Modern Genetics Outline
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
CHEM 642-09 Powerpoint
... specifies each amino acid. Codons for the same amino acid tend to contain the same nucleotides at the first and second positions, and vary at the third position. Three codons do not specify any amino acid but act as termination sites (stop codons), signaling the end of the protein- coding sequence. ...
... specifies each amino acid. Codons for the same amino acid tend to contain the same nucleotides at the first and second positions, and vary at the third position. Three codons do not specify any amino acid but act as termination sites (stop codons), signaling the end of the protein- coding sequence. ...
Biomolecules Worksheet
... 1). In diagram form, give the general structure of an amino acid, and label any functional groups. Since amino acids have the same general structure, what makes them all different? ...
... 1). In diagram form, give the general structure of an amino acid, and label any functional groups. Since amino acids have the same general structure, what makes them all different? ...
Trimble County High School CP Biology Teacher: Debby Griffin Date
... of DNA, mRNA,tRNA and amino acids and model the processes of transcription and translation [C.1.c] Use mRNA codon charts to determine amino acid sequences of example polypeptides [C.1.d] Use mRNA codon charts to determin the effects of different types of mutation on amino acid sequences and protein ...
... of DNA, mRNA,tRNA and amino acids and model the processes of transcription and translation [C.1.c] Use mRNA codon charts to determine amino acid sequences of example polypeptides [C.1.d] Use mRNA codon charts to determin the effects of different types of mutation on amino acid sequences and protein ...
Free Form Amino Acids
... wheat, soy and dairy products and are formulated without the use of preservatives, artificial flavors or colors. Solgar's L-Arginine/L-Ornithine Vegetable Capsules are a pure mixture of natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body mu ...
... wheat, soy and dairy products and are formulated without the use of preservatives, artificial flavors or colors. Solgar's L-Arginine/L-Ornithine Vegetable Capsules are a pure mixture of natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body mu ...
MS Word - Wonderstruck
... As proteins not only catalyze the vast majority of reactions in living cells, they control virtually all of the cellular processes. This makes amino acids vital for life. In addition, proteins contain within their amino acid sequences the information needed to determine how that protein can fold int ...
... As proteins not only catalyze the vast majority of reactions in living cells, they control virtually all of the cellular processes. This makes amino acids vital for life. In addition, proteins contain within their amino acid sequences the information needed to determine how that protein can fold int ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Explain the differences and
... strand. Once finished the mRNA strand may be further processed by alternative splicing (if needed) to create the final mRNA strand that is then taken out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where the small ribosomal subunit will bind with it. The small ribosomal subunit (with the mRNA strand) will the ...
... strand. Once finished the mRNA strand may be further processed by alternative splicing (if needed) to create the final mRNA strand that is then taken out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where the small ribosomal subunit will bind with it. The small ribosomal subunit (with the mRNA strand) will the ...
Proteins Multiple choice Proteins can be classified as Polyesters
... 5. Salivary amylase is an enzyme found in the human body which converts starch to maltose. The pH of saliva is about 7, which is close to the optimum temperature of an enzyme. Amylase stops functioning when it enters the stomach which has a pH of 2. What happens to the enzyme on entering the stomach ...
... 5. Salivary amylase is an enzyme found in the human body which converts starch to maltose. The pH of saliva is about 7, which is close to the optimum temperature of an enzyme. Amylase stops functioning when it enters the stomach which has a pH of 2. What happens to the enzyme on entering the stomach ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... The Genetic Code • Each gene on a strand of DNA is read in 3 base sequences called codons • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating copyright cmassengale ...
... The Genetic Code • Each gene on a strand of DNA is read in 3 base sequences called codons • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating copyright cmassengale ...
Genomics wordsearch
... nucleotides in a DNA/RNA molecule which codes for an amino acid Cytosine – A nucleotide component of DNA/RNA ...
... nucleotides in a DNA/RNA molecule which codes for an amino acid Cytosine – A nucleotide component of DNA/RNA ...
Chapter 15: Translation of mRNA
... _____ 12. The interaction of two or more polypeptides For questions 13 to 15, complete the sentence with the most appropriate term(s): 13. The 21st and 22nd amino acids are ________ and ________. 14. ________ are proteins that bind to polypeptides and facilitate their proper folding. 15. Codons that ...
... _____ 12. The interaction of two or more polypeptides For questions 13 to 15, complete the sentence with the most appropriate term(s): 13. The 21st and 22nd amino acids are ________ and ________. 14. ________ are proteins that bind to polypeptides and facilitate their proper folding. 15. Codons that ...
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
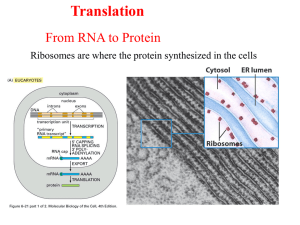
... from DNA Translation takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm; translates mRNA to tRNA to amino acid ...
... from DNA Translation takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm; translates mRNA to tRNA to amino acid ...
Mutation Activity - Northwest ISD Moodle
... The genetic makeup of all known living things is carried in a genetic material known as DNA. The bases pair very specifically (A only with T and C only with G) so that when the DNA molecule replicates every cell has an exact copy of the DNA strand. The order of the bases in a DNA molecule is the key ...
... The genetic makeup of all known living things is carried in a genetic material known as DNA. The bases pair very specifically (A only with T and C only with G) so that when the DNA molecule replicates every cell has an exact copy of the DNA strand. The order of the bases in a DNA molecule is the key ...
Mutations Practice
... The genetic makeup of all known living things is carried in a genetic material known as DNA. The bases pair very specifically (A only with T and C only with G) so that when the DNA molecule replicates every cell has an exact copy of the DNA strand. The order of the bases in a DNA molecule is the key ...
... The genetic makeup of all known living things is carried in a genetic material known as DNA. The bases pair very specifically (A only with T and C only with G) so that when the DNA molecule replicates every cell has an exact copy of the DNA strand. The order of the bases in a DNA molecule is the key ...
sg 10
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
AP Biology
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
Practice Question for Replication, Genetics and Biotechnology
... 28. A trait that expresses itself as a heterozygote is ______________ (dominant or recessive). 29. Sex linked traits are found on the _____________________ chromosome. 30. People who have one copy of an allele for a recessive disorder, but do not exhibit symptoms are called _________ 31. Is blood ty ...
... 28. A trait that expresses itself as a heterozygote is ______________ (dominant or recessive). 29. Sex linked traits are found on the _____________________ chromosome. 30. People who have one copy of an allele for a recessive disorder, but do not exhibit symptoms are called _________ 31. Is blood ty ...
Mutation Activity
... The genetic makeup of all known living things is carried in a genetic material known as DNA. The bases pair very specifically (A only with T and C only with G) so that when the DNA molecule replicates every cell has an exact copy of the DNA strand. The order of the bases in a DNA molecule is the key ...
... The genetic makeup of all known living things is carried in a genetic material known as DNA. The bases pair very specifically (A only with T and C only with G) so that when the DNA molecule replicates every cell has an exact copy of the DNA strand. The order of the bases in a DNA molecule is the key ...
BIS2A TM Murphy Page 1 PROBLEMS ON MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... d. One base in one position is different. The amino acid chain 4) lacks most of the amino acids in 2), because the base change produced a new termination codon. e. Sequence 5) has an additional A after the seventh base. This addition changes the third codon and the codons that follow, because it cha ...
... d. One base in one position is different. The amino acid chain 4) lacks most of the amino acids in 2), because the base change produced a new termination codon. e. Sequence 5) has an additional A after the seventh base. This addition changes the third codon and the codons that follow, because it cha ...
BIS2A TM Murphy Page 1 PROBLEMS ON MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... d. One base in one position is different. The amino acid chain 4) lacks most of the amino acids in 2), because the base change produced a new termination codon. e. Sequence 5) has an additional A after the seventh base. This addition changes the third codon and the codons that follow, because it cha ...
... d. One base in one position is different. The amino acid chain 4) lacks most of the amino acids in 2), because the base change produced a new termination codon. e. Sequence 5) has an additional A after the seventh base. This addition changes the third codon and the codons that follow, because it cha ...
Transcription and Translation Candy
... Where does translation take place? __________________ The final product of translation is _________________. What are the main types of RNA and what is each of their function? ...
... Where does translation take place? __________________ The final product of translation is _________________. What are the main types of RNA and what is each of their function? ...
Domain Genetics - preassessment questions
... 17. In protein synthesis, translation is the process that directly results in the A. production of amino acid chains B. manufacture of mRNA C. copying of one DNA molecule into two molecules D. movement of protein from one cell to another ...
... 17. In protein synthesis, translation is the process that directly results in the A. production of amino acid chains B. manufacture of mRNA C. copying of one DNA molecule into two molecules D. movement of protein from one cell to another ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Define: Nucleotide
... the sequence would encode methionine, but is not recognized as a start codon in this example because it is not at the beginning. 30. The nucleotide sequence of each structural gene determines the codon sequence of a specific m-RNA molecule, which in turn determines the amino acid sequence (primary s ...
... the sequence would encode methionine, but is not recognized as a start codon in this example because it is not at the beginning. 30. The nucleotide sequence of each structural gene determines the codon sequence of a specific m-RNA molecule, which in turn determines the amino acid sequence (primary s ...
fix my dna text
... Protein structure is determined by the DNA base code. Proteins are made from lots of amino acids joined together. Each amino acid is coded by the sequence (order) of three bases. For example, GGT codes are found in glycine but TCA codes are found in serine, a different amino acid. The sequence of ba ...
... Protein structure is determined by the DNA base code. Proteins are made from lots of amino acids joined together. Each amino acid is coded by the sequence (order) of three bases. For example, GGT codes are found in glycine but TCA codes are found in serine, a different amino acid. The sequence of ba ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.