DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Define: Nucleotide
... the sequence would encode methionine, but is not recognized as a start codon in this example because it is not at the beginning. 30. The nucleotide sequence of each structural gene determines the codon sequence of a specific m-RNA molecule, which in turn determines the amino acid sequence (primary s ...
... the sequence would encode methionine, but is not recognized as a start codon in this example because it is not at the beginning. 30. The nucleotide sequence of each structural gene determines the codon sequence of a specific m-RNA molecule, which in turn determines the amino acid sequence (primary s ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... mRNA, tRNA, and a ribosome work together in constructing a protein mRNA = “messenger”; it contains the message that is being translated. tRNA = “transfer”; it transfers (delivers) the right a.a. to the right codon. It is the ...
... mRNA, tRNA, and a ribosome work together in constructing a protein mRNA = “messenger”; it contains the message that is being translated. tRNA = “transfer”; it transfers (delivers) the right a.a. to the right codon. It is the ...
How cells use DNA, part 1: TRANSCRIPTION
... Often this means a change of script, from one we don’t understand to another we can read. ...
... Often this means a change of script, from one we don’t understand to another we can read. ...
bonds form when water is removed to hold acids together.
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of _____________ in a process called __________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make ________________________ which can join together to make a _____________________. 25. _______________ bonds form when water is removed t ...
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of _____________ in a process called __________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make ________________________ which can join together to make a _____________________. 25. _______________ bonds form when water is removed t ...
Figure S1. Architecture of genetic elements in bacteria different of K
... We performed the same analysis as for E. coli strain K-12 MG1655 in E. coli strains K-12 W3110 and BL21 (DE3), in Salmonella typhimurium SL1344, and in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PA14 and PAO1 (see, Table S2 and S3). A) Consensus architecture of E. coli K12 MG1655, B) Summary o ...
... We performed the same analysis as for E. coli strain K-12 MG1655 in E. coli strains K-12 W3110 and BL21 (DE3), in Salmonella typhimurium SL1344, and in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PA14 and PAO1 (see, Table S2 and S3). A) Consensus architecture of E. coli K12 MG1655, B) Summary o ...
Chapter 9 - Proteins and their synthesis
... 3’ GAA UGU CAA AUA ACU AUG CCU CUU CC 5’ 5’ C UUA CAG UUU AUU GAU ACG GAG AAG G 3’ 3’ G AAU GUC AAA UAA CUA UGC CUC UUC C 5’ 5’ CU UAC AGU UUA UUG AUA CGG AGA AGG 3’ 3’ GA AUG UCA AAU AAC UAU GCC UCU UCC 5’ ...
... 3’ GAA UGU CAA AUA ACU AUG CCU CUU CC 5’ 5’ C UUA CAG UUU AUU GAU ACG GAG AAG G 3’ 3’ G AAU GUC AAA UAA CUA UGC CUC UUC C 5’ 5’ CU UAC AGU UUA UUG AUA CGG AGA AGG 3’ 3’ GA AUG UCA AAU AAC UAU GCC UCU UCC 5’ ...
Biological Macromolecules
... D. Nucleic Acids Overall function. • The sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid molecule serves as a blueprint to encode the correct sequence of amino acids for a protein. The code for a specific protein is called a “gene.” • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): DNA molecules (chromosomes) serve as the ...
... D. Nucleic Acids Overall function. • The sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid molecule serves as a blueprint to encode the correct sequence of amino acids for a protein. The code for a specific protein is called a “gene.” • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): DNA molecules (chromosomes) serve as the ...
DNA Strand 2
... there are 20 amino acids and these amino acids float around in high concentration in the liquid cytoplasm of the cell along with ribosomes. All proteins are made up of amino acids bonded together, and the amino acids are bonded together by the ribosomes. Humans get amino acids from foods we eat. So, ...
... there are 20 amino acids and these amino acids float around in high concentration in the liquid cytoplasm of the cell along with ribosomes. All proteins are made up of amino acids bonded together, and the amino acids are bonded together by the ribosomes. Humans get amino acids from foods we eat. So, ...
Quiz:1
... 7. The non-polar amino acids such as iso-leucine, leucine, valine, alanine, phenyl alanine are soluble in water but when they are present in a peptide (joined together by amide bond), the peptide is insoluble in water. Why? 8. What will be the net charge on a poly-lysine peptide at neutral pH and at ...
... 7. The non-polar amino acids such as iso-leucine, leucine, valine, alanine, phenyl alanine are soluble in water but when they are present in a peptide (joined together by amide bond), the peptide is insoluble in water. Why? 8. What will be the net charge on a poly-lysine peptide at neutral pH and at ...
Unit 6: Genetics
... Describe the role of ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and the nucleus in the production of specific types of proteins. ◦ Ribosomes: A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. ◦ Endoplasmic reticulum: An organelle, conta ...
... Describe the role of ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and the nucleus in the production of specific types of proteins. ◦ Ribosomes: A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. ◦ Endoplasmic reticulum: An organelle, conta ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 17. How many nucleotide bases are there?_____________ How many amino acids?______________ ...
... 17. How many nucleotide bases are there?_____________ How many amino acids?______________ ...
Read the passage. (i) Name the substance in cells which carries
... of producing drip dry shirts made from natural fibres. Other cotton plants are being genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. When they have perfected these new types of cotton plants, the scientists will use cloning techniques to produce large numbers of them. ...
... of producing drip dry shirts made from natural fibres. Other cotton plants are being genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. When they have perfected these new types of cotton plants, the scientists will use cloning techniques to produce large numbers of them. ...
Mutation
... Chromosome mutations are gross changes to the structure of chromosomes. These can arise in a number of ways, but one way is the failure of chromosomes to separate during cell division – this is termed non-disjunction. In humans a failure in separation of chromosome 21 during meiosis results in an eg ...
... Chromosome mutations are gross changes to the structure of chromosomes. These can arise in a number of ways, but one way is the failure of chromosomes to separate during cell division – this is termed non-disjunction. In humans a failure in separation of chromosome 21 during meiosis results in an eg ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... Transcription does not happen all the time Operon – the “switch” to ...
... Transcription does not happen all the time Operon – the “switch” to ...
From DNA to Protein
... proteins as the parent cell. A skin cell should be able to produce skin proteins, a hair follicle cell hair proteins. The linear polymer DNA with all the information about proteins can be easily duplicated in cell division. How does it work? To make new proteins, the living cell uses the genetic cod ...
... proteins as the parent cell. A skin cell should be able to produce skin proteins, a hair follicle cell hair proteins. The linear polymer DNA with all the information about proteins can be easily duplicated in cell division. How does it work? To make new proteins, the living cell uses the genetic cod ...
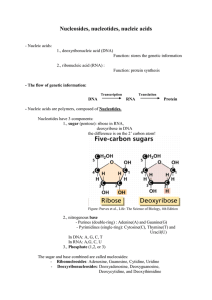
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... The nucleotide sequence (=base sequence) carries the genetic information, this information will be translated into amino-acid sequence during protein synthesis. - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single strande ...
... The nucleotide sequence (=base sequence) carries the genetic information, this information will be translated into amino-acid sequence during protein synthesis. - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single strande ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... DNA is responsible for making proteins. RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a speci ...
... DNA is responsible for making proteins. RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a speci ...
BIOS 1700 Dr. Tanda 8 September 2016 Week 3, Session 2 1
... 3. What is the purpose of chaperones? ...
... 3. What is the purpose of chaperones? ...
Amino Acids Worksheet and Problem Set
... What does the R group determine for an amino acid and why is it important? Which are the aliphatic amino acids? (Group 1) Which are the Group 2 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 3 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 4 amino acids and why? Chapter 3.3: Draw the normal structure of a gener ...
... What does the R group determine for an amino acid and why is it important? Which are the aliphatic amino acids? (Group 1) Which are the Group 2 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 3 amino acids and why? Which are the Group 4 amino acids and why? Chapter 3.3: Draw the normal structure of a gener ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
DNA, RNA, Genetic Engineering
... Codon (triplet) matches to anticodon on tRNA tRNA brings AA to ribosome to build peptide chain Start codon= Met (yes, codes for AA & can be inside sequence) Stop codon= stop (no AA & terminates sequence) ...
... Codon (triplet) matches to anticodon on tRNA tRNA brings AA to ribosome to build peptide chain Start codon= Met (yes, codes for AA & can be inside sequence) Stop codon= stop (no AA & terminates sequence) ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.