Protein synthesis sequencing task
... The next step is for a second tRNA to approach the mRNA and match with the second codon on the mRNA. A peptide bond forms between the amino acids. The ribosome moves along the mRNA one codon. The first tRNA is released without its amino acid. The next matching tRNA brings in the next amino acid. Ano ...
... The next step is for a second tRNA to approach the mRNA and match with the second codon on the mRNA. A peptide bond forms between the amino acids. The ribosome moves along the mRNA one codon. The first tRNA is released without its amino acid. The next matching tRNA brings in the next amino acid. Ano ...
Biology 102, Lectures 17 and 18 Study Guide
... c. Explain why Mutant A could only grow on arginine, whereas Mutant B can grow on either citruline or arginine. d. What was the key conclusion that Beadle and Tatum arrived at with these experiments (so important that they won the Nobel Prize for developing this concept)? ...
... c. Explain why Mutant A could only grow on arginine, whereas Mutant B can grow on either citruline or arginine. d. What was the key conclusion that Beadle and Tatum arrived at with these experiments (so important that they won the Nobel Prize for developing this concept)? ...
Translasyon
... • Work with nucleotide copolymers (poly (A,C), etc.), revealed some of the codes • But Marshall Nirenberg and Philip Leder cracked the entire code in 1964 • They showed that trinucleotides bound to ribosomes could direct the binding of specific aminoacyl-tRNAs • By using C-14 labelled amino acids wi ...
... • Work with nucleotide copolymers (poly (A,C), etc.), revealed some of the codes • But Marshall Nirenberg and Philip Leder cracked the entire code in 1964 • They showed that trinucleotides bound to ribosomes could direct the binding of specific aminoacyl-tRNAs • By using C-14 labelled amino acids wi ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... An anticodon on a tRNA has the sequence ...
... An anticodon on a tRNA has the sequence ...
Genes Expression or Genes and How They Work: Transcription
... ___________ before translation. • In prokaryotes, translation begins at the AUG codon preceded by a special nucleotide sequence. • Eukaryotic mRNA molecules have introns cut out and exons joined together before ____________. • Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes. ...
... ___________ before translation. • In prokaryotes, translation begins at the AUG codon preceded by a special nucleotide sequence. • Eukaryotic mRNA molecules have introns cut out and exons joined together before ____________. • Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes. ...
Pre – AP Biology
... bacteria. The bacteria will then be able to Transcribe and Translate off of this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange ...
... bacteria. The bacteria will then be able to Transcribe and Translate off of this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange ...
Teacher resource 1
... Compare the amino acid sequence with the original sequence. What has happened? How might this affect the protein made? Answer: ...
... Compare the amino acid sequence with the original sequence. What has happened? How might this affect the protein made? Answer: ...
Lab 9
... codons (triplets) are stop codons. The rest of the codons are amino acids. Several codons can code the same amino acid. Below is a table giving all the 64 possible triplets of the 4 bases and their corresponding codes (start, stop or one of the 20 amino acids). If we have a BSequence how do we know ...
... codons (triplets) are stop codons. The rest of the codons are amino acids. Several codons can code the same amino acid. Below is a table giving all the 64 possible triplets of the 4 bases and their corresponding codes (start, stop or one of the 20 amino acids). If we have a BSequence how do we know ...
Model Description Sheet
... pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to slice virus mRNA, protecting the cells from infection. In the miRNA pathway, Ago-2 utilizes naturally occurring miRNA to slice cellular mRNAs to control protein production. Ago-2 works by binding small (~22 nucleotide) regulatory RNAs (si ...
... pathway, small RNAs derived from viruses are used by Ago-2 to slice virus mRNA, protecting the cells from infection. In the miRNA pathway, Ago-2 utilizes naturally occurring miRNA to slice cellular mRNAs to control protein production. Ago-2 works by binding small (~22 nucleotide) regulatory RNAs (si ...
DNA and RNA Part 2 Protein Synthesis
... 6. As the process continues a chain of amino acids is formed until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA strand UAA, UAG, UGA ...
... 6. As the process continues a chain of amino acids is formed until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA strand UAA, UAG, UGA ...
DNA replication is molecular mechanism of
... 18. What happens to the RNA molecule that is made when a gene in the DNA (on a chromosome) is transcribed? ...
... 18. What happens to the RNA molecule that is made when a gene in the DNA (on a chromosome) is transcribed? ...
Ch. 17 Protein Synthesis
... Eukaryote—continues past termination signal, to a poly(A) tail (AAUAAA) in the pre-mRNA ...
... Eukaryote—continues past termination signal, to a poly(A) tail (AAUAAA) in the pre-mRNA ...
Problems in Replication and Protein Synthesis
... • Silent – although the wrong codon is produced but the correct amino acid is sill added (thus no change) • Wobble – more than one codon can code for the same amino acid. (makes silent mutations possible) ...
... • Silent – although the wrong codon is produced but the correct amino acid is sill added (thus no change) • Wobble – more than one codon can code for the same amino acid. (makes silent mutations possible) ...
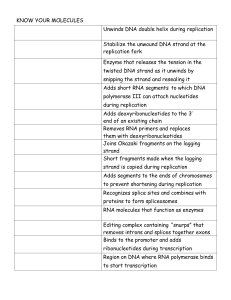
Know your molecules organizer
... Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA primers and replaces them with deoxyribonucleotides Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging ...
... Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA primers and replaces them with deoxyribonucleotides Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging ...
RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA) NOTES
... What would happen if nucleotides did not pair correctly? What would happen if a nucleotide got squeezed out? What would happen if an extra nucleotide got put in? These are all types of DNA, RNA, or protein sequence ______________________. Mutations are __________________ in the _____________________ ...
... What would happen if nucleotides did not pair correctly? What would happen if a nucleotide got squeezed out? What would happen if an extra nucleotide got put in? These are all types of DNA, RNA, or protein sequence ______________________. Mutations are __________________ in the _____________________ ...
Translation: Changing languages
... standard amino acids. What any structure was likely to have was a specific pattern of atomic groups that could form hydrogen bonds. I therefore proposed a theory in which there were twenty adaptors (one for each amino acid), together with twenty special enzymes. Each enzyme would join one particular ...
... standard amino acids. What any structure was likely to have was a specific pattern of atomic groups that could form hydrogen bonds. I therefore proposed a theory in which there were twenty adaptors (one for each amino acid), together with twenty special enzymes. Each enzyme would join one particular ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... ________ is copied down as a form of RNA called ___________. This process is called __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _________________ ...
... ________ is copied down as a form of RNA called ___________. This process is called __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _________________ ...
DNA is an abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid
... Cloning is one aspect of genetic engineering, the part that allows scientists to use a variety of methods to duplicate copies of already existing organisms or genetic material. But the term "genetic engineering" is much broader, encompassing a wide range of procedures designed to alter genetic mate ...
... Cloning is one aspect of genetic engineering, the part that allows scientists to use a variety of methods to duplicate copies of already existing organisms or genetic material. But the term "genetic engineering" is much broader, encompassing a wide range of procedures designed to alter genetic mate ...
bomb squad and movie mania 2012
... (_____________________________). Once the messenger is done he/she will slip out through a secret tunnel in the safe (_________________________) and into the ocean (_________________________). Once in the ocean (_________________) you will need to find the underwater bomb making factory (___________ ...
... (_____________________________). Once the messenger is done he/she will slip out through a secret tunnel in the safe (_________________________) and into the ocean (_________________________). Once in the ocean (_________________) you will need to find the underwater bomb making factory (___________ ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... DNA findes I celle kernen (Eukaryoter) base paring T substituted with U in RNA Reading direction Reading frame (1,2,3,-1,-2,-3) 64 codons DNA -> mRNA Intron, exon & UTR (non-coding exon) Intron/Exon splice site ...
... DNA findes I celle kernen (Eukaryoter) base paring T substituted with U in RNA Reading direction Reading frame (1,2,3,-1,-2,-3) 64 codons DNA -> mRNA Intron, exon & UTR (non-coding exon) Intron/Exon splice site ...
PROTEINS - Hyndland Secondary School
... Peptide bond • Amino acids joined by a peptide bond • Condensation reaction between – COOH of 1st amino acid and NH2 of 2nd amino acid •Chains are called peptides (short)/ polypeptides ...
... Peptide bond • Amino acids joined by a peptide bond • Condensation reaction between – COOH of 1st amino acid and NH2 of 2nd amino acid •Chains are called peptides (short)/ polypeptides ...
RNA - Mr. Dudley's Website
... DNA does not leave the Nucleus The DNA code needs to “written” in RNA form that can leave the nucleus Process is similar to DNA replication on the leading strand. ...
... DNA does not leave the Nucleus The DNA code needs to “written” in RNA form that can leave the nucleus Process is similar to DNA replication on the leading strand. ...
Sem2 CA Bio Standards
... c. how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. e. why approximately half of an individual's DNA sequence comes from each parent. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of a ...
... c. how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. e. why approximately half of an individual's DNA sequence comes from each parent. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of a ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.