Lecture16 Biol302 Spring 2011
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 14. Proteins are made in the (nucleus / cytoplasm). 15. (tRNA / mRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus / cytoplasm). 17. (Translation / Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm / nucleus). 19. (one / three) codon ...
... 14. Proteins are made in the (nucleus / cytoplasm). 15. (tRNA / mRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus / cytoplasm). 17. (Translation / Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm / nucleus). 19. (one / three) codon ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Port Washington School District
... There are 64 ways you can combine the four Nitrogenous bases in sets of 3 – AAA, GCC, ATA, ATC, GTA etc. – Sometimes more than one codon can code for the same amino acid • Ex: AAA and AAG both code for phenylalanine ...
... There are 64 ways you can combine the four Nitrogenous bases in sets of 3 – AAA, GCC, ATA, ATC, GTA etc. – Sometimes more than one codon can code for the same amino acid • Ex: AAA and AAG both code for phenylalanine ...
Translation PPT
... While RNA is single-stranded, it does not “combine” to make double-stranded DNA.DNA and RNA are two entirely different molecules. RNA contains ribose sugar while DNA contains deoxyribose, and RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). ...
... While RNA is single-stranded, it does not “combine” to make double-stranded DNA.DNA and RNA are two entirely different molecules. RNA contains ribose sugar while DNA contains deoxyribose, and RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). ...
Chapter 3- DNA, Proteins and Proteomes
... shape determined by the number and sequence of amino acids. (Critical for its function e.g. enzymes) QUATERNARY STRUCTURE- four polypeptide chains combining ...
... shape determined by the number and sequence of amino acids. (Critical for its function e.g. enzymes) QUATERNARY STRUCTURE- four polypeptide chains combining ...
The genetic code is a degenerate, non-overlapping set of
... There are 21 genetically-encoded amino acids universally found in the species from all three domains of life. ( There is a 22nd genetically-encooded amino acid, Pyl, but so far it has only been found in a handful of Archaea and Bacteria species.) Yet there are only four different nucleotides in DNA ...
... There are 21 genetically-encoded amino acids universally found in the species from all three domains of life. ( There is a 22nd genetically-encooded amino acid, Pyl, but so far it has only been found in a handful of Archaea and Bacteria species.) Yet there are only four different nucleotides in DNA ...
Translation - Fog.ccsf.edu
... free amino group of incoming amino acid Proteins are synthesized from its Nterminus to its C-terminus ...
... free amino group of incoming amino acid Proteins are synthesized from its Nterminus to its C-terminus ...
RNA Ribonucleic Acid - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... the code from the nucleus into the cytoplasm then to the ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Part of the ribosome, links up proteins ...
... the code from the nucleus into the cytoplasm then to the ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Part of the ribosome, links up proteins ...
Aminoacids_followup
... Amino acids with hydroxyl group In biology hydroxyl groups –OH are important as they can be modified by different molecules as phosphate (-PO4) or a long range of ...
... Amino acids with hydroxyl group In biology hydroxyl groups –OH are important as they can be modified by different molecules as phosphate (-PO4) or a long range of ...
Chapter 12.3 and 12.4 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Role of RNA
... D. Since there are only 4 letters (AUCG) 1. If each letter made an amino acid – we would have 41 = 4 amino acids 2. If two letters made an amino acid – we would have 42 = 16 amino acids 3. If three letters made an amino acid – we would have 43 = 64 amino acids a. 64 combos are more than enough to co ...
... D. Since there are only 4 letters (AUCG) 1. If each letter made an amino acid – we would have 41 = 4 amino acids 2. If two letters made an amino acid – we would have 42 = 16 amino acids 3. If three letters made an amino acid – we would have 43 = 64 amino acids a. 64 combos are more than enough to co ...
Organic Notes.graffle
... What are proteins? Proteins are macromolecules (polymers) that are made by adding amino acids (monomers) together. There can be thousands of different proteins found in a single cell. If the 20 different amino acids are put together in various combinations there can be endless numbers of proteins. ...
... What are proteins? Proteins are macromolecules (polymers) that are made by adding amino acids (monomers) together. There can be thousands of different proteins found in a single cell. If the 20 different amino acids are put together in various combinations there can be endless numbers of proteins. ...
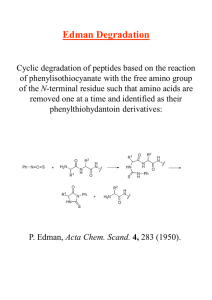
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
organic compounds outline
... ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copyin ...
... ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copyin ...
bio_ch08-5_transcript redo
... You might consider it to be odd to describe the genetic as a punctuation of stop and start codes. The Latin word puctum means “point” and is derived form an older form meaning “to pierce or puncture.” Punctuation, in a general sense, signifies an interruption. The word punctuate can also be used to ...
... You might consider it to be odd to describe the genetic as a punctuation of stop and start codes. The Latin word puctum means “point” and is derived form an older form meaning “to pierce or puncture.” Punctuation, in a general sense, signifies an interruption. The word punctuate can also be used to ...
RNA
... transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
... transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
The Genetic Code The nucleotide bases of the DNA strand
... Once the tRNA has found it’s position along the mRNA it locks into a distinct place. The tRNA also carries – as a specific correlation to its nucleotide sequence - one distinct amino acid. A tRNA is therefore distinct for its three nucleotides at one end, and its proper amino acid at the other end o ...
... Once the tRNA has found it’s position along the mRNA it locks into a distinct place. The tRNA also carries – as a specific correlation to its nucleotide sequence - one distinct amino acid. A tRNA is therefore distinct for its three nucleotides at one end, and its proper amino acid at the other end o ...
anth-260-midterm-review-sheet
... • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
... • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
Chemical Compounds in Cells and in Our Food
... • Contain C, H, O, N and sometimes Sulfur • Found in many foods • In the cell, used as: -part of cell membranes -structures of organelles -muscles in the body ...
... • Contain C, H, O, N and sometimes Sulfur • Found in many foods • In the cell, used as: -part of cell membranes -structures of organelles -muscles in the body ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
The Chemistry of Molecular Biology
... The Basics of Amino Acids • 20 amino acids • All amino acids in nature are L form • Structure consists of Ca, to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a • Amino acids are classed variable group according to their R group ...
... The Basics of Amino Acids • 20 amino acids • All amino acids in nature are L form • Structure consists of Ca, to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a • Amino acids are classed variable group according to their R group ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation
... transcription produces RNA and translation produces polypeptides/protein; RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosomes for translation / ribosomes in translation ...
... transcription produces RNA and translation produces polypeptides/protein; RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosomes for translation / ribosomes in translation ...
doc
... Double helix — term used to describe the structure of DNA; two strands that are coiled Gamete — specialized reproductive cell involved in sexual reproduction. They have one half the total number of chromosomes as the organism’s normal body cells. Gene — section of DNA that codes for a trait Gene The ...
... Double helix — term used to describe the structure of DNA; two strands that are coiled Gamete — specialized reproductive cell involved in sexual reproduction. They have one half the total number of chromosomes as the organism’s normal body cells. Gene — section of DNA that codes for a trait Gene The ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.