GENE to PROTEIN
... 1. Misssense – still codes for an amino acid 2. Nonsense – does not code for an amino acid but changes to a code for STOP. This makes the chain too short and usually leads to nonfunctioning ...
... 1. Misssense – still codes for an amino acid 2. Nonsense – does not code for an amino acid but changes to a code for STOP. This makes the chain too short and usually leads to nonfunctioning ...
GENE to PROTEIN
... 1. Misssense – still codes for an amino acid 2. Nonsense – does not code for an amino acid but changes to a code for STOP. This makes the chain too short and usually leads to nonfunctioning ...
... 1. Misssense – still codes for an amino acid 2. Nonsense – does not code for an amino acid but changes to a code for STOP. This makes the chain too short and usually leads to nonfunctioning ...
Study Guide for Macromolecules
... What are the 4 types of macromolecule and their subunits Synthesis by dehydration and breakdown by hydrolysis Carbohydrates: How defined, basic structure, aldose vs. ketose, hexose, pentose, etc. How sugar rings are derived from linear molecules; sugar rings contain an O atom, and have a C that is n ...
... What are the 4 types of macromolecule and their subunits Synthesis by dehydration and breakdown by hydrolysis Carbohydrates: How defined, basic structure, aldose vs. ketose, hexose, pentose, etc. How sugar rings are derived from linear molecules; sugar rings contain an O atom, and have a C that is n ...
I. DNA A. WHAT IS IT?
... (AUG) • 2) ribosome “reads” the codon & identifies the anticodon. •(EX. codon AUG is with anticodon UAC) ...
... (AUG) • 2) ribosome “reads” the codon & identifies the anticodon. •(EX. codon AUG is with anticodon UAC) ...
The Dna code - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... DNA stores information to build proteins in sequences of nucleotides - DNA nucleotides contain one of 4 nitrogen bases A T C G - there are 20 different amino acids used to build protein ...
... DNA stores information to build proteins in sequences of nucleotides - DNA nucleotides contain one of 4 nitrogen bases A T C G - there are 20 different amino acids used to build protein ...
Dna sequence and Cell Activity
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
DNA Transcription / Translation
... What are the sections of mRNA that code for a protein called? ...
... What are the sections of mRNA that code for a protein called? ...
Fishy Genetics: From DNA to Protein: The Central Dogma of Biology
... for by the code. The molecule RNA is a key player in the process. RNA is a nucleic acid just like DNA but there are several differences. RNA has one strand, not two. Thymine (T) is replaced with Uracil (U) ...
... for by the code. The molecule RNA is a key player in the process. RNA is a nucleic acid just like DNA but there are several differences. RNA has one strand, not two. Thymine (T) is replaced with Uracil (U) ...
Name: :
... *This cladogram is organized using anatomical (body) features.* 5. Does the cladogram organized by genetic information agree with the cladogram organized by anatomical features? Why or why not? ...
... *This cladogram is organized using anatomical (body) features.* 5. Does the cladogram organized by genetic information agree with the cladogram organized by anatomical features? Why or why not? ...
From DNA to Protein
... • dipeptide on 2nd amino acid is connected to amino acid of 3nd tRNA by peptide bond ...
... • dipeptide on 2nd amino acid is connected to amino acid of 3nd tRNA by peptide bond ...
Protein Synthesis - Quakertown Community School District
... Building Blocks of Proteins • Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids • These subunits are comprised of : ...
... Building Blocks of Proteins • Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids • These subunits are comprised of : ...
protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... codon is read. At this point, the tRNA detaches and the protein chain of amino acids is left. The tRNA goes back into the cytoplasm to pick up more amino acid. Determine the tRNA (anticodon) for each codon below: 18. GGU : ...
... codon is read. At this point, the tRNA detaches and the protein chain of amino acids is left. The tRNA goes back into the cytoplasm to pick up more amino acid. Determine the tRNA (anticodon) for each codon below: 18. GGU : ...
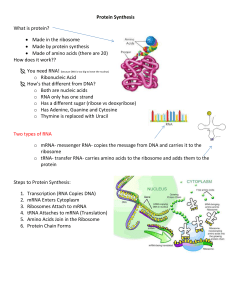
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
Homeostasis
... Identify phenotypes & genotypes in Punnett Square Identify phenotypes & genotypes in Pedigrees Genetic Mutations and how they arise Sex Linked Traits and Multiple Alleles Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Trisomy and Monosomy Karyotyping Determining Blood Types in Punnett Squares Structure of DNA ...
... Identify phenotypes & genotypes in Punnett Square Identify phenotypes & genotypes in Pedigrees Genetic Mutations and how they arise Sex Linked Traits and Multiple Alleles Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Trisomy and Monosomy Karyotyping Determining Blood Types in Punnett Squares Structure of DNA ...
Genetics Practice Questions C 1. Describe transcription
... ・Universality・・・・All known living things have the same genetic code. ...
... ・Universality・・・・All known living things have the same genetic code. ...
TALKING POINT The puzzling origin of the genetic
... adaptor was later identified as transfer RNA (tRNA) does not rule out a primordial origin based on the stereochemical hypothesis. ...
... adaptor was later identified as transfer RNA (tRNA) does not rule out a primordial origin based on the stereochemical hypothesis. ...
MBch15
... A high magnesium concentration circumvents the need for initiation factors and the special initiator tRNA, allowing chain elongation to occur without proper signals in the mRNA. Poly-U was the first synthetic polyribonucleotide discovered to have mRNA activity. CCC: proline AAA: lysine Poly-G forms ...
... A high magnesium concentration circumvents the need for initiation factors and the special initiator tRNA, allowing chain elongation to occur without proper signals in the mRNA. Poly-U was the first synthetic polyribonucleotide discovered to have mRNA activity. CCC: proline AAA: lysine Poly-G forms ...
Genetic Control ms
... (ii) many / several / more than one, triplet for each amino acid ; A codon an e.g. from Table 3.1 ; degenerate code / description e.g. 64 possible triplets for 20 amino acids ; A codons AVP ; e.g. may be an intron in this region, different nucleotides at the beginning (signal sequence) [2 max] (d) ( ...
... (ii) many / several / more than one, triplet for each amino acid ; A codon an e.g. from Table 3.1 ; degenerate code / description e.g. 64 possible triplets for 20 amino acids ; A codons AVP ; e.g. may be an intron in this region, different nucleotides at the beginning (signal sequence) [2 max] (d) ( ...
File - Thomas Tallis School
... acids fixes the way the protein folds into its three-dimensional shape. The shape gives the protein its chemical properties. DNA contains the genetic code which instructs the cell to join up the amino acids in the right order to make a particular protein. The genetic code is contained in the sequenc ...
... acids fixes the way the protein folds into its three-dimensional shape. The shape gives the protein its chemical properties. DNA contains the genetic code which instructs the cell to join up the amino acids in the right order to make a particular protein. The genetic code is contained in the sequenc ...
Human Genetic Variation - Mediapolis Community School
... • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
... • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
Macromolecules (Biomolecules)
... 3) What is the name given to small molecules that make up larger molecules? 4) Listed below are the names of the four major classes of macromolecules as well as their monomers. Match up the monomer(s) with their parent compound: lipids, amino acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates, glycerol, monosacchari ...
... 3) What is the name given to small molecules that make up larger molecules? 4) Listed below are the names of the four major classes of macromolecules as well as their monomers. Match up the monomer(s) with their parent compound: lipids, amino acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates, glycerol, monosacchari ...
Stages and mechanisms of translation, regulation of translat
... -Ribosomal subunits -mRNA template to be translated -Initiator tRNA molecule -Protein initiation factors ...
... -Ribosomal subunits -mRNA template to be translated -Initiator tRNA molecule -Protein initiation factors ...
Name:
... 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there, and what about them determines the nature of the protein being built? 6. If there ar ...
... 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there, and what about them determines the nature of the protein being built? 6. If there ar ...
Translation
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
... In order for a cell to make a protein, DNA must be transcribed into ____________ and the mRNA must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. T ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.