Biosem1Finalreview - Uplift Summit International
... Chargaff, Wilkins and Franklin, Watson and Crick Structure of DNA Base pairing rules DNA replication Central dogma Three types of RNA Transcription Translation Genetic code, codons; Interpreting the genetic code Steps in genetic engineering – cutting DNA, making recombinant DNA, Cloning, Screening C ...
... Chargaff, Wilkins and Franklin, Watson and Crick Structure of DNA Base pairing rules DNA replication Central dogma Three types of RNA Transcription Translation Genetic code, codons; Interpreting the genetic code Steps in genetic engineering – cutting DNA, making recombinant DNA, Cloning, Screening C ...
ap ch 17 powerpoint - Pregitzersninjascienceclasses
... Codon recognition occurs as mRNA in the Asite of ribosome bonds with anticodon of tRNA (with amino acid). This requires GTP. Amino acid in P-site binds to amino acid in Asite with a peptide bond to build the protein. Translocation - ribosome moves tRNA in A-site to P-site. tRNA in P-site is released ...
... Codon recognition occurs as mRNA in the Asite of ribosome bonds with anticodon of tRNA (with amino acid). This requires GTP. Amino acid in P-site binds to amino acid in Asite with a peptide bond to build the protein. Translocation - ribosome moves tRNA in A-site to P-site. tRNA in P-site is released ...
Molecular Genetics (Unit 6 and Unit 6.2) Study Guide Each of the
... Each of the major scientists, their experiment, their contribution to molecular biology Structure of DNA and RNA o Direction, components, differences and similarities between the two, reads/builds, 5’ and 3’ ends, antiparallel, H-bonding, nucleotide/nucleoside, o Types of RNA – job of each, structur ...
... Each of the major scientists, their experiment, their contribution to molecular biology Structure of DNA and RNA o Direction, components, differences and similarities between the two, reads/builds, 5’ and 3’ ends, antiparallel, H-bonding, nucleotide/nucleoside, o Types of RNA – job of each, structur ...
71071_Protein_synthesis
... of DNA that codes for a specific protein • Only a very small percentage of our DNA (perhaps 1%) actually does this ...
... of DNA that codes for a specific protein • Only a very small percentage of our DNA (perhaps 1%) actually does this ...
1. Overview of Gene Expression Overview of Gene Expression Chapter 10B:
... Translation (“protein synthesis”) The building of a polypeptide, 1 amino acid at a time, by ribosomes using info in mRNA: • ribosomes bind directly to mRNA, “read” codon by codon • ribosomes always start at AUG (methionine) • translation also involves tRNAs, each of which is attached to 1 of the 20 ...
... Translation (“protein synthesis”) The building of a polypeptide, 1 amino acid at a time, by ribosomes using info in mRNA: • ribosomes bind directly to mRNA, “read” codon by codon • ribosomes always start at AUG (methionine) • translation also involves tRNAs, each of which is attached to 1 of the 20 ...
model 3 - Instructure
... b. Is the RBS closer to the 5' or 3' end of the mRNA? _____ b. Which are more prevalent in the RBS, pyrimidines or purines? __________________ c. What types of bonds hold the mRNA and small ribosomal subunit together? __________ 7. a. Does the first tRNA bind before or after the ribosome is complete ...
... b. Is the RBS closer to the 5' or 3' end of the mRNA? _____ b. Which are more prevalent in the RBS, pyrimidines or purines? __________________ c. What types of bonds hold the mRNA and small ribosomal subunit together? __________ 7. a. Does the first tRNA bind before or after the ribosome is complete ...
AASK Additional Activities
... a shape that simultaneously satisfies all the 4 principles of chemistry. This is a good teaching moment in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such proteins would not be selected from the enormous pool of possible protein sequences. How can students arrive at a perfectly optimi ...
... a shape that simultaneously satisfies all the 4 principles of chemistry. This is a good teaching moment in that the teacher can use these examples to emphasize that such proteins would not be selected from the enormous pool of possible protein sequences. How can students arrive at a perfectly optimi ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... 6. A DNA strand has the nucleotide sequence: ATCGAAGGTCTC. a. What will be the corresponding mRNA sequence? ____________________________ b. How many codons are present? _______ c. What will be the corresponding tRNA sequence? _____________________________ d. What part do the tRNA anticodons play in ...
... 6. A DNA strand has the nucleotide sequence: ATCGAAGGTCTC. a. What will be the corresponding mRNA sequence? ____________________________ b. How many codons are present? _______ c. What will be the corresponding tRNA sequence? _____________________________ d. What part do the tRNA anticodons play in ...
PowerPoint Notes
... Hershey and Chase offered further evidence that DNA, not proteins, is the genetic material. Only the DNA of the old generation of viruses is incorporated into the new generation. ...
... Hershey and Chase offered further evidence that DNA, not proteins, is the genetic material. Only the DNA of the old generation of viruses is incorporated into the new generation. ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Organic Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
... Organic Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
Bacterial Gene Finding
... Given training examples of some known genes, can we distinguish ORFs that are genes from those that are not? ...
... Given training examples of some known genes, can we distinguish ORFs that are genes from those that are not? ...
DNA
... • tRNA then goes back into the cytoplasm, to pick up another amino acid. • All 20 Amino Acids are floating free and waiting in the Cytoplasm. • The amino acid chain is left to become the functioning Protein. ...
... • tRNA then goes back into the cytoplasm, to pick up another amino acid. • All 20 Amino Acids are floating free and waiting in the Cytoplasm. • The amino acid chain is left to become the functioning Protein. ...
document
... The Crick, Brenner et al. experiment was the first to demonstrate that codons consist of three DNA bases. Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich J. Matthai were the first to elucidate the nature of a codon in 1961 at the National Institutes of Health. They used a cell-free system to translate a poly-uracil ...
... The Crick, Brenner et al. experiment was the first to demonstrate that codons consist of three DNA bases. Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich J. Matthai were the first to elucidate the nature of a codon in 1961 at the National Institutes of Health. They used a cell-free system to translate a poly-uracil ...
File
... Site 1 discharges the tRNA from the ribosome once the amino acid has become part of the polypeptide chain ...
... Site 1 discharges the tRNA from the ribosome once the amino acid has become part of the polypeptide chain ...
Transcription and Translation
... UAC codes for tyrosine. UAA is a stop codon. By substituting a single nucleotide for another, the message changes from “add a tyrosine” to “stop adding nucleotides here.” This results in a shorter-than-normal peptide that may not be functional in this shorter form. This single change can “knock out” ...
... UAC codes for tyrosine. UAA is a stop codon. By substituting a single nucleotide for another, the message changes from “add a tyrosine” to “stop adding nucleotides here.” This results in a shorter-than-normal peptide that may not be functional in this shorter form. This single change can “knock out” ...
Genetics
... – Found on the X or Y chromosome • Males have a greater chance of having a disorder if the allele is on the X because they have only one ...
... – Found on the X or Y chromosome • Males have a greater chance of having a disorder if the allele is on the X because they have only one ...
Biology - The Roblesite
... ________________, which lets the enzyme recognize the start of a gene. 13. When mRNA is being assembled, it grows in the ________to __________direction. 14. These numbers are based on the position of ____________atoms in the ________________molecules, which, along with phosphate groups, comprise the ...
... ________________, which lets the enzyme recognize the start of a gene. 13. When mRNA is being assembled, it grows in the ________to __________direction. 14. These numbers are based on the position of ____________atoms in the ________________molecules, which, along with phosphate groups, comprise the ...
AUG
... Deciphering the code 61 codons encode amino acids, 3 codons do not specify amino acids Specialized codons: - for start of translation - AUG - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
... Deciphering the code 61 codons encode amino acids, 3 codons do not specify amino acids Specialized codons: - for start of translation - AUG - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
chapter12
... The termination of transcription is controlled by a specific base sequence. Different genes may have different promoter sequences upstream from the protein-coding sequence. Once the RNA polymerase has recognized the promoter, it unwinds the helix and begins transcription. DNA-dependent RNA polymeras ...
... The termination of transcription is controlled by a specific base sequence. Different genes may have different promoter sequences upstream from the protein-coding sequence. Once the RNA polymerase has recognized the promoter, it unwinds the helix and begins transcription. DNA-dependent RNA polymeras ...
DNA & THE GENETIC CODE (protein synthesis)
... • Translation involves decoding/reading the triplet message on mRNA. • Each codon, 3 bases, has a natural complementary sequence of 3 bases, called the anticodon. • This set of 3 bases is attached to a specific tRNA molecule that carries and transfers a specific amino acid. • The specific amino aci ...
... • Translation involves decoding/reading the triplet message on mRNA. • Each codon, 3 bases, has a natural complementary sequence of 3 bases, called the anticodon. • This set of 3 bases is attached to a specific tRNA molecule that carries and transfers a specific amino acid. • The specific amino aci ...
Name: DUE Date: ______ ____ period Chapter 17: From Gene to
... not leave this assignment until the night before it its due. This is an individual assignment, as such, it is expected that all work on this will be your own. ...
... not leave this assignment until the night before it its due. This is an individual assignment, as such, it is expected that all work on this will be your own. ...
Biology Chapter 6 Section 4 Test-The Building Blocks of Life
... 16. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are ___________________________. 17. _____________________ are made from amino acids that are joined by _____________ bonds. 18. DNA and RNA are examples of ____________________ __________________. 19. Glycogen, starch, cellulose and chitin are a ...
... 16. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are ___________________________. 17. _____________________ are made from amino acids that are joined by _____________ bonds. 18. DNA and RNA are examples of ____________________ __________________. 19. Glycogen, starch, cellulose and chitin are a ...
Chapter25_Outline
... 25.8 Novel Amino Acids Can Be Inserted at Certain Stop Codons • The insertion of selenocysteine at some UGA codons requires the action of an unusual tRNA in combination with several proteins. • The unusual amino acid pyrrolysine can be inserted at certain UAG codons. • The UGA codon specifies both ...
... 25.8 Novel Amino Acids Can Be Inserted at Certain Stop Codons • The insertion of selenocysteine at some UGA codons requires the action of an unusual tRNA in combination with several proteins. • The unusual amino acid pyrrolysine can be inserted at certain UAG codons. • The UGA codon specifies both ...
In experiments with a 3 base codon system it was shown that the
... the chemical that do not require the nutrient supplement for survival (become prototroph or wild-type strain) at a higher rate then normal (due to natural errors in replication) the chemical is considered a mutagen. ...
... the chemical that do not require the nutrient supplement for survival (become prototroph or wild-type strain) at a higher rate then normal (due to natural errors in replication) the chemical is considered a mutagen. ...
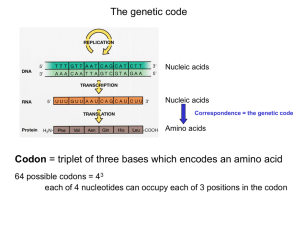
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.