Discriminative Auditory Fear Learning Requires Both Tuned
... sound discrimination. • The nonlemniscal stream has less selective neurons, which are not tonotopically organized, and is thought to be important for multimodal processing and for several forms of learning. ...
... sound discrimination. • The nonlemniscal stream has less selective neurons, which are not tonotopically organized, and is thought to be important for multimodal processing and for several forms of learning. ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
Case Study 48
... Well-delineated T2 bright lesion in the left cerebellar hemisphere with a thickened foliar architecture pattern. There is minimal surrounding edema, no significant mass effect or midline shift. No hemorrhage is seen on T1 and there is no abnormal contrast enhancement. (There is also a small enhancin ...
... Well-delineated T2 bright lesion in the left cerebellar hemisphere with a thickened foliar architecture pattern. There is minimal surrounding edema, no significant mass effect or midline shift. No hemorrhage is seen on T1 and there is no abnormal contrast enhancement. (There is also a small enhancin ...
What is Learning? - APUSH-HBHS
... Peter-fear of white rats “Degrees of Toleration” Extinction + learning relaxation to CS = relaxed response to CS ...
... Peter-fear of white rats “Degrees of Toleration” Extinction + learning relaxation to CS = relaxed response to CS ...
Module 15- Classical Conditioning
... Read the situation described on p. 281. Has this ever happened to you? Did you realize that this is actually learning? -Classical conditioning is a form of learning by association. There is a stimulus which produces a response. After a while the response will always be paired with the stimulus. (It ...
... Read the situation described on p. 281. Has this ever happened to you? Did you realize that this is actually learning? -Classical conditioning is a form of learning by association. There is a stimulus which produces a response. After a while the response will always be paired with the stimulus. (It ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
... roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas o ...
... roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. Areas o ...
Modification of brain circuits as a result of experience
... correlate with a stimulus. • Time scale: days, weeks ???? ...
... correlate with a stimulus. • Time scale: days, weeks ???? ...
Excitatory Cerebellar Nucleocortical Circuit Provides Internal
... et al., 1999; Mostofi et al., 2010), we observed that nucleocortical MFs of these animals were found predominantly in regions negative for Zebrin II, including the trough of the lobule simplex (Figures 3A–3C). More specifically, we observed that 90.5% (±3.3%), 88.5% (±6.2%), and 93.7% (±2.8%) of the ...
... et al., 1999; Mostofi et al., 2010), we observed that nucleocortical MFs of these animals were found predominantly in regions negative for Zebrin II, including the trough of the lobule simplex (Figures 3A–3C). More specifically, we observed that 90.5% (±3.3%), 88.5% (±6.2%), and 93.7% (±2.8%) of the ...
Learning
... • They still cowered in fear • They had learned/think they are helpless • People do this with depression…what we think matters ...
... • They still cowered in fear • They had learned/think they are helpless • People do this with depression…what we think matters ...
Focusing on connections and signaling mechanisms to
... research, the development and plasticity of the central visual system, we have learned something about how to study problems in which neural activity operates to alter connections. I believe that some of these approaches should also be pursued in order to understand learning. Many of my thoughts on ...
... research, the development and plasticity of the central visual system, we have learned something about how to study problems in which neural activity operates to alter connections. I believe that some of these approaches should also be pursued in order to understand learning. Many of my thoughts on ...
Os textos são da exclusiva responsabilidade dos autores
... 2- Division of Behavioral Neurology and Cognitive Neuroscience, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine Grant nº 201/08 Background: Acquisition of novel perceptual or perceptual-motor skills appears to depend on multiple brain areas, including the posterior parietal cortex (PPC). Functional ne ...
... 2- Division of Behavioral Neurology and Cognitive Neuroscience, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine Grant nº 201/08 Background: Acquisition of novel perceptual or perceptual-motor skills appears to depend on multiple brain areas, including the posterior parietal cortex (PPC). Functional ne ...
Eyeblink Conditioning During an Interstimulus Interval Switch in
... initially trained with a 250-ms ISI learned comparably to controls, but those initially trained with a 750-ms ISI were severely impaired. These results suggest that functional input from cerebellar cortex becomes increasingly important for the interpositus nucleus to learn delay eyeblink conditionin ...
... initially trained with a 250-ms ISI learned comparably to controls, but those initially trained with a 750-ms ISI were severely impaired. These results suggest that functional input from cerebellar cortex becomes increasingly important for the interpositus nucleus to learn delay eyeblink conditionin ...
BN21 subcortical motor control
... no feedback during execution direction, force, & timing Motor learning shift from conscious unconscious ~ ...
... no feedback during execution direction, force, & timing Motor learning shift from conscious unconscious ~ ...
Medial Temporal Lobe Switches Memory Encoding in Neocortex
... Damage to the medial temporal lobe impairs the encoding of new memories and the retrieval of memories acquired immediately before the damage in human. In this study, we demonstrated that artificial visuo-auditory memory traces can be established in the rat auditory cortex and that their encoding dep ...
... Damage to the medial temporal lobe impairs the encoding of new memories and the retrieval of memories acquired immediately before the damage in human. In this study, we demonstrated that artificial visuo-auditory memory traces can be established in the rat auditory cortex and that their encoding dep ...
Learning - Westmoreland Central School
... § process by which a stimulus (food) increases the chances that a preceding behavior (a rat pressing a lever) will occur again ...
... § process by which a stimulus (food) increases the chances that a preceding behavior (a rat pressing a lever) will occur again ...
classical conditioning
... Insight = the sudden perception of the connection of parts of a problem that allows one to see a clear solution the aha! moments ...
... Insight = the sudden perception of the connection of parts of a problem that allows one to see a clear solution the aha! moments ...
AP Psychology Unit Six Curriculum Map
... extinction effect, punishment, learned helplessness, latent Provide examples of how biological constraints create learning, cognitive map, insight, observational learning, learning predispositions. vicarious learning Describe the essential characteristics of insight learning, latent learning, and so ...
... extinction effect, punishment, learned helplessness, latent Provide examples of how biological constraints create learning, cognitive map, insight, observational learning, learning predispositions. vicarious learning Describe the essential characteristics of insight learning, latent learning, and so ...
Quiz 3 ch 5 Sp 13
... D) Upon hearing the loud noise, Little Albert “jumped violently, fell forward, and began to whimper.” E) Watson clearly showed a disregard for Little Albert’s welfare during the time he worked with him. 11) Who came up with the law of effect? A) Edward Thorndike B) B. F. Skinner C) Albert Bandura D) ...
... D) Upon hearing the loud noise, Little Albert “jumped violently, fell forward, and began to whimper.” E) Watson clearly showed a disregard for Little Albert’s welfare during the time he worked with him. 11) Who came up with the law of effect? A) Edward Thorndike B) B. F. Skinner C) Albert Bandura D) ...
HB Operate Conditioning-3
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
... dogs. Many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. Treatment of phobias or anxiety problems. Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. (Safe Enviro ...
Learning - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... Check for understanding: An experimenter sounds a tone just before delivering an air puff to your blinking eye. After several repetitions, you blink to the tone alone. NS = tone before procedure US = air puff UR = blink to air puff CS = tone after procedure CR = blink to tone ...
... Check for understanding: An experimenter sounds a tone just before delivering an air puff to your blinking eye. After several repetitions, you blink to the tone alone. NS = tone before procedure US = air puff UR = blink to air puff CS = tone after procedure CR = blink to tone ...
CHAPTER 7—LEARNING I. Introduction A. Learning – involves the
... Learning – involves the acquisition of new knowledge, skills, or responses from experience that result in a relatively permanent change in the state of the learner 1. Learning is based on experience 2. Learning produces changes in the organism 3. These changes are relatively permanent Classical Cond ...
... Learning – involves the acquisition of new knowledge, skills, or responses from experience that result in a relatively permanent change in the state of the learner 1. Learning is based on experience 2. Learning produces changes in the organism 3. These changes are relatively permanent Classical Cond ...
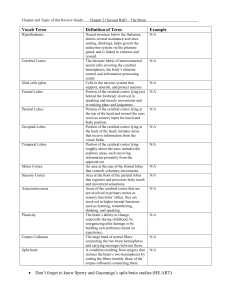
Learning Activity 1
... 3 The cerebral cortex consists mainly of neurons. 4 Cortical areas may be classifi ed as: • sensory cortex areas, which receive and process information from our different senses • motor cortex area, which receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements • association cortex ...
... 3 The cerebral cortex consists mainly of neurons. 4 Cortical areas may be classifi ed as: • sensory cortex areas, which receive and process information from our different senses • motor cortex area, which receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements • association cortex ...
Learning
... Study of animals: reveals same principles of learning that apply to humans How does a dog learn to sit on command? ...
... Study of animals: reveals same principles of learning that apply to humans How does a dog learn to sit on command? ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... by adjusting the operation of motor centers in the cortex and brain stem while a movement is in progress as well as during repetitions of the same movement. Three aspects of the cerebellum's organization underlie this function. First, the cerebellum is provided with extensive information about the g ...
... by adjusting the operation of motor centers in the cortex and brain stem while a movement is in progress as well as during repetitions of the same movement. Three aspects of the cerebellum's organization underlie this function. First, the cerebellum is provided with extensive information about the g ...