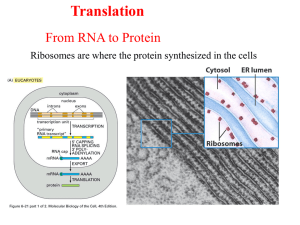
Making Proteins
... nucleotide bases to DNA, using one side as a template. 3. The mRNA strand is created. It now compliments the original DNA strand (G-C and A-U). 4. Ligase helps the strand of DNA to close and again. 5. mRNA strand moves out of nucleus to ribosomes, and the DNA zips up. ...
... nucleotide bases to DNA, using one side as a template. 3. The mRNA strand is created. It now compliments the original DNA strand (G-C and A-U). 4. Ligase helps the strand of DNA to close and again. 5. mRNA strand moves out of nucleus to ribosomes, and the DNA zips up. ...
File
... What protein are you synthesizing in this step? ________________________ Record the nucleotide sequence in the DNA molecule used in this step. ...
... What protein are you synthesizing in this step? ________________________ Record the nucleotide sequence in the DNA molecule used in this step. ...
RNA polymerase
... • Recall that in humans there are 20 amino acids (the basic units of proteins). However, there are only 4 different nucleotides. Therefore, if it only took 1 nucleotide to code for 1 amino acid only 4 amino acids could be produced. If 2 nucleotides in a row coded for 1 amino acid, you still could no ...
... • Recall that in humans there are 20 amino acids (the basic units of proteins). However, there are only 4 different nucleotides. Therefore, if it only took 1 nucleotide to code for 1 amino acid only 4 amino acids could be produced. If 2 nucleotides in a row coded for 1 amino acid, you still could no ...
Wade Chapter Twenty-Four Outline: Amino Acids and Peptides
... o Remove N-protection w CF3COOH (release CO2 and isobutylene) o Couple to second aa with DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) o Rinse solid support to remove by-products like CH2=CMe2 o Add second N-protected amino acid via C-terminus ...
... o Remove N-protection w CF3COOH (release CO2 and isobutylene) o Couple to second aa with DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) o Rinse solid support to remove by-products like CH2=CMe2 o Add second N-protected amino acid via C-terminus ...
How Proteins are Made - MDC Faculty Web Pages
... starting. – The genetic code is universal (same for bacteria and humans) and is good evidence for a common inheritance (evolution). ...
... starting. – The genetic code is universal (same for bacteria and humans) and is good evidence for a common inheritance (evolution). ...
Homework Assignment #7
... The table below lists partial information for the DNA, mRNA codon, tRNA anticodon and polypeptide amino acid sequence for a portion of a protein coding gene. Use the information provided and the genetic code on page 360 and on the wiki site http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_code#Start.2Fstop_codo ...
... The table below lists partial information for the DNA, mRNA codon, tRNA anticodon and polypeptide amino acid sequence for a portion of a protein coding gene. Use the information provided and the genetic code on page 360 and on the wiki site http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_code#Start.2Fstop_codo ...
Protocol S1.
... of disruption peaks in the middle of gp120 gene (data not shown). But because (i) analysing using SCHEMA a small number of chimera and (ii) in reason of the small length of sequence available with structural data, these analyses lack statistical basis and could only be used as a raw indication of ho ...
... of disruption peaks in the middle of gp120 gene (data not shown). But because (i) analysing using SCHEMA a small number of chimera and (ii) in reason of the small length of sequence available with structural data, these analyses lack statistical basis and could only be used as a raw indication of ho ...
Aim 24: How does DNA code for the production of proteins through
... _____________________ floating in the ___________________ of the cell Once transcription in the nucleus occurs, the mRNA that is created travels to a ribosome. Step 1: ___________ leaves the ____________________ and travels to a __________________ Step 2: The ribosome travels along the mRNA strand a ...
... _____________________ floating in the ___________________ of the cell Once transcription in the nucleus occurs, the mRNA that is created travels to a ribosome. Step 1: ___________ leaves the ____________________ and travels to a __________________ Step 2: The ribosome travels along the mRNA strand a ...
Proein Synthesis Note Fill-in
... 6. What are the 4 nitrogen bases that make up DNA? 7. How do the 4 bases complement each other? 8. A _____________________________ is always paired with a __________________________ due to complimentary base pairing. 9. The shape of the DNA molecule is referred to as a double _______________________ ...
... 6. What are the 4 nitrogen bases that make up DNA? 7. How do the 4 bases complement each other? 8. A _____________________________ is always paired with a __________________________ due to complimentary base pairing. 9. The shape of the DNA molecule is referred to as a double _______________________ ...
Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics
... The ribosome binds to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG) that is recognized only by the initiator tRNA. The ribosome proceeds to the elongation phase of protein synthesis. During this stage, complexes, composed of an amino acid linked to tRNA, sequentially bind to the appropriate codon in mRNA by for ...
... The ribosome binds to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG) that is recognized only by the initiator tRNA. The ribosome proceeds to the elongation phase of protein synthesis. During this stage, complexes, composed of an amino acid linked to tRNA, sequentially bind to the appropriate codon in mRNA by for ...
tacttgaaagttcaccggagg
... ribosomes are cell Cytoplasm organelles that help protein production. Another kind of RNA then comes into play. Transfer RNA (or tRNA see * in picture to right) has a ...
... ribosomes are cell Cytoplasm organelles that help protein production. Another kind of RNA then comes into play. Transfer RNA (or tRNA see * in picture to right) has a ...
anth-260-midterm-review-sheet-2016
... • All of the following are true of the relationship between DNA and proteins EXCEPT: a. a sequence of three DNA base-pairs codes for one amino acid b. a single codon codes for one amino acid c. an amino acid is coded by only one codon d. sequences of codons code for sequences of amino acids • A prim ...
... • All of the following are true of the relationship between DNA and proteins EXCEPT: a. a sequence of three DNA base-pairs codes for one amino acid b. a single codon codes for one amino acid c. an amino acid is coded by only one codon d. sequences of codons code for sequences of amino acids • A prim ...
Protein Synthesis - Doral Academy High School
... The Genetic Code • Three adjacent nucleotides (letters) in mRNA codes for a specific amino acid (word) • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating ...
... The Genetic Code • Three adjacent nucleotides (letters) in mRNA codes for a specific amino acid (word) • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating ...
No Slide Title
... The P site tRNA leaves the ribosome The ribosome translocates (moves) the other tRNA from the A site over to the P site This movement then exposes the next mRNA codon to be translated (at the A site) and the process then repeats itself ...
... The P site tRNA leaves the ribosome The ribosome translocates (moves) the other tRNA from the A site over to the P site This movement then exposes the next mRNA codon to be translated (at the A site) and the process then repeats itself ...
genetic code and translation
... The code is composed of codons Codon is composed of 3 bases ( e.g. ACG or UAG). Each codon is translated into one amino acid. ...
... The code is composed of codons Codon is composed of 3 bases ( e.g. ACG or UAG). Each codon is translated into one amino acid. ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in DNA, recruits RNA polymerase o RNA polymerases actually transcribes the DNA strand o Presence or absence of transcription factor dictates whether ...
... • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in DNA, recruits RNA polymerase o RNA polymerases actually transcribes the DNA strand o Presence or absence of transcription factor dictates whether ...
CHEM 642-09 Powerpoint
... The standard one-letter abbreviation for each amino acid is presented below its three-letter abbreviation (see Panel 3–1, pp. 132–133, for the full name of each amino acid and its structure). By convention, codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino ...
... The standard one-letter abbreviation for each amino acid is presented below its three-letter abbreviation (see Panel 3–1, pp. 132–133, for the full name of each amino acid and its structure). By convention, codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino ...
DNA - California State University, Stanislaus
... Types of Mutation • Spontaneous mutation- occurs as a result of natural processes in cells • Induced mutation- caused by mutagens, substances that cause a much higher rate of mutation ...
... Types of Mutation • Spontaneous mutation- occurs as a result of natural processes in cells • Induced mutation- caused by mutagens, substances that cause a much higher rate of mutation ...
Unit I
... Protein synthesis involves two basic processes, transcription and translation, that make use of another nucleic acid, RNA. RNA, like DNA, is made up of a chain of nucleotides. I transcription, enzymes catalyze the transfer of DNA’s information to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. The mRNA molecules th ...
... Protein synthesis involves two basic processes, transcription and translation, that make use of another nucleic acid, RNA. RNA, like DNA, is made up of a chain of nucleotides. I transcription, enzymes catalyze the transfer of DNA’s information to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. The mRNA molecules th ...
Bio1001Ch13W
... • The bridge between DNA and ________ synthesis is RNA. • RNA differs from DNA 1. RNA contains _____as its sugar ...
... • The bridge between DNA and ________ synthesis is RNA. • RNA differs from DNA 1. RNA contains _____as its sugar ...
GSLC Protein Synthesis Computer Activity (word)
... What could happen to a protein if a DNA base in the gene that codes for that protein was deleted (removed)? ...
... What could happen to a protein if a DNA base in the gene that codes for that protein was deleted (removed)? ...
Protein synthesis sequencing task
... During the first step in protein synthesis, the DNA / gene is transcripted into mRNA in the nucleus. The DNA unzips and free nucleotides come in and produce the mRNA strand using the complementary base pairing rule: the enzyme that controls this process is RNA polymerase. The mRNAs migrate from the ...
... During the first step in protein synthesis, the DNA / gene is transcripted into mRNA in the nucleus. The DNA unzips and free nucleotides come in and produce the mRNA strand using the complementary base pairing rule: the enzyme that controls this process is RNA polymerase. The mRNAs migrate from the ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: MUTATIONS
... 1. a) This would have no effect at all on the protein produced. Both TCA and TCC code for serine. b) The replacement gives TGA - a stop codon. The rest of the protein following this mutation won’t be produced. Unless this happens very close to the real end of the chain, the resulting polypeptide isn ...
... 1. a) This would have no effect at all on the protein produced. Both TCA and TCC code for serine. b) The replacement gives TGA - a stop codon. The rest of the protein following this mutation won’t be produced. Unless this happens very close to the real end of the chain, the resulting polypeptide isn ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
... • Each “word” in the mRNA strand is composed of a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.