drugs and neuronal plasticity summary
... (LTD) in neuronal circuits associated with the addiction process, suggesting a way for the behavioral consequences of drug-taking to become reinforced by learning mechanisms. Addicted features of drugs suggest that it may be an exceptionally powerful form of neuronal plasticity, which can be broadly ...
... (LTD) in neuronal circuits associated with the addiction process, suggesting a way for the behavioral consequences of drug-taking to become reinforced by learning mechanisms. Addicted features of drugs suggest that it may be an exceptionally powerful form of neuronal plasticity, which can be broadly ...
Chapter 7
... principles of learning that are the same for all species tested, including humans. Classical conditioning also provided an example to the young field of psychology of how complex, internal processes could be studied objectively. In addition, classical conditioning has proven to have many helpful app ...
... principles of learning that are the same for all species tested, including humans. Classical conditioning also provided an example to the young field of psychology of how complex, internal processes could be studied objectively. In addition, classical conditioning has proven to have many helpful app ...
Slide ()
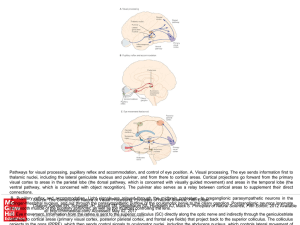
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Classical Conditioning
... We (and virtually all organisms) naturally connect events that occur in sequence Associative Learning: learning that two events occur ...
... We (and virtually all organisms) naturally connect events that occur in sequence Associative Learning: learning that two events occur ...
Learning Practice Questions
... 1. The type of learning most associated B.F. Skinner is a. classical conditioning b. operant conditioning c. observational learning d. modeling e. insight learning 2. In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as a a. CS b. CR c. discriminative stimulus d. US e. UR 3. Learning that o ...
... 1. The type of learning most associated B.F. Skinner is a. classical conditioning b. operant conditioning c. observational learning d. modeling e. insight learning 2. In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as a a. CS b. CR c. discriminative stimulus d. US e. UR 3. Learning that o ...
Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Classical Conditioning Notes 3. Real
... • Watson wanted to apply Pavlov’s study to humans • Believed that human behavior (even things we thought were instinct) were a result of the environment (could be LEARNED) • Emotionally and physically healthy 9-month old male raised in a hospital environment • Seeks to condition this baby to have an ...
... • Watson wanted to apply Pavlov’s study to humans • Believed that human behavior (even things we thought were instinct) were a result of the environment (could be LEARNED) • Emotionally and physically healthy 9-month old male raised in a hospital environment • Seeks to condition this baby to have an ...
Cerebellar control of the inferior olive
... NO fibres. However, other physiological evidence later confirmed the inhibitory nature of the pathway. High frequency activation of the inferior olive, followed by low frequency stimulation, resulted in a strong depression of olivary responding during the low frequency stimulation period (26). It wa ...
... NO fibres. However, other physiological evidence later confirmed the inhibitory nature of the pathway. High frequency activation of the inferior olive, followed by low frequency stimulation, resulted in a strong depression of olivary responding during the low frequency stimulation period (26). It wa ...
Document
... – Ascending, descending, and transverse tracts that interconnect other portions of the CNS ...
... – Ascending, descending, and transverse tracts that interconnect other portions of the CNS ...
Cranial Nerve Locations CN I Olfactory ----------
... Appears to have a high iron content and is more vascular than the surrounding tissue - in some brains is pinkish Inputs arise from motor areas of the brain and in particular the deep cerebellar nuclei (via superior cerebellar peduncle; crossed projection) and the motor cortex Outputs: rubrospi ...
... Appears to have a high iron content and is more vascular than the surrounding tissue - in some brains is pinkish Inputs arise from motor areas of the brain and in particular the deep cerebellar nuclei (via superior cerebellar peduncle; crossed projection) and the motor cortex Outputs: rubrospi ...
MS-PowerPoint
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
04/09 PPT
... an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for depth are provided by points just proximal or distal to the fixation point. ...
... an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for depth are provided by points just proximal or distal to the fixation point. ...
Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB
... neurotransmitter that inhibits surrounding neural messages allowing them master control over motor movements. The loss of or damage to Purkinje cells can give rise to certain neurological diseases. During embryonic growth, Purkinje cells can be permanently destroyed by exposure to alcohol thereby co ...
... neurotransmitter that inhibits surrounding neural messages allowing them master control over motor movements. The loss of or damage to Purkinje cells can give rise to certain neurological diseases. During embryonic growth, Purkinje cells can be permanently destroyed by exposure to alcohol thereby co ...
Learning - McMurray VMC
... the unconditioned stimulus no longer followed the conditioned stimulus? When the US (food) does not follow the CS (tone), CR (salivation) begins to decrease and eventually causes extinction. ...
... the unconditioned stimulus no longer followed the conditioned stimulus? When the US (food) does not follow the CS (tone), CR (salivation) begins to decrease and eventually causes extinction. ...
Learning - WordPress.com
... sounds or people with scenarios that occurred during war which can trigger depression, hallucinations, outburst etc. + Drug Addiction- some addicts may associate places/people/objects with drugs and the happy feelings that came with the use. Seeing a trigger can cause a craving for the drug ...
... sounds or people with scenarios that occurred during war which can trigger depression, hallucinations, outburst etc. + Drug Addiction- some addicts may associate places/people/objects with drugs and the happy feelings that came with the use. Seeing a trigger can cause a craving for the drug ...
Learning Today What is Learning? Learning The Biological Basis
... • Conditioned responses (CRs) occurring to stimuli other than the CS used for training • The more similar the second stimulus is to the CS the more generalization will occur • Generalization is a critical feature of learning because we rarely encounter the exact same stimulus twice – Consider drug-s ...
... • Conditioned responses (CRs) occurring to stimuli other than the CS used for training • The more similar the second stimulus is to the CS the more generalization will occur • Generalization is a critical feature of learning because we rarely encounter the exact same stimulus twice – Consider drug-s ...
Classical Conditioning
... learns to associate 2 events. • Extinction - Extinction is the gradual decrease in the strength or rate of a CR that occurs when the UCS is no longer presented. • Spontaneous Recovery - In CC, spontaneous recovery is the reappearance of a CR when the CS is presented, following a rest period after th ...
... learns to associate 2 events. • Extinction - Extinction is the gradual decrease in the strength or rate of a CR that occurs when the UCS is no longer presented. • Spontaneous Recovery - In CC, spontaneous recovery is the reappearance of a CR when the CS is presented, following a rest period after th ...
File
... light goes on, goes off, and then shock occurs Delayed conditioning—CS precedes UCS and stays on for part of UCS--light goes on and stays on for first part of shock ...
... light goes on, goes off, and then shock occurs Delayed conditioning—CS precedes UCS and stays on for part of UCS--light goes on and stays on for first part of shock ...
Self-Organization in the Nervous System
... The nerve fibers from ganglion cells in the retina project via the thalamus to the primary visual cortex. They do that as said in a topographic manner, such that nearby locations in the retina project onto neighboring locations in the cortex. The mapping process now has to be rather sophisticated, s ...
... The nerve fibers from ganglion cells in the retina project via the thalamus to the primary visual cortex. They do that as said in a topographic manner, such that nearby locations in the retina project onto neighboring locations in the cortex. The mapping process now has to be rather sophisticated, s ...
Classical Conditioning
... to mindless mechanisms. Research indicates that, for many animals, cognitive appraisals are important for learning. That is, thoughts and perceptions are important to the conditioning process. However, later behaviorists suggested that animals learn predictability of a stimulus, thus learning expect ...
... to mindless mechanisms. Research indicates that, for many animals, cognitive appraisals are important for learning. That is, thoughts and perceptions are important to the conditioning process. However, later behaviorists suggested that animals learn predictability of a stimulus, thus learning expect ...
Learning Packet 6A
... Habituation: To become used to something over time. (don’t even feel, piercings, glasses, feel of chair, etc after you become used to them. Dishabituation: Becoming aware of change in environment. (For example: when something that was ongoing stops you become aware of it. Reappearance of your initia ...
... Habituation: To become used to something over time. (don’t even feel, piercings, glasses, feel of chair, etc after you become used to them. Dishabituation: Becoming aware of change in environment. (For example: when something that was ongoing stops you become aware of it. Reappearance of your initia ...
Motor Systems II Loops and Tracts
... indirect pathway. Thus, the balance between the direct and indirect pathways becomes tipped in favor of the direct pathway. Without their normal inhibitory inputs, thalamic neurons can fire randomly and inappropriately, causing the motor cortex to execute motor programs without proper control. ...
... indirect pathway. Thus, the balance between the direct and indirect pathways becomes tipped in favor of the direct pathway. Without their normal inhibitory inputs, thalamic neurons can fire randomly and inappropriately, causing the motor cortex to execute motor programs without proper control. ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... specialized areas that enable us to perceive, think, and speak. Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They suppor ...
... specialized areas that enable us to perceive, think, and speak. Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They suppor ...
3D Classical Conditioning
... Spontaneous Recovery • The return of an extinguished classically conditioned response after a rest period ...
... Spontaneous Recovery • The return of an extinguished classically conditioned response after a rest period ...