Lecture 5
... - Polypeptide Chain: series of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (think of box cars linked together) - Protein: one or more polypeptide chains joined and folded in a 3D configuration (folds occur due to electrical charges of amino acids) - Codon: 3 letter nucleotide sequence in messenger RNA that ...
... - Polypeptide Chain: series of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (think of box cars linked together) - Protein: one or more polypeptide chains joined and folded in a 3D configuration (folds occur due to electrical charges of amino acids) - Codon: 3 letter nucleotide sequence in messenger RNA that ...
Chapter 16 Quiz - Home - Union Academy Charter School
... b. DNA serves as a template for RNA production c. tRNA bonds to a specific codon d. Amino acids are bonded together e. RNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm The correct order of these events is a. BEACD b. DAECB c. BCEDA d. CBAED ...
... b. DNA serves as a template for RNA production c. tRNA bonds to a specific codon d. Amino acids are bonded together e. RNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm The correct order of these events is a. BEACD b. DAECB c. BCEDA d. CBAED ...
Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids
... except they always differ in their effect on polarized light and how they react with other chiral molecules. ...
... except they always differ in their effect on polarized light and how they react with other chiral molecules. ...
Cells Use DNA and RNA to Make Proteins
... DNA and the Genetic Code 1. nucleotides: A, T, C, G 2. Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine 3. A pairs with T; C pairs with G 4. every three bases codes for one amino acid – called a DNA triplet 5. ex: GAC codes for aspartic acid 6. ex: CAG codes for glutamine ...
... DNA and the Genetic Code 1. nucleotides: A, T, C, G 2. Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine 3. A pairs with T; C pairs with G 4. every three bases codes for one amino acid – called a DNA triplet 5. ex: GAC codes for aspartic acid 6. ex: CAG codes for glutamine ...
MolBioIntro
... proteins – tRNA acts in translation of biological macromolecules from the language of nucleic acids to amino acids ...
... proteins – tRNA acts in translation of biological macromolecules from the language of nucleic acids to amino acids ...
SBI4U Translation
... – At the wobble position, U on the anticodon can bind with A or G in the third position of a codon ...
... – At the wobble position, U on the anticodon can bind with A or G in the third position of a codon ...
No Slide Title
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
DNA to Protein - Seabreeze High School
... Things to think About & Discuss 1. What if a mutation occurs in the DNA? Explain how could that affect the organism’s protein? 2. What if a mutation occurs in 3rd base of the codon? Will it always code for a different amino acid? Explain. ...
... Things to think About & Discuss 1. What if a mutation occurs in the DNA? Explain how could that affect the organism’s protein? 2. What if a mutation occurs in 3rd base of the codon? Will it always code for a different amino acid? Explain. ...
Transcription/Translation Notes Handout
... The transcription process is similar to replication. -Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary _________________. *Both processes take place in the nucleus -The two processes have different end results. * Replication copies all the ________________; transcription ...
... The transcription process is similar to replication. -Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary _________________. *Both processes take place in the nucleus -The two processes have different end results. * Replication copies all the ________________; transcription ...
2. If 20% of the DNA in a guinea pig cell is adenine, what
... amino acids. If you were doing these experiments, what sequences would you try next? Explain your logic. There are many possible ways to answer this question. One possibility follows: Continue as above and make the remaining three types of mRNA made up of only one type of nucleotide—that is, poly G, ...
... amino acids. If you were doing these experiments, what sequences would you try next? Explain your logic. There are many possible ways to answer this question. One possibility follows: Continue as above and make the remaining three types of mRNA made up of only one type of nucleotide—that is, poly G, ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism
... Suppose you analyze a Snork’s chromosome and you determine that it has the DNA sequence below. Each gene is separated by the vertical lines – since each gene has ___ bases, each gene codes for ___ amino acids. Your job is to determine the sequence of amino acids that this DNA codes for. In the chart ...
... Suppose you analyze a Snork’s chromosome and you determine that it has the DNA sequence below. Each gene is separated by the vertical lines – since each gene has ___ bases, each gene codes for ___ amino acids. Your job is to determine the sequence of amino acids that this DNA codes for. In the chart ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... code is redundant - more than one triplet can code for the same amino acid ...
... code is redundant - more than one triplet can code for the same amino acid ...
DNA and Protein Synthesisx
... Use the genetic code shown in your textbook to determine which amino acids are specified by the following m-RNA codons. ...
... Use the genetic code shown in your textbook to determine which amino acids are specified by the following m-RNA codons. ...
Biology Chapter 6 Section 4 Test-The Building Blocks of Life
... 16. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are ___________________________. 17. _____________________ are made from amino acids that are joined by _____________ bonds. 18. DNA and RNA are examples of ____________________ __________________. 19. Glycogen, starch, cellulose and chitin are a ...
... 16. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are ___________________________. 17. _____________________ are made from amino acids that are joined by _____________ bonds. 18. DNA and RNA are examples of ____________________ __________________. 19. Glycogen, starch, cellulose and chitin are a ...
University of North Carolina researchers provide evidence for how
... there was a second, earlier code that made possible the peptide-RNA interactions necessary to launch a selection process that we can envision creating the first life on Earth.” Thus, Carter said, RNA did not have to invent itself from the primordial soup. Instead, even before there were cells, it se ...
... there was a second, earlier code that made possible the peptide-RNA interactions necessary to launch a selection process that we can envision creating the first life on Earth.” Thus, Carter said, RNA did not have to invent itself from the primordial soup. Instead, even before there were cells, it se ...
notes Protein_Synthe.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... It reads the codon (AKA triplet) which is a set of 3 nitrogenous bases that codes for a particular amino acid. What is translation? - creation of a polypeptide by a ribosome using the code from mRNA and individual amino acids from tRNA How does translation occur? - mRNA aligns with a ribosome - 2 co ...
... It reads the codon (AKA triplet) which is a set of 3 nitrogenous bases that codes for a particular amino acid. What is translation? - creation of a polypeptide by a ribosome using the code from mRNA and individual amino acids from tRNA How does translation occur? - mRNA aligns with a ribosome - 2 co ...
Recitation 8 Solutions
... mutant form of the gene that produces a protein that is now 381 amino acids long. Indicate the identity of one new base pair that could take its place. You should change the stop codon immediately after the codon for 380th amino acid to get a protein that is 381 amino acids long. Please note that th ...
... mutant form of the gene that produces a protein that is now 381 amino acids long. Indicate the identity of one new base pair that could take its place. You should change the stop codon immediately after the codon for 380th amino acid to get a protein that is 381 amino acids long. Please note that th ...
Protein Synthesis PowerPoint
... rRNA puts the amino acids together to build the amino acid chain = PROTEIN ...
... rRNA puts the amino acids together to build the amino acid chain = PROTEIN ...
Sem2 Final Practice Test
... carries amino acid to ribosome moves out of the nucleus attaches to its anticodon attaches to its amino acid attaches to its codon ...
... carries amino acid to ribosome moves out of the nucleus attaches to its anticodon attaches to its amino acid attaches to its codon ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... http://library.thinkquest.org/20465/g_DNATranscription.html ...
... http://library.thinkquest.org/20465/g_DNATranscription.html ...
Chapter 15
... protein synthesis to occur. This is accomplished by activating enzymes called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. There is one enzyme for each of the 20 amino acids. • tRNA molecules are bifunctional; they need to interact with amino acids and mRNA molecules. • There is an acceptor stem, where amino acid bi ...
... protein synthesis to occur. This is accomplished by activating enzymes called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. There is one enzyme for each of the 20 amino acids. • tRNA molecules are bifunctional; they need to interact with amino acids and mRNA molecules. • There is an acceptor stem, where amino acid bi ...
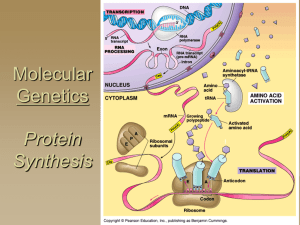
Molecular Genetics
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.