Biology 1 Notes Chapter 12 - DNA and RNA Prentice Hall pages
... The four bases (letters) of mRNA (A, U, G, and C) are read three letters at a time (and translated) to determine the order in which amino acids are added to a protein. ...
... The four bases (letters) of mRNA (A, U, G, and C) are read three letters at a time (and translated) to determine the order in which amino acids are added to a protein. ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 7
... 4. The RNA is edited by removing the _______________ introns = pieces of _____ that do not code for proteins 5. The remaining pieces of RNA, known as exons, are _______________ together to form the completely complementary strand of RNA known as mRNA exons = DNA sequences that ________ for prote ...
... 4. The RNA is edited by removing the _______________ introns = pieces of _____ that do not code for proteins 5. The remaining pieces of RNA, known as exons, are _______________ together to form the completely complementary strand of RNA known as mRNA exons = DNA sequences that ________ for prote ...
slides
... Single base substitutions Missense mutations: replace one amino acid codon with another Nonsense mutations: replace amino acid codon with stop codon ...
... Single base substitutions Missense mutations: replace one amino acid codon with another Nonsense mutations: replace amino acid codon with stop codon ...
Gene action
... Because the code can usually continue after the changed sequence. In this case, just one amino Tyr – gly – trp – ser ile - asn … acid has changed. BUT if it changes a stop or start codon… then you’re in trouble (as we saw before) ATG-CCG-ACC-TAG-TTG C ...
... Because the code can usually continue after the changed sequence. In this case, just one amino Tyr – gly – trp – ser ile - asn … acid has changed. BUT if it changes a stop or start codon… then you’re in trouble (as we saw before) ATG-CCG-ACC-TAG-TTG C ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 22. Describe the process of translation.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
... 22. Describe the process of translation.____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ...
What is RNA, and How Does it Differ from DNA?
... – Change in amino-acid sequence may or may not change function of protein; typically involves changes in shape or charge – Point mutations: change in one base (often random; mutation rates can be increased by mutagens) • If wobble effect, no change in amino acid • Enzymes repair mutations at given r ...
... – Change in amino-acid sequence may or may not change function of protein; typically involves changes in shape or charge – Point mutations: change in one base (often random; mutation rates can be increased by mutagens) • If wobble effect, no change in amino acid • Enzymes repair mutations at given r ...
Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids and are
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ____________ in a process called ______________________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make __________________________ which can join together to make a _______________________________________. 25. _______________ bon ...
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ____________ in a process called ______________________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make __________________________ which can join together to make a _______________________________________. 25. _______________ bon ...
In the nucleus
... Starting point of a reading frame can be off by one or two bases during Translation. Mutations- changes in DNA ...
... Starting point of a reading frame can be off by one or two bases during Translation. Mutations- changes in DNA ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Genetics plays a big role in determining who we are and what we look like Genetic research provides us with a unique perspective on life - tying together the past with the present and the future History of genetic research Gregor Mendel developed some incredible genetic insights at a time when ...
... Genetics plays a big role in determining who we are and what we look like Genetic research provides us with a unique perspective on life - tying together the past with the present and the future History of genetic research Gregor Mendel developed some incredible genetic insights at a time when ...
chapter 10
... a. one binding site for DNA. b. three binding sites used during translation. c. four binding sites for tRNA. d. no binding sites since the proteins must detach. ____ 18. Transfer RNA a. carries an amino acid to its correct codon. b. synthesizes amino acids as they are needed. c. produces codons to m ...
... a. one binding site for DNA. b. three binding sites used during translation. c. four binding sites for tRNA. d. no binding sites since the proteins must detach. ____ 18. Transfer RNA a. carries an amino acid to its correct codon. b. synthesizes amino acids as they are needed. c. produces codons to m ...
Genetics - Doc Ireland
... Practical Level • Transcription occurs in a similar fashion to Replication, with the RNA Polymerase doing most of the duties. • The Hardest Part is telling the difference between coding and template strands. • Coding = the information • Template = the compliment of coding that is used to make the R ...
... Practical Level • Transcription occurs in a similar fashion to Replication, with the RNA Polymerase doing most of the duties. • The Hardest Part is telling the difference between coding and template strands. • Coding = the information • Template = the compliment of coding that is used to make the R ...
Ex. glucose, fructose and galactose: these are isomers
... a. Nitrogenous bases pair up: i. A and ______ ii. G and ______ ...
... a. Nitrogenous bases pair up: i. A and ______ ii. G and ______ ...
1 Questions: Concept Check 11.1 1. How did Griffith`s experiments
... in red blood cells, and is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to various parts of the body for use in respiration. Normal adult hemoglobin is a four part protein consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. Mutant forms of this gene is responsible for the sickling of red blood cel ...
... in red blood cells, and is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to various parts of the body for use in respiration. Normal adult hemoglobin is a four part protein consisting of two alpha chains and two beta chains. Mutant forms of this gene is responsible for the sickling of red blood cel ...
Evolution and Genetic Engineering Keystone Vocabulary
... sequence though the processes of transcription of DNA and to RNA and the translation of RNA to a polypeptide chain. 33. A proposed explanation in evolutionary biology stating that species are generally stable over long periods of time. Occasionally there are rapid changes that affect some species wh ...
... sequence though the processes of transcription of DNA and to RNA and the translation of RNA to a polypeptide chain. 33. A proposed explanation in evolutionary biology stating that species are generally stable over long periods of time. Occasionally there are rapid changes that affect some species wh ...
Translation is the process where mRNA codons are used to produce
... Note: – The first AUG encountered by the ribosome sets the “Reading Frame” for all base-triplets (codons) that come after it, mRNA is read 3 bases at a time. – A single mRNA can have several ribosomes on it at one time – In prokaryotes a Shine-Delgano Sequence of –AGGA- must precede the AUG for init ...
... Note: – The first AUG encountered by the ribosome sets the “Reading Frame” for all base-triplets (codons) that come after it, mRNA is read 3 bases at a time. – A single mRNA can have several ribosomes on it at one time – In prokaryotes a Shine-Delgano Sequence of –AGGA- must precede the AUG for init ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the idea that all biological catalysts are proteins. Introns may play a regulatory role in the cell. Specific functions have not been identified for most introns, but some contain sequences that regulate gene expression, and many affect gene products ...
... The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the idea that all biological catalysts are proteins. Introns may play a regulatory role in the cell. Specific functions have not been identified for most introns, but some contain sequences that regulate gene expression, and many affect gene products ...
Transcription and Translation
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
3.2.1: Transcription and Translation
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
HomeworkCh7
... b. What is the role of transcription factors in Archaea and Eukarya? Hint. Same as sigma factors in bacteria. c. What is a promotor? d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you ...
... b. What is the role of transcription factors in Archaea and Eukarya? Hint. Same as sigma factors in bacteria. c. What is a promotor? d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you ...
Biology Packet 7: DNA & RNA
... Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of DNA replication. Describe how errors are corrected during DNA replication. Relate the DNA molecule to chromosome structure. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. Name the three type ...
... Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of DNA replication. Describe how errors are corrected during DNA replication. Relate the DNA molecule to chromosome structure. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. Name the three type ...
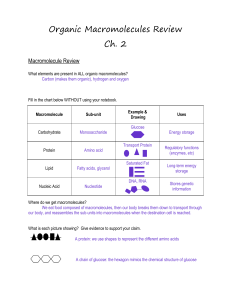
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
Chapter 3-1 • Definitions: - Genetics: the scientific study of heredity
... • Meiosis: process by which chromosome # is reduced when forming sex cells ...
... • Meiosis: process by which chromosome # is reduced when forming sex cells ...
paper a - Fiitjee
... Name the two semi-dwarf varieties of wheat introduced into all wheat growing places of India. ...
... Name the two semi-dwarf varieties of wheat introduced into all wheat growing places of India. ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.