Teacher Instructions Lesson 4
... Another option would be to have more advanced students create these tools as part of an extension or enrichment activity. The instructions for these stamps are explained in detail in Lesson 1. All 20 amino acids could be be made into stamps, or another option is to make only the amino acids coding f ...
... Another option would be to have more advanced students create these tools as part of an extension or enrichment activity. The instructions for these stamps are explained in detail in Lesson 1. All 20 amino acids could be be made into stamps, or another option is to make only the amino acids coding f ...
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
... the third nucleotide has changed, both codons code for tyrosine, so the final protein is the same. Sometimes point mutations result in a frame-shift mutation. In this case, a single nucleotide is added or deleted to the DNA sequence. This causes a shift in what is called the reading frame. Because DN ...
... the third nucleotide has changed, both codons code for tyrosine, so the final protein is the same. Sometimes point mutations result in a frame-shift mutation. In this case, a single nucleotide is added or deleted to the DNA sequence. This causes a shift in what is called the reading frame. Because DN ...
on Translation
... translated in six different ways into amino acid sequences. These six different ways of parsing a coding sequence are called reading frames. If we search the genome for coding regions of genes, all six reading frames have to be considered. ...
... translated in six different ways into amino acid sequences. These six different ways of parsing a coding sequence are called reading frames. If we search the genome for coding regions of genes, all six reading frames have to be considered. ...
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
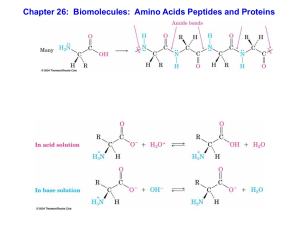
... • In acidic solution, the carboxylate and amine are in their conjugate acid forms, an overall cation • In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion • In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present • This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
... • In acidic solution, the carboxylate and amine are in their conjugate acid forms, an overall cation • In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion • In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present • This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... How Proteins Unfold • When bonds are broken proteins will unfold – Caused by: » High Temperature » Change in pH » Enzymes my cause denaturatuin ...
... How Proteins Unfold • When bonds are broken proteins will unfold – Caused by: » High Temperature » Change in pH » Enzymes my cause denaturatuin ...
Name
... leaving the nucleus B-mRNA segment at the ribosome •Then label the following items: C-tRNA D-ribosome E-a codon F-an anticodon G-use the table to identify the three specific amino acids on the 3 tRNA’s) H-nucleus ...
... leaving the nucleus B-mRNA segment at the ribosome •Then label the following items: C-tRNA D-ribosome E-a codon F-an anticodon G-use the table to identify the three specific amino acids on the 3 tRNA’s) H-nucleus ...
Chapter One
... 1 base codon - 41 = 4 possible amino acids 2 base codon - 42 = 16 possible amino acids 3 base codon - 43 = 64 possible amino acids ...
... 1 base codon - 41 = 4 possible amino acids 2 base codon - 42 = 16 possible amino acids 3 base codon - 43 = 64 possible amino acids ...
Nedmolecularbio1of32013 40 KB
... then emerges 5’-3’ from RNA polymerase in linear fashion. Prokaryotic genes are under the control of one promoter & operator, acting in cis. In eukaryotes, the genes that emerge from txn can be combinatorially spliced into multiple variants (exons are retained as coding information, while introns ar ...
... then emerges 5’-3’ from RNA polymerase in linear fashion. Prokaryotic genes are under the control of one promoter & operator, acting in cis. In eukaryotes, the genes that emerge from txn can be combinatorially spliced into multiple variants (exons are retained as coding information, while introns ar ...
DNA and Its Proccesses
... • Create ONE strand of mRNA from a piece of DNA • Unzip strands • Add mRNA base pairs to one side • Base-pairing rules: ...
... • Create ONE strand of mRNA from a piece of DNA • Unzip strands • Add mRNA base pairs to one side • Base-pairing rules: ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Introduction: The first stage of building a protein involves a process known as transcription. In transcription, a segment of DNA serves as a template to produce a complementary strand of RNA. This complementary strand is called messenger RNA, or mRNA. 3. Experiment: Like DNA, RNA follows base-pairi ...
... Introduction: The first stage of building a protein involves a process known as transcription. In transcription, a segment of DNA serves as a template to produce a complementary strand of RNA. This complementary strand is called messenger RNA, or mRNA. 3. Experiment: Like DNA, RNA follows base-pairi ...
The Chemistry of Molecular Biology
... nature are L form • Structure consists of Ca, to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a • Amino acids are classed variable group according to their R group ...
... nature are L form • Structure consists of Ca, to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a • Amino acids are classed variable group according to their R group ...
of translation Initiation: brings together mRNA, a tRNA (with the first
... • A ribosome requires less than a minute to translate an average-sized mRNA into a polypeptide. • Multiple ribosomes, polyribosomes, may trail along the same mRNA. • Thus, a single mRNA is used to make many copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. ...
... • A ribosome requires less than a minute to translate an average-sized mRNA into a polypeptide. • Multiple ribosomes, polyribosomes, may trail along the same mRNA. • Thus, a single mRNA is used to make many copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. ...
Transcription and Translation
... RNA nucleotides line up along one strand of the DNA following the base-pairing rules. ...
... RNA nucleotides line up along one strand of the DNA following the base-pairing rules. ...
AS 2.1.1 Protein Structure
... • Ionic bonds: the R groups are sometimes charged (+ve or –ve) so they attract each other • Hydrogen bonds: +ve hydrogen atoms and –ve oxygen ...
... • Ionic bonds: the R groups are sometimes charged (+ve or –ve) so they attract each other • Hydrogen bonds: +ve hydrogen atoms and –ve oxygen ...
(a) A(1) - at www.arxiv.org.
... The 20 standard amino acids together with 64 tri-nucleotide codons selected in the genetic code constitute a paradigm of complexity in Nature.1 Atomic rationals for the choice of nucleobases by Nature have recently received much attention.2 For the importance of stereoelectronic effect in noncovalen ...
... The 20 standard amino acids together with 64 tri-nucleotide codons selected in the genetic code constitute a paradigm of complexity in Nature.1 Atomic rationals for the choice of nucleobases by Nature have recently received much attention.2 For the importance of stereoelectronic effect in noncovalen ...
Protein Synthesis PP
... polypeptides and then proteins. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. For example: Leucine is ...
... polypeptides and then proteins. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. For example: Leucine is ...
Bi 12 Biological Molecules Current.pptx
... ¨ occurs when two or more proteins are joined together to form a protein complex. ¨ Held together by hydrogen bonds or disulphide bridges ...
... ¨ occurs when two or more proteins are joined together to form a protein complex. ¨ Held together by hydrogen bonds or disulphide bridges ...
DNA Replication Transcription translation [Read
... • Triplets of bases that code for a particular amino acid • Start Codon: (AUG) - marks the start of a polypeptide • Stop Codon: (UAA, UAG, UGA) - marks the end ...
... • Triplets of bases that code for a particular amino acid • Start Codon: (AUG) - marks the start of a polypeptide • Stop Codon: (UAA, UAG, UGA) - marks the end ...
Bio 301, Biochemistry I
... 17. Which of the following best characterizes the relationship between amino acids and tRNAs? a. The activation of an amino acid by formation of an aminoacyl-tRNA is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP to AMP + 2 Pi. b. The conformation of an aminoacyl-tRNA facilitates the direct interaction between th ...
... 17. Which of the following best characterizes the relationship between amino acids and tRNAs? a. The activation of an amino acid by formation of an aminoacyl-tRNA is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP to AMP + 2 Pi. b. The conformation of an aminoacyl-tRNA facilitates the direct interaction between th ...
Quiz 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
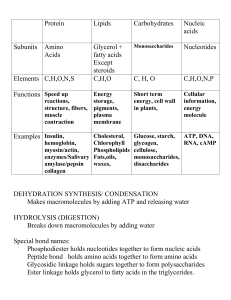
... 8. The chemical reaction where water is removed during the formation of a covalent bond linking two monomers is known as. a) dehydration; b) hydrolysis; c) photosynthesis; d) protein synthesis 9. Proteins are composed of which of these monomers? a) amino acids; b) glucose; c) fatty acids; d) nucleot ...
... 8. The chemical reaction where water is removed during the formation of a covalent bond linking two monomers is known as. a) dehydration; b) hydrolysis; c) photosynthesis; d) protein synthesis 9. Proteins are composed of which of these monomers? a) amino acids; b) glucose; c) fatty acids; d) nucleot ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.