Precise Manipulation of Chromosomes in Vivo
... Conclusions and Future Directions • Successfully replaced all TAG occurrences with TAA codons • Improve future genome engineering efforts – Dynamic method to introduce change in cell ...
... Conclusions and Future Directions • Successfully replaced all TAG occurrences with TAA codons • Improve future genome engineering efforts – Dynamic method to introduce change in cell ...
protein
... – This occurs when a termination codon reaches the A site. – A Release factor (enzyme) enters the A site causing a hydrolysis reaction to occur that releases the protein from the last tRNA molecule (which is sitting in the P site). – After the hydrolysis reaction occurs, the ribosome detaches and th ...
... – This occurs when a termination codon reaches the A site. – A Release factor (enzyme) enters the A site causing a hydrolysis reaction to occur that releases the protein from the last tRNA molecule (which is sitting in the P site). – After the hydrolysis reaction occurs, the ribosome detaches and th ...
Why teach a course in bioinformatics?
... companies competing to recruit one of the handful of properly qualified scientists who bothered to show up. Sounds like a pie-inthe-sky dream, doesn't it? But according to Victor Markovitz, vice president of ...
... companies competing to recruit one of the handful of properly qualified scientists who bothered to show up. Sounds like a pie-inthe-sky dream, doesn't it? But according to Victor Markovitz, vice president of ...
Name of structure?
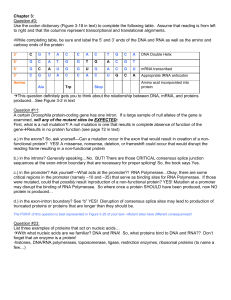
... 5. The nucleotide sequence of a DNA codon is GTA. The mRNA complementary sequence codon is _____. 6. The above codon codes for the _________ amino acid. ...
... 5. The nucleotide sequence of a DNA codon is GTA. The mRNA complementary sequence codon is _____. 6. The above codon codes for the _________ amino acid. ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
teachers.oregon.k12.wi.us
... Key Point: If the cell wants the information stored in DNA to be expressed as protein, we need to have a messenger take the information from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
... Key Point: If the cell wants the information stored in DNA to be expressed as protein, we need to have a messenger take the information from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
... double helix is used as a template by the RNA polymerase. During this step, mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. During this step, mRNA goes through different types of maturation including one called splicing, when the non-coding sequences are eliminated. The coding mRNA sequence can be ...
The DNA Connection
... • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different ...
... • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different ...
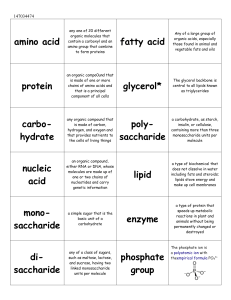
Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]
... Amino acids are most logically grouped according to the physical properties of their side chains. ...
... Amino acids are most logically grouped according to the physical properties of their side chains. ...
Quiz: DNA, RNA and Protein
... 11. What kind of bond holds the DNA bases together? 12. A three nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a _______________. 13. How many different amino acids are there? 14. State three differences between DNA and RNA. 15. The base uracil pairs with what DNA nucleotide 16. If the DNA coding strand is GT ...
... 11. What kind of bond holds the DNA bases together? 12. A three nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a _______________. 13. How many different amino acids are there? 14. State three differences between DNA and RNA. 15. The base uracil pairs with what DNA nucleotide 16. If the DNA coding strand is GT ...
Protein Synthesis
... exons can be spliced together in diff sequences to produce diff mRNA’s = diff proteins) We have 25,000 genes but produce more than 100,000 diff proteins = splicing ...
... exons can be spliced together in diff sequences to produce diff mRNA’s = diff proteins) We have 25,000 genes but produce more than 100,000 diff proteins = splicing ...
Unit 4 Review KEY File
... Above picture is translation. tRNA molecules are reading the mRNA strand to create a A.A (amino acid chain) and build a protein. B. Name the molecules I, II, III, IV in the picture above. Also, what process is occurring and where is it occurring.I=tRNA Anticodon, II=mRNA III=Amino Acids IV=tRNA C. W ...
... Above picture is translation. tRNA molecules are reading the mRNA strand to create a A.A (amino acid chain) and build a protein. B. Name the molecules I, II, III, IV in the picture above. Also, what process is occurring and where is it occurring.I=tRNA Anticodon, II=mRNA III=Amino Acids IV=tRNA C. W ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Learning Objectives The
... 13. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. What three properties allow some RNA molecules to function as ribozymes? 14. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can produce is much greater than its number of genes. The Synthesis of Protein ...
... 13. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. What three properties allow some RNA molecules to function as ribozymes? 14. Explain why, due to alternative RNA splicing, the number of different protein products an organism can produce is much greater than its number of genes. The Synthesis of Protein ...
DNA - Valhalla High School
... These strands of chromatin are made up of many genes. A gene can be hundreds or thousands of nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
... These strands of chromatin are made up of many genes. A gene can be hundreds or thousands of nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
Document
... A certain Drosophila protein-coding gene has one intron. If a large sample of null alleles of the gene is examined, will any of the mutant sites be EXPECTED: First, what is a null mutation?! A null mutation is one that results in complete absence of function of the geneResults in no protein functio ...
... A certain Drosophila protein-coding gene has one intron. If a large sample of null alleles of the gene is examined, will any of the mutant sites be EXPECTED: First, what is a null mutation?! A null mutation is one that results in complete absence of function of the geneResults in no protein functio ...
DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
Chapter 12-3: RNA and Protein Synthesis
... __________________________ mutations: involve changes in one or a few __________________ at one point in the DNA sequence. a. __________________________________: where one base is changed to another. These usually affect only one amino acid. b. Frameshift mutations (Insertions or Deletions): an extr ...
... __________________________ mutations: involve changes in one or a few __________________ at one point in the DNA sequence. a. __________________________________: where one base is changed to another. These usually affect only one amino acid. b. Frameshift mutations (Insertions or Deletions): an extr ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... 2. Gene expression (protein synthesis) is when the product of a gene (specific protein) is being actively produced by a cell. a. some genes are – rarely expressed -adrenaline b. some genes are – constantly expressed – ...
... 2. Gene expression (protein synthesis) is when the product of a gene (specific protein) is being actively produced by a cell. a. some genes are – rarely expressed -adrenaline b. some genes are – constantly expressed – ...
Initiation
... 1. Initiation – attachment of mRNA to the ribosome (This was already covered in Step # 3) 2. Elongation – the addition of amino acids to the growing protein chain A Site P site ...
... 1. Initiation – attachment of mRNA to the ribosome (This was already covered in Step # 3) 2. Elongation – the addition of amino acids to the growing protein chain A Site P site ...
Protein Synthesis part 2
... Translation - This is the part of actually making the protein. A. This process occurs at the Ribosome “the Translator”. B. The process turns the mRNA into a primary (1’) sequence of amino acids for making of the protein. C. This process needs the assistance of tRNA (transfer RNA) to transfer free am ...
... Translation - This is the part of actually making the protein. A. This process occurs at the Ribosome “the Translator”. B. The process turns the mRNA into a primary (1’) sequence of amino acids for making of the protein. C. This process needs the assistance of tRNA (transfer RNA) to transfer free am ...
Ch 25 Origin of Life on Earth Guided Rdg
... Origin of Life on Earth Guide Reading Biology, 8th Edition, 25.1 (507-510). If any of the questions is not explicitly defined in the reading, you are responsible for using your text or another reliable source to answer the questions. 1. Define the term macroevolution. ...
... Origin of Life on Earth Guide Reading Biology, 8th Edition, 25.1 (507-510). If any of the questions is not explicitly defined in the reading, you are responsible for using your text or another reliable source to answer the questions. 1. Define the term macroevolution. ...
word
... These factors participate, among other things, in the binding of aminoacyl-tRNAs to the A site on the ribosome C. Peptidyltransferase is an enzyme that participates during elongation and catalyzes transfer of the growing peptide chain on the peptidyl-tRNA at the P site to the activated amino acid on ...
... These factors participate, among other things, in the binding of aminoacyl-tRNAs to the A site on the ribosome C. Peptidyltransferase is an enzyme that participates during elongation and catalyzes transfer of the growing peptide chain on the peptidyl-tRNA at the P site to the activated amino acid on ...
CHAP Twenty-Five - Foothill College
... ii) Edman Degradation: N terminus iii) DNFB to identify N-terminus iv) Chymotripsin at C-terminus v) With cyanogen bromide BrCN at methionine C terminus vi) With chymotripsin at C end of phe, tyr, trp vii) With Tripsin at C end of lys, arg D) Separation and Identification of aa fragments via Gel ele ...
... ii) Edman Degradation: N terminus iii) DNFB to identify N-terminus iv) Chymotripsin at C-terminus v) With cyanogen bromide BrCN at methionine C terminus vi) With chymotripsin at C end of phe, tyr, trp vii) With Tripsin at C end of lys, arg D) Separation and Identification of aa fragments via Gel ele ...
Protein synthesis - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... DNA at a specific site known as a promoter, near the beginning of the gene. Promoter regions are often sequences of A's and T's. Elongation: the RNA polymerase adds ribonucleotides (A/U, G/C) to complement the DNA sequence. Elongation occurs along only one of the DNA strands, called the template str ...
... DNA at a specific site known as a promoter, near the beginning of the gene. Promoter regions are often sequences of A's and T's. Elongation: the RNA polymerase adds ribonucleotides (A/U, G/C) to complement the DNA sequence. Elongation occurs along only one of the DNA strands, called the template str ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.







![Amino Acids as Protein Building Blocks [2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001231379_1-1c71e58dd2b4a4d156753bc870eff68b-300x300.png)