, 1959 ...
... 1. Feldberg W & Vogt M. Acetylcholine synthesis in different regions of the central nervous system. J. Physiology 107:372-81, 1948. (Cited 265 times since 1955.) 2. Carisson A. The occurrence, distribution and physiological role of catecholamines in the nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 11:490-3, 1959 ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... Memories can be “manipulated” by manipulating (consciously or not) their relationship to other memories – false memories. Eye witness testimony. Implanted memories ...
... Memories can be “manipulated” by manipulating (consciously or not) their relationship to other memories – false memories. Eye witness testimony. Implanted memories ...
Chapter 6
... • Spontaneous recovery: After a rest, the reappearance of an extinguished conditioned response • Resistance to extinction: Associations that are difficult to unlearn ...
... • Spontaneous recovery: After a rest, the reappearance of an extinguished conditioned response • Resistance to extinction: Associations that are difficult to unlearn ...
Poster Sensopac
... crude torque commands. Total torque is delayed (on account of the biological motor pathways) and supplied to the robot plant. The difference between the actual robot trajectory and the desired one is also delayed and used by the teaching signal computation module to calculate the inferior olive (IO) ...
... crude torque commands. Total torque is delayed (on account of the biological motor pathways) and supplied to the robot plant. The difference between the actual robot trajectory and the desired one is also delayed and used by the teaching signal computation module to calculate the inferior olive (IO) ...
Learning - sevenlakespsychology
... Learning - any process through which experience at one time can alter an individual’s behavior at a future time ...
... Learning - any process through which experience at one time can alter an individual’s behavior at a future time ...
Guided Notes – Learning – Classical Conditioning
... INTRODUCTORY PSYCHOLOGY: LEARNING (CLASSICAL CONDITIONING) Learning: The Basics ...
... INTRODUCTORY PSYCHOLOGY: LEARNING (CLASSICAL CONDITIONING) Learning: The Basics ...
NervousSystem3
... The reticular formation. In contrast to the large aggregations of cell bodies within the cns, designated nuclei and grey matter, and the aggregation of axonal fibers, designated tracts, a dispersed network of neurons, observed under the light microscope as a meshwork of cell bodies and processes, is ...
... The reticular formation. In contrast to the large aggregations of cell bodies within the cns, designated nuclei and grey matter, and the aggregation of axonal fibers, designated tracts, a dispersed network of neurons, observed under the light microscope as a meshwork of cell bodies and processes, is ...
Lecture - Weizmann Institute of Science
... “The Law of Effect is that: Of several responses made to the same situation, those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction to the animal will, other things being equal, be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur” Edward L ...
... “The Law of Effect is that: Of several responses made to the same situation, those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction to the animal will, other things being equal, be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur” Edward L ...
Karen Iler Kirk - Purdue University
... •Single-neuron extracellular recording -awake animals •Sound and electrical stimulation •Neuroanatomy •Intracellular recording in brain slices -synaptics, dynamic clamp •Modeling of neurons and circuits ...
... •Single-neuron extracellular recording -awake animals •Sound and electrical stimulation •Neuroanatomy •Intracellular recording in brain slices -synaptics, dynamic clamp •Modeling of neurons and circuits ...
Learning - Morgan Park High School
... o Conditioned response (CR); the learned response to a neutral conditioned stimulus o Conditioned stimulus (CS); what a neutral stimulus becomes after being paired with a UCS and thus will elicit a conditioned response Conditioning is usually considered an acquisition process, the learning process i ...
... o Conditioned response (CR); the learned response to a neutral conditioned stimulus o Conditioned stimulus (CS); what a neutral stimulus becomes after being paired with a UCS and thus will elicit a conditioned response Conditioning is usually considered an acquisition process, the learning process i ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... Pulvinar- is the most caudal thalamic nucleus. It receives projections from the auditory, somatosensory and visual cortex regions. It is involved in visual attention, suppression of irrelevant stimuli and utilizing information to initiate eye movements. Reticular and interlaminar nuclei- connected t ...
... Pulvinar- is the most caudal thalamic nucleus. It receives projections from the auditory, somatosensory and visual cortex regions. It is involved in visual attention, suppression of irrelevant stimuli and utilizing information to initiate eye movements. Reticular and interlaminar nuclei- connected t ...
Essential Questions, Vocabulary, and Review Charts
... Unconditioned response Stimulus (US) the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the Unconditioned unconditioned stimulus (US) Response (UR) an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association Conditioned with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a Stimulus (CS) conditioned resp ...
... Unconditioned response Stimulus (US) the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the Unconditioned unconditioned stimulus (US) Response (UR) an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association Conditioned with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a Stimulus (CS) conditioned resp ...
Chapter 6 - Montezuma Schools
... Experience is our teacher What are somethings you can think of that you learned from experience/observation? Applies to good and bad behaviors Good news, you can unlearn through retraining, counseling, and perseverance Types: classical, operant, cognitive-social, and evolution ...
... Experience is our teacher What are somethings you can think of that you learned from experience/observation? Applies to good and bad behaviors Good news, you can unlearn through retraining, counseling, and perseverance Types: classical, operant, cognitive-social, and evolution ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... The cerebellar cortex is divided into three lobes: anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular. Each lobe consists of thin folds called folia. This sheet is laid over four cerebellar nuclei (CN) on each side. Three cerebellar peduncles on each side connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. The cortex c ...
... The cerebellar cortex is divided into three lobes: anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular. Each lobe consists of thin folds called folia. This sheet is laid over four cerebellar nuclei (CN) on each side. Three cerebellar peduncles on each side connect the cerebellum to the brain stem. The cortex c ...
Slide ()
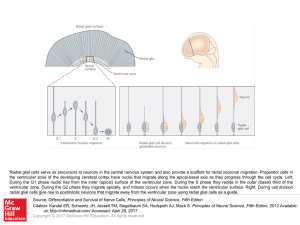
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
internal structure of the brain stem
... a.Superior medullary velum . b. Open medulla and pons . c. Superior cerebellar peduncles . d. Inferior cerebellar peduncles . 14- The roof of 4th ventricle is formed by : a.Superior medullary velum . b. Open medulla and pons . c. Superior cerebellar peduncles . d. Inferior cerebellar peduncles ...
... a.Superior medullary velum . b. Open medulla and pons . c. Superior cerebellar peduncles . d. Inferior cerebellar peduncles . 14- The roof of 4th ventricle is formed by : a.Superior medullary velum . b. Open medulla and pons . c. Superior cerebellar peduncles . d. Inferior cerebellar peduncles ...
Neuroanatomy
... inhibatory , and this inhibtion effect is due to neurons found in the cerebellar cortex that synapse with purkinje cell such as golgi cell , basket , stellate and granular. The affect of them on the purkinje cell are inhibitory and the result is that the axon of the purkinje cell is inhibitory . Not ...
... inhibatory , and this inhibtion effect is due to neurons found in the cerebellar cortex that synapse with purkinje cell such as golgi cell , basket , stellate and granular. The affect of them on the purkinje cell are inhibitory and the result is that the axon of the purkinje cell is inhibitory . Not ...