Hemoglobin, or haemoglobin, is an iron
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is an iron-containing protein in the red blood cells of mammals and other vertebrates. Hb is released under certain pathological conditions, such as malarial infection and allergic drug reaction. This free Hb is toxic and causes damage to blood vessels and surrounding tissues. Haptog ...
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is an iron-containing protein in the red blood cells of mammals and other vertebrates. Hb is released under certain pathological conditions, such as malarial infection and allergic drug reaction. This free Hb is toxic and causes damage to blood vessels and surrounding tissues. Haptog ...
Protein Synthesis: Like a Banana Split
... 3. Examine the mRNA sequences for each amino acid recorded in Data Table 2. What pattern do you see?_______________________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. Examine the mRNA sequences for each amino acid recorded in Data Table 2. What pattern do you see?_______________________________________________________________________ ...
Genes and How they work!
... • Crick 1961 – elucidated the genetic code • Logic used - How many bases (nucleotides) are needed to code for 20 amino acids? • One base can code for 4 amino acids (41) • Two bases can code for 16 amino acids (42) • Three bases can code for 64 amino acids (43) • Therefore a sequence of three bases i ...
... • Crick 1961 – elucidated the genetic code • Logic used - How many bases (nucleotides) are needed to code for 20 amino acids? • One base can code for 4 amino acids (41) • Two bases can code for 16 amino acids (42) • Three bases can code for 64 amino acids (43) • Therefore a sequence of three bases i ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... • DNA provides workers with the instructions for making the proteins and the workers build the proteins • Other workers bring parts, the amino acids, over to the assembly line • The workers for protein synthesis are RNA molecules, which take the instructions from DNA and assemble the protein amino ...
... • DNA provides workers with the instructions for making the proteins and the workers build the proteins • Other workers bring parts, the amino acids, over to the assembly line • The workers for protein synthesis are RNA molecules, which take the instructions from DNA and assemble the protein amino ...
Operons - Haiku Learning
... Use the amino acid chart from question #3 …glycine…serine…glycine… 4. Which of the following DNA strands would code for the amino acid sequence shown above? ...
... Use the amino acid chart from question #3 …glycine…serine…glycine… 4. Which of the following DNA strands would code for the amino acid sequence shown above? ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... Translation- cellular process that converts the mRNA codons into amino acids to build proteins. First let’s practice reading the mRNA into amino acids and then I will outline the process of how it’s done step by step. Look at the sequence of mRNA below and the chart in Fig. ___ on page _____. ...
... Translation- cellular process that converts the mRNA codons into amino acids to build proteins. First let’s practice reading the mRNA into amino acids and then I will outline the process of how it’s done step by step. Look at the sequence of mRNA below and the chart in Fig. ___ on page _____. ...
Topic 7 The Discovery of DNA & Its Roles
... A substitution of one nucleotide pair for another produces silent, missense, or nonsense mutations An indel (insertion or deletion of a base pair) produces a ...
... A substitution of one nucleotide pair for another produces silent, missense, or nonsense mutations An indel (insertion or deletion of a base pair) produces a ...
How DNA Determines Traits - Liberty Union High School District
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyze ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyze ...
n-formyl methionine
... Formylmethionine (fMet) is an amino acid found in all living cells. It is a derivative of the amino acid methionine. It is a modified form of methionine in which a formyl group has been added to methionine's amino group. It plays a crucial part in the protein synthesis of bacteria, mitochondria and ...
... Formylmethionine (fMet) is an amino acid found in all living cells. It is a derivative of the amino acid methionine. It is a modified form of methionine in which a formyl group has been added to methionine's amino group. It plays a crucial part in the protein synthesis of bacteria, mitochondria and ...
BIO 103 - Genes
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
Cloze passage 4
... Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 scientist who put ...
... Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 scientist who put ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... 2. What is the basic building block of a protein? _______________________ 3. How many amino acids exist in humans? _______________________ 4. Name one amino acid. _______________________ 5. What type of bond holds amino acids together?_______________________ 6. How many nucleotides code for each ami ...
... 2. What is the basic building block of a protein? _______________________ 3. How many amino acids exist in humans? _______________________ 4. Name one amino acid. _______________________ 5. What type of bond holds amino acids together?_______________________ 6. How many nucleotides code for each ami ...
Ch. 15 Genetic Code and Translation & Protein Structure
... We will focus our discussion of translation as a “Nonoverlapping Code” ...
... We will focus our discussion of translation as a “Nonoverlapping Code” ...
Translation - Genes to proteins
... phenotypes but that 3-base insertions or deletions were almost always wildtype. Translation, or protein synthesis, is directed in eukaryotic cells by an mRNA molecule. Translation can be seen to occur in two phases: (1) information transfer, in which RNA base sequence of the mRNA determines the sequ ...
... phenotypes but that 3-base insertions or deletions were almost always wildtype. Translation, or protein synthesis, is directed in eukaryotic cells by an mRNA molecule. Translation can be seen to occur in two phases: (1) information transfer, in which RNA base sequence of the mRNA determines the sequ ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
... helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
Chapter 17 Power Point
... genome than what was expected • The human genome contains about 21,000 protein-encoding genes, but the total number of proteins in human cells is estimated to be between 250,000 to one million. ...
... genome than what was expected • The human genome contains about 21,000 protein-encoding genes, but the total number of proteins in human cells is estimated to be between 250,000 to one million. ...
Translation
... mRNA is transported "om the nucleus cytoplasm where it attached with the ribosomes which are the site of protein synthesis. ...
... mRNA is transported "om the nucleus cytoplasm where it attached with the ribosomes which are the site of protein synthesis. ...
13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons ...
... The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons ...
...the story of making proteins continued… After transcription occurs
... then joined together this is called a ________________________________. Both tRNA’s shift down a seat and the next tRNA comes into the ribosome with it’s matching anticodon and amino acid. This third amino acid gets bonded to the other two a chain is starting to form! This keeps continuing unti ...
... then joined together this is called a ________________________________. Both tRNA’s shift down a seat and the next tRNA comes into the ribosome with it’s matching anticodon and amino acid. This third amino acid gets bonded to the other two a chain is starting to form! This keeps continuing unti ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... Chapter 3 Section 4 THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that spec ...
... Chapter 3 Section 4 THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that spec ...
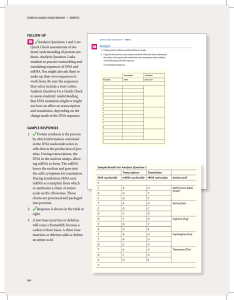
✓ 10 FOLLOW-UP
... by which information contained in the DNA nucleotide series in cells directs the production of proteins. During transcription, the DNA in the nucleus unzips, allowing mRNA to form. The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cell’s cytoplasm for translation. During translation, tRNA uses mRNA as a ...
... by which information contained in the DNA nucleotide series in cells directs the production of proteins. During transcription, the DNA in the nucleus unzips, allowing mRNA to form. The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cell’s cytoplasm for translation. During translation, tRNA uses mRNA as a ...
The Central Dogma of Genetics
... are added to the mRNA chain using anticoding DNA as template. –New RNA nucleotides are added to 3’ end (like DNA) ...
... are added to the mRNA chain using anticoding DNA as template. –New RNA nucleotides are added to 3’ end (like DNA) ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.