From Genetic Code to Protein Structure Worksheet
... In this activity you will explore the relationship between the codons and the shape of the protein. It is important to think about what this model shows, as well as what of the translation and transcription process it is not representing when answering the questions. 1. Open the From Genetic Code to ...
... In this activity you will explore the relationship between the codons and the shape of the protein. It is important to think about what this model shows, as well as what of the translation and transcription process it is not representing when answering the questions. 1. Open the From Genetic Code to ...
review sheet
... 2. Briefly describe the process of replication. Where in the cell does replication occur? When in the cell cycle does replication occur? ...
... 2. Briefly describe the process of replication. Where in the cell does replication occur? When in the cell cycle does replication occur? ...
A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered
... Researchers are attempting to reproduce the conditions and events that resulted in this defective amino acid sequence. Which statement is the best prediction of the conditions and events that the researchers will most likely find produced the defective polypeptide? ...
... Researchers are attempting to reproduce the conditions and events that resulted in this defective amino acid sequence. Which statement is the best prediction of the conditions and events that the researchers will most likely find produced the defective polypeptide? ...
DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
... 32. Can you change the order, add, or take an amino acid out and NOT change the protein? 33. What is the mRNA start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 34. What are the 3 mRNA stop codons and what amino acids do they code for? 35. What process makes DNA? 36. What 3 processes in order make pr ...
... 32. Can you change the order, add, or take an amino acid out and NOT change the protein? 33. What is the mRNA start codon and what amino acid does it code for? 34. What are the 3 mRNA stop codons and what amino acids do they code for? 35. What process makes DNA? 36. What 3 processes in order make pr ...
Kent Noreen G. Modanza III-Galileo GENETIC CODE The genetic
... (DNA ormRNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. The code defines how sequences of three nucleotides, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions,[1] a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid seq ...
... (DNA ormRNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. The code defines how sequences of three nucleotides, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions,[1] a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid seq ...
Print Version
... "anticodons"; they form base pairs with the code words (codons) in the mRNA his ...
... "anticodons"; they form base pairs with the code words (codons) in the mRNA his ...
Teacher Instructions Lesson 4
... should make these tools as part of the Teacher Preparation instructions in Lesson 1. Another option would be to have more advanced students create these tools as part of an extension or enrichment activity. The instructions for these stamps are explained in detail in Lesson 1. All 20 amino acids cou ...
... should make these tools as part of the Teacher Preparation instructions in Lesson 1. Another option would be to have more advanced students create these tools as part of an extension or enrichment activity. The instructions for these stamps are explained in detail in Lesson 1. All 20 amino acids cou ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... Proteins are the link between: Why are some people lactose intolerant or turn red when they drink? Protein Synthesis: (p. 192; Fig. 10.6A & p. 194; Fig. 10.8B) Two phases in making proteins (Prokaryotic cells): 1) Transcription: 2) Translation: Three phases in making proteins (Eukaryotic cells): 1) ...
... Proteins are the link between: Why are some people lactose intolerant or turn red when they drink? Protein Synthesis: (p. 192; Fig. 10.6A & p. 194; Fig. 10.8B) Two phases in making proteins (Prokaryotic cells): 1) Transcription: 2) Translation: Three phases in making proteins (Eukaryotic cells): 1) ...
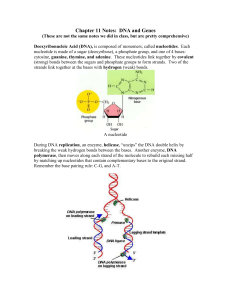
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the pro ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the pro ...
Ketogenic amino acids
... examples: Only the 20 proteinogenic amino acids are included in the genetic code and therefore regularly found in proteins. The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. DNA serves as the ...
... examples: Only the 20 proteinogenic amino acids are included in the genetic code and therefore regularly found in proteins. The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. DNA serves as the ...
the code of translation
... • An Anticodon is the complimentary group of three nucleotides on a tRNA • When the codon is recognized by the complimentary anticodon on the tRNA the correct amino acid corresponding to that codon is made available. ...
... • An Anticodon is the complimentary group of three nucleotides on a tRNA • When the codon is recognized by the complimentary anticodon on the tRNA the correct amino acid corresponding to that codon is made available. ...
Mutations
... Note that inserting or deleting 3 bases in the DNA wouldn’t shift the reading frame, it just adds or removes an amino acid. ...
... Note that inserting or deleting 3 bases in the DNA wouldn’t shift the reading frame, it just adds or removes an amino acid. ...
Protein Synthesis part 2
... end and an open bond on the 3’ end… so this is where the amino acid gets attached so that it can be transported to the ribosome (construction site). 6. This connection between the tRNA molecule and the amino acid is constructed using the Aminoacyl – tRNA synthetase enzyme. (Can you see the definitio ...
... end and an open bond on the 3’ end… so this is where the amino acid gets attached so that it can be transported to the ribosome (construction site). 6. This connection between the tRNA molecule and the amino acid is constructed using the Aminoacyl – tRNA synthetase enzyme. (Can you see the definitio ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1
... 2. *Formation of RNA (pg. 251) a. cell activates b. enzyme attaches and unzips DNA c. RNA copies DNA – forms single chain d. RNA breaks away; DNA rejoins *remember U takes the place of T 3. Types of RNA a. mRNA – codes for polypeptides/proteins b. rRNA – makes up ribosomes ...
... 2. *Formation of RNA (pg. 251) a. cell activates b. enzyme attaches and unzips DNA c. RNA copies DNA – forms single chain d. RNA breaks away; DNA rejoins *remember U takes the place of T 3. Types of RNA a. mRNA – codes for polypeptides/proteins b. rRNA – makes up ribosomes ...
II - Humble ISD
... The function of tRNA is to transfer the _____________________ specified by the __________________ to the ____________________ for protein synthesis. The _______________ of the cell is stocked with all 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis. The tRNA molecule carries an ________________ at one ...
... The function of tRNA is to transfer the _____________________ specified by the __________________ to the ____________________ for protein synthesis. The _______________ of the cell is stocked with all 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis. The tRNA molecule carries an ________________ at one ...
gene expression - Aurora City Schools
... Translation 1. ribosome attaches to mRNA 2. tRNA with amino acid matches mRNA codon (area on tRNA that matches called an anticodon). This process is called initiation. 2 tRNAs can fit at one time. 3. ribosome moves down and matches next codon. 4. Amino acids form peptide bond and protein continues ...
... Translation 1. ribosome attaches to mRNA 2. tRNA with amino acid matches mRNA codon (area on tRNA that matches called an anticodon). This process is called initiation. 2 tRNAs can fit at one time. 3. ribosome moves down and matches next codon. 4. Amino acids form peptide bond and protein continues ...
Answers
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
DNA to Eye Color? Just How does it Happen?
... proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
... proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
Lecture4 Biol302 Spring2012
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
Chapter 12 Translation and the Genetic Code
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations - Mrs. Gracie Gonzalez Biology Class
... (messenger) in the nucleus with the help of RNA polymerase. 2. When transcribing from DNA to RNA, Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. Only one side of the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome in the cytoplasm Translation: (translating for an amin ...
... (messenger) in the nucleus with the help of RNA polymerase. 2. When transcribing from DNA to RNA, Thymine is replaced by Uracil. 3. Only one side of the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome in the cytoplasm Translation: (translating for an amin ...
Transcription, Translation, and Protein Synthesis
... template cards. This person will write down the number of the card and transcribe the code into mRNA. The DNA card can not leave the nucleus. 3. The RNA polymerase will then travel through the cytoplasm (the classroom) to the group table and give the mRNA to the ribosome. 4. The ribosome will ...
... template cards. This person will write down the number of the card and transcribe the code into mRNA. The DNA card can not leave the nucleus. 3. The RNA polymerase will then travel through the cytoplasm (the classroom) to the group table and give the mRNA to the ribosome. 4. The ribosome will ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.