Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels
... Amino Acids: -there are only 20 different amino acids (AA). -each has a central carbon atom. ...
... Amino Acids: -there are only 20 different amino acids (AA). -each has a central carbon atom. ...
molecular biology and phylogeny
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
All amino acids participate in these reactions at some
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
... All amino acids participate in these reactions at some point in their catabolism *** This is false; serine and threonine are not transaminated ¾ they are oxidatively deaminated (release NH3) by a dehydratase enzyme to form pyruvate and propionyl coA respectively. The first step in the catabolism of ...
Quiz 15
... 7. Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) t ...
... 7. Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) t ...
BEBERAPA MUTASI GEN katG
... polymerase, with the highest frequency at codon 526 and 531. While Isoniazid is a prodrug, must be activated by the enzyme catalase-peroxidase encoded by the gene katG of M. tuberculosis, this gene mutation resulting in INH resistant. The purpose of this research is to obtain information on the caus ...
... polymerase, with the highest frequency at codon 526 and 531. While Isoniazid is a prodrug, must be activated by the enzyme catalase-peroxidase encoded by the gene katG of M. tuberculosis, this gene mutation resulting in INH resistant. The purpose of this research is to obtain information on the caus ...
Day 2 (Jan. 23) Scribe Notes
... by introns. Sometimes regions I, II, and IV might be spliced together, to make up form 1. At other times regions II, III, and IV might be spliced together to make up form 2. So far it appears that the average number of alternate splicings of any given region is three or four. Some regions can only b ...
... by introns. Sometimes regions I, II, and IV might be spliced together, to make up form 1. At other times regions II, III, and IV might be spliced together to make up form 2. So far it appears that the average number of alternate splicings of any given region is three or four. Some regions can only b ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... Name the three parts that combine to form a nucleotide. What is the name of the "twisted ladder" shape of the DNA molecule? ...
... Name the three parts that combine to form a nucleotide. What is the name of the "twisted ladder" shape of the DNA molecule? ...
CHONPS Creature Creation
... A mad scientist has been at work here in Parker, Colorado. He has created a special strand of DNA. He wants to insert this strand into a fetal cell culture where the DNA, with the help of various enzymes, will then be transcribed and translated into specific proteins. His hope is that the fetal cell ...
... A mad scientist has been at work here in Parker, Colorado. He has created a special strand of DNA. He wants to insert this strand into a fetal cell culture where the DNA, with the help of various enzymes, will then be transcribed and translated into specific proteins. His hope is that the fetal cell ...
Document
... Genetic material can be altered by natural events or by artificial means. Errors can be made during replication. Environmental conditions may increase the rate of mutation. Mutagens are chemical or physical agents in the environment that cause mutations. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely ...
... Genetic material can be altered by natural events or by artificial means. Errors can be made during replication. Environmental conditions may increase the rate of mutation. Mutagens are chemical or physical agents in the environment that cause mutations. The effects of mutations on genes vary widely ...
Chapter 17 * from gene to protein
... Garrod discovered that proteins (enzymes) are the link between genotype and phenotype. He figured out that some inherited diseases are the inability to make enzymes He noticed that the diaper of a baby was very brown. He determined that the baby had alkaptonuria, which is a recessively inherited dis ...
... Garrod discovered that proteins (enzymes) are the link between genotype and phenotype. He figured out that some inherited diseases are the inability to make enzymes He noticed that the diaper of a baby was very brown. He determined that the baby had alkaptonuria, which is a recessively inherited dis ...
Chapter 1-2: Genetics Progressed from Mendel to DNA in Less Than
... Drosophila, fruit fly, the most common model organism in genetics. • These mutations can be found in the genes of gametes and are passed through sexual reproduction. ...
... Drosophila, fruit fly, the most common model organism in genetics. • These mutations can be found in the genes of gametes and are passed through sexual reproduction. ...
2013 ProSyn PREAP
... Every codon codes for an amino acid (building block of protein) Amino acids are abbreviated most times by using the first 3 letters of the amino acid’s name. Met = methonine Leu = leucine ...
... Every codon codes for an amino acid (building block of protein) Amino acids are abbreviated most times by using the first 3 letters of the amino acid’s name. Met = methonine Leu = leucine ...
Protein Synthesis - Katy Independent School District
... Every codon codes for an amino acid (building block of protein) Amino acids are abbreviated most times by using the first 3 letters of the amino acid’s name. Met = methonine Leu = leucine ...
... Every codon codes for an amino acid (building block of protein) Amino acids are abbreviated most times by using the first 3 letters of the amino acid’s name. Met = methonine Leu = leucine ...
Molecular Genetics - Ursuline High School
... the cytoplasm, waiting for some amino acids to assemble into protein….you already have the instructions, remember the mRNA, …… but you can’t get the amino acids yourself…… you need help…. you need tRNA. The tRNA can pick up specified amino acids.… and bring them to you in the correct order…..but how ...
... the cytoplasm, waiting for some amino acids to assemble into protein….you already have the instructions, remember the mRNA, …… but you can’t get the amino acids yourself…… you need help…. you need tRNA. The tRNA can pick up specified amino acids.… and bring them to you in the correct order…..but how ...
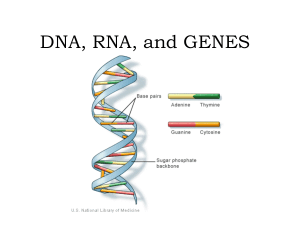
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence of a cell’s gene or chromosome. • Mutations can be caused by outside factors like X-rays, sunlight, and chemicals. • A change in gene or chromosome can change the traits of an organism. ...
... • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence of a cell’s gene or chromosome. • Mutations can be caused by outside factors like X-rays, sunlight, and chemicals. • A change in gene or chromosome can change the traits of an organism. ...
TRANSLASI - alanindra
... initiation sites. There can be several different initiation sites on a messenger RNA: a prokaryotic mRNA can code for several different proteins. Translation begins at an AUG codon, or sometimes a GUG. The modified amino acid Nformyl methionine is always the first amino acid of the new polypeptide. ...
... initiation sites. There can be several different initiation sites on a messenger RNA: a prokaryotic mRNA can code for several different proteins. Translation begins at an AUG codon, or sometimes a GUG. The modified amino acid Nformyl methionine is always the first amino acid of the new polypeptide. ...
Microbial Genetics - Austin Community College
... • 1. DNA is partially unwound with the help of an enzyme called a helicase. The point where the helicase pauses the unwinding is called the replication fork. • 2. A molecule, called an RNA primer, is place on the DNA to help the nucleotides begin to bind. The complementary bases are then added to th ...
... • 1. DNA is partially unwound with the help of an enzyme called a helicase. The point where the helicase pauses the unwinding is called the replication fork. • 2. A molecule, called an RNA primer, is place on the DNA to help the nucleotides begin to bind. The complementary bases are then added to th ...
The genetic code and the “central dogma` Genetic information and
... feasibility of changes of this type in a limited number of cases ...
... feasibility of changes of this type in a limited number of cases ...
The “m”
... This chart shows the amino acids coded for by each of the 64 possible mRNA codons. To find which amino acid the codon CAA codes for, follow these steps. (1) Look on the left side of the chart to find the large row of codons that begin with C. (2) Move across this row until you get to the column of ...
... This chart shows the amino acids coded for by each of the 64 possible mRNA codons. To find which amino acid the codon CAA codes for, follow these steps. (1) Look on the left side of the chart to find the large row of codons that begin with C. (2) Move across this row until you get to the column of ...
12-3: RNA
... Mutations can affect the reproductive cells of an organism by changing the sequence of nucleotides within a ________ in a sperm or an egg cell. If this cell takes part in fertilization, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring. The mutation may produce a new trait or ...
... Mutations can affect the reproductive cells of an organism by changing the sequence of nucleotides within a ________ in a sperm or an egg cell. If this cell takes part in fertilization, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring. The mutation may produce a new trait or ...
2.3 Carbon Compounds
... Amino acids are the monomers of proteins. Each amino acid has three distinct parts: an amino group, an R group, and a carboxyl group. An amino group has the formula –NH2, a carboxyl group is –COOH, and the R group varies from one amino acid to another. Two amino acids are joined in a chemical reacti ...
... Amino acids are the monomers of proteins. Each amino acid has three distinct parts: an amino group, an R group, and a carboxyl group. An amino group has the formula –NH2, a carboxyl group is –COOH, and the R group varies from one amino acid to another. Two amino acids are joined in a chemical reacti ...
What is a protein?
... •The ______________________ binds with a ribosome where it is decoded. Since this is where the DNA language is changed to the protein language, this is called Translation. •The code on the m-RNA is read _______ bases at a time. This is called a triplet code or __________________. •Each codon stands ...
... •The ______________________ binds with a ribosome where it is decoded. Since this is where the DNA language is changed to the protein language, this is called Translation. •The code on the m-RNA is read _______ bases at a time. This is called a triplet code or __________________. •Each codon stands ...
Chapter 13.1 and 13.2 RNA, Ribosomes, and Protein Synthesis
... – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino acids bond and move along the mRNA – Continues until reaches STOP codon and forms polypeptide and mRNA is released. ...
... – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino acids bond and move along the mRNA – Continues until reaches STOP codon and forms polypeptide and mRNA is released. ...
Protein Synthesis
... most important parts are left in the mRNA. The excess information that is cut out is called introns and the important information that remains are called exons. ...
... most important parts are left in the mRNA. The excess information that is cut out is called introns and the important information that remains are called exons. ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.