QUESTION - Assignment Expert
... QUESTION: How to calculate the molecular mass and length of a segment of B-DNA specifying a 40-kD protein? SOLUTION: Average molecular weight of amino acid = 105.2 dalton Assume that the 40 kDa protein is composed of 380 amino acids(40000 Da/105.2 Da = 380). 1 amino acid = 3 nucleotides Number of nu ...
... QUESTION: How to calculate the molecular mass and length of a segment of B-DNA specifying a 40-kD protein? SOLUTION: Average molecular weight of amino acid = 105.2 dalton Assume that the 40 kDa protein is composed of 380 amino acids(40000 Da/105.2 Da = 380). 1 amino acid = 3 nucleotides Number of nu ...
DNA and Proteins
... place at the ribosomes. • The process of converting the information in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in a protein. ...
... place at the ribosomes. • The process of converting the information in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in a protein. ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of a SNORK
... 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? ____________________ 4) What is the side that is NOT copied called? _______________________________ 5) What different nitrogen base had to be used to make mRNA? ____ ...
... 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? ____________________ 4) What is the side that is NOT copied called? _______________________________ 5) What different nitrogen base had to be used to make mRNA? ____ ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Is the production of proteins • Remember proteins are made up of polypeptides • Polypeptides are sequences of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds ...
... • Is the production of proteins • Remember proteins are made up of polypeptides • Polypeptides are sequences of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... Ribosomal RNA= ribosome that reads the mRNA Transfer RNA= transfers the amino acid from the code ...
... Ribosomal RNA= ribosome that reads the mRNA Transfer RNA= transfers the amino acid from the code ...
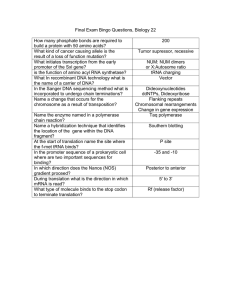
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
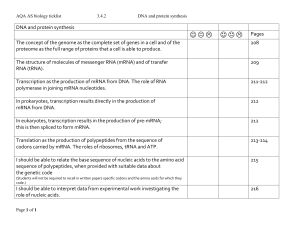
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Transcription as the production of mRNA from DNA. The role of RNA polymerase in joining mRNA nucleotides. ...
... Transcription as the production of mRNA from DNA. The role of RNA polymerase in joining mRNA nucleotides. ...
4TH 6 WEEKS EXAM REVIEW!
... The 3 bases on the tRNA are known as the _________ and are complimentary to mRNA’s __________ (3 bases) ...
... The 3 bases on the tRNA are known as the _________ and are complimentary to mRNA’s __________ (3 bases) ...
DNA and Proteins
... occur in sequences of 3 . For example, 3 U’s in a row codes as UUU and equals the amino acid Penylalanine. The letter code is called a Codon. With the letters available – U, A, G, and C; there are 64 possible combinations. There are only 20 amino acids that occur in nature. This means that some amin ...
... occur in sequences of 3 . For example, 3 U’s in a row codes as UUU and equals the amino acid Penylalanine. The letter code is called a Codon. With the letters available – U, A, G, and C; there are 64 possible combinations. There are only 20 amino acids that occur in nature. This means that some amin ...
bio12_sm_07_1
... 1. Beadle and Tatum found that they could cause mutations in cells limiting the cells’ ability to produce certain molecules, like arginine, essential to regular metabolism. The mutations could take place in any of the enzymes involved in the multistep process of arginine synthesis. 2. Beadle and Tat ...
... 1. Beadle and Tatum found that they could cause mutations in cells limiting the cells’ ability to produce certain molecules, like arginine, essential to regular metabolism. The mutations could take place in any of the enzymes involved in the multistep process of arginine synthesis. 2. Beadle and Tat ...
Lesson 4 Protein Synthesis.notebook
... which can be assembled in an unlimited number of ways to form proteins • codon is a 3 base code for amino acids each triplet represents a different amino acids -- ex GCA or CCG Alanine ...
... which can be assembled in an unlimited number of ways to form proteins • codon is a 3 base code for amino acids each triplet represents a different amino acids -- ex GCA or CCG Alanine ...
Document
... The aminoacyl-tRNA structure • Each tRNA specific for one amino acid and for a codon in mRNA • The amino acid is attached to the appropriate tRNA by an enzyme aminoacyltRNA synthetase specific for that amino acid as well as for the tRNA assigned to it. ...
... The aminoacyl-tRNA structure • Each tRNA specific for one amino acid and for a codon in mRNA • The amino acid is attached to the appropriate tRNA by an enzyme aminoacyltRNA synthetase specific for that amino acid as well as for the tRNA assigned to it. ...
Non-natural amino acid
... proteins by engineering novel aaRS/tRNA pairs The aaRS/tRNA pair needs to be “orthogonal” to the existing sets of aaRS/tRNA to ensure nonnatural amino acids are introduced selectively at ...
... proteins by engineering novel aaRS/tRNA pairs The aaRS/tRNA pair needs to be “orthogonal” to the existing sets of aaRS/tRNA to ensure nonnatural amino acids are introduced selectively at ...
Document
... RNA has catalytic role (snRNA) in Eukaryotic Cells and in protozoan (p. 336) Why can RNA act as an enzyme (Ribozyme)? Alternative RNA splicing --- One exon codes for one domain of a protein (p. 336) Introns allow for more crossing over without disrupting domain coding = new proteins sequences. ...
... RNA has catalytic role (snRNA) in Eukaryotic Cells and in protozoan (p. 336) Why can RNA act as an enzyme (Ribozyme)? Alternative RNA splicing --- One exon codes for one domain of a protein (p. 336) Introns allow for more crossing over without disrupting domain coding = new proteins sequences. ...
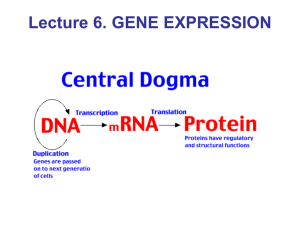
Remember, transcription copies the DNA into mRNA
... This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). ...
... This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). ...
1. Suppose the nucleotide composition of a DNA virus was found to
... In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, many ribosomes translate simultaneously from the same mRNA, allowing protein to be made more quickly from the same mRNA molecule. On the diagram below, label the following: a. 5’ and 3’ ends b. the stop codon c. N-terminus of the protein(s) d. The first ribosome ( ...
... In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, many ribosomes translate simultaneously from the same mRNA, allowing protein to be made more quickly from the same mRNA molecule. On the diagram below, label the following: a. 5’ and 3’ ends b. the stop codon c. N-terminus of the protein(s) d. The first ribosome ( ...
Translation
... Translation ● Converts mRNA from transcription into protein (polypeptide) ● Codon- a sequence of 3 RNA nucleotides that code for an amino acid ○ there are 20 amino acids in our body ○ amino acid- monomer of protein ...
... Translation ● Converts mRNA from transcription into protein (polypeptide) ● Codon- a sequence of 3 RNA nucleotides that code for an amino acid ○ there are 20 amino acids in our body ○ amino acid- monomer of protein ...
Lecture 8 LC710- 1st + 2nd hr
... * Step 1 - De-blocking (detritylation): The DMT group is removed with a solution of an acid, such as TCA or Dichloroacetic acid (DCA), in an inert solvent (dichloromethane or toluene) and washed out, resulting in a free 5' hydroxyl group on the first base. * Step 2 - Coupli ng: A nucleoside phosphor ...
... * Step 1 - De-blocking (detritylation): The DMT group is removed with a solution of an acid, such as TCA or Dichloroacetic acid (DCA), in an inert solvent (dichloromethane or toluene) and washed out, resulting in a free 5' hydroxyl group on the first base. * Step 2 - Coupli ng: A nucleoside phosphor ...
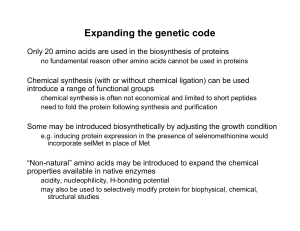
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.