Document
... DNA sequences with different codons compositions have different properties, and may evolve on different evolutionary trajectories with different rates of substitution. ...
... DNA sequences with different codons compositions have different properties, and may evolve on different evolutionary trajectories with different rates of substitution. ...
biochem2
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
Organic Compounds
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
5.3 Presentation: Protein Synthesis
... amounts of proteins • The cell produces proteins that are structural (forms part of cell materials) or functional (enzymes and hormones). • All of an organisms cells have the same DNA, but the cells differ on the expression of the genes. • Each individual in a sexually reproducing population has sli ...
... amounts of proteins • The cell produces proteins that are structural (forms part of cell materials) or functional (enzymes and hormones). • All of an organisms cells have the same DNA, but the cells differ on the expression of the genes. • Each individual in a sexually reproducing population has sli ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Gene: A section of DNA that codes for a protein (polypeptide) Codon (including start and stop): Three sequential bases of mRNA (usually codes for an amino acid)- Start=AUGStop=UAA, UAG, UGA- 64 possibilities -Group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid -Group that can be thought of a ...
... Gene: A section of DNA that codes for a protein (polypeptide) Codon (including start and stop): Three sequential bases of mRNA (usually codes for an amino acid)- Start=AUGStop=UAA, UAG, UGA- 64 possibilities -Group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid -Group that can be thought of a ...
2.Molecular basis of heredity. Realization of hereditary information
... been activated by an enzyme. 2. One end of the tRNA molecule possesses an anticodon, a triplet of nucleotides that recognizes the complementary codon in mRNA. Ribosomal RNA associates with many different proteins (including enzymes) to form ribosomes. 1. rRNA associates with mRNA and tRNA during pro ...
... been activated by an enzyme. 2. One end of the tRNA molecule possesses an anticodon, a triplet of nucleotides that recognizes the complementary codon in mRNA. Ribosomal RNA associates with many different proteins (including enzymes) to form ribosomes. 1. rRNA associates with mRNA and tRNA during pro ...
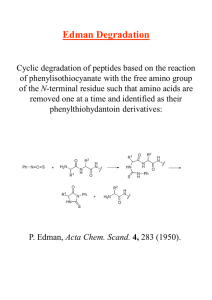
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Unit 9 Test Review
... • Why are the messenger RNA molecules received by eukaryotic ribosomes shorter than the messenger RNA molecules formed by transcription of DNA? • A. Base deletion mutations make the mRNA shorter. • B. Start codons are not at the end of the mRNA molecule. • C. Introns are removed before the RNA is t ...
... • Why are the messenger RNA molecules received by eukaryotic ribosomes shorter than the messenger RNA molecules formed by transcription of DNA? • A. Base deletion mutations make the mRNA shorter. • B. Start codons are not at the end of the mRNA molecule. • C. Introns are removed before the RNA is t ...
amino acids, peptides and proteins
... AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND PROTEINS Vienna, August 3rd to 7th, 2009 ...
... AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND PROTEINS Vienna, August 3rd to 7th, 2009 ...
level two biology: gene expression
... I can explain why RNA is necessary for protein synthesis by comparing the size and importance of RNA and DNA. I can show that I understand the processes of transcription and translation by stating the result of each process and why each process is necessary for protein synthesis. I can differentiate ...
... I can explain why RNA is necessary for protein synthesis by comparing the size and importance of RNA and DNA. I can show that I understand the processes of transcription and translation by stating the result of each process and why each process is necessary for protein synthesis. I can differentiate ...
Topic 3 – The Chemistry of Life
... each codes for the addition of an amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain the genetic code is degenerate meaning more than one codon can code for a partiuclar amino acid the genetic code is universal meaning it is the same in almost all organisms (AUG is the) start codon some (nonsen ...
... each codes for the addition of an amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain the genetic code is degenerate meaning more than one codon can code for a partiuclar amino acid the genetic code is universal meaning it is the same in almost all organisms (AUG is the) start codon some (nonsen ...
Station A
... Transcription = the process of transferring information from DNA to mRNA Translation = the process of decoding an mRNA message into a protein Codon = three consecutive mRNA bases Differentiation = specializing of a cell’s function Frameshift Mutation = involves a change that affects the entire amino ...
... Transcription = the process of transferring information from DNA to mRNA Translation = the process of decoding an mRNA message into a protein Codon = three consecutive mRNA bases Differentiation = specializing of a cell’s function Frameshift Mutation = involves a change that affects the entire amino ...
Bioinformatics Powerpoint - Heredity
... sequences of cytochrome c from a variety of species and draw conclusions about their relatedness based upon this Before you begin this activity you will need to open the cytochrome c data file and save it onto your desk top. To open the file you will need to click on the button at the bottom of this ...
... sequences of cytochrome c from a variety of species and draw conclusions about their relatedness based upon this Before you begin this activity you will need to open the cytochrome c data file and save it onto your desk top. To open the file you will need to click on the button at the bottom of this ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... 7. The protein ______ participates in oxygen dispersal in muscle. 8. A polypeptide can fold into an individual unit of structure called a ______________. 9. A protein that contains more than one subunit is called ______. 10. A secondary structure which forms a coiled shape with a specific repeating ...
... 7. The protein ______ participates in oxygen dispersal in muscle. 8. A polypeptide can fold into an individual unit of structure called a ______________. 9. A protein that contains more than one subunit is called ______. 10. A secondary structure which forms a coiled shape with a specific repeating ...
MUTATIONS TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 10: (22) The
... APRIL 2006 – 11: 7 Which of these best explains how mutation can be beneficial to an organism? A* Phenotypic change may create an advantage over other organisms. B Recombined genetic material improves genotype stability. C Mitosis becomes a favored means of reproduction. D Deoxyribose sugars develop ...
... APRIL 2006 – 11: 7 Which of these best explains how mutation can be beneficial to an organism? A* Phenotypic change may create an advantage over other organisms. B Recombined genetic material improves genotype stability. C Mitosis becomes a favored means of reproduction. D Deoxyribose sugars develop ...
Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of
... alphabet toward future biotechnology Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of the genetic alphabet toward future biotechnology In nature, all organisms store genetic information within sequences consisting of the four standard bases, A, G, C, and T, in nucleic acids. Throu ...
... alphabet toward future biotechnology Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of the genetic alphabet toward future biotechnology In nature, all organisms store genetic information within sequences consisting of the four standard bases, A, G, C, and T, in nucleic acids. Throu ...
amino acid - Humble ISD
... proteins. Even though there are only 20 amino acids, there are many, many proteins. It is the number and arrangement of the amino acids that makes every protein unique. ...
... proteins. Even though there are only 20 amino acids, there are many, many proteins. It is the number and arrangement of the amino acids that makes every protein unique. ...
Lecture 4
... RNA has a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of the sugar. Not like DNA uses thymine (T), RNA uses uracil (U). Because of the extra hydroxyl group on the sugar, RNA is too bulky to form a stable double helix. RNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form wher ...
... RNA has a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of the sugar. Not like DNA uses thymine (T), RNA uses uracil (U). Because of the extra hydroxyl group on the sugar, RNA is too bulky to form a stable double helix. RNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form wher ...
The Mac Daddies of Molecules
... Proteins are chains of amino acids (the monomer of proteins), like a beaded necklace, that sometimes fold into weird shapes Their functions are VAST!!!!! ...
... Proteins are chains of amino acids (the monomer of proteins), like a beaded necklace, that sometimes fold into weird shapes Their functions are VAST!!!!! ...
1 Name: Date: Block: _____ PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: MAKING
... Proteins are required for almost every reaction that occurs in your body! ...
... Proteins are required for almost every reaction that occurs in your body! ...
DNA NOTES
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
Ch. 10: Presentation Slides
... • When a stop codon is encountered, the tRNA holding the polypeptide remains in the P site, and a release factor (RF) binds with the ribosome. • GTP hydrolysis provides the energy to cleave the polypeptide from the tRNA to which it is attached • The 40S and 60S subunits are recycled to initiate tran ...
... • When a stop codon is encountered, the tRNA holding the polypeptide remains in the P site, and a release factor (RF) binds with the ribosome. • GTP hydrolysis provides the energy to cleave the polypeptide from the tRNA to which it is attached • The 40S and 60S subunits are recycled to initiate tran ...
NOTES: 13.1-13.2 - Protein Synthesis (powerpoint)
... • How does it go from mRNA (copy of DNA) to amino acids (building blocks of proteins)? A group of 3 mRNA bases makes up a “codon” (think of as a “code word”) ...
... • How does it go from mRNA (copy of DNA) to amino acids (building blocks of proteins)? A group of 3 mRNA bases makes up a “codon” (think of as a “code word”) ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.