Protein Synthesis Review
... 4. Name three types of RNA (one is from DNA replication, two from protein synthesis) described and explain the function of each. 5. How many different DNA triplets are possible? 6. The DNA triplet “CGA” is transcribed into which RNA codon? a) GUT (b) GUC (c) GCU (d) AUG 7. Which enzyme “reads” the m ...
... 4. Name three types of RNA (one is from DNA replication, two from protein synthesis) described and explain the function of each. 5. How many different DNA triplets are possible? 6. The DNA triplet “CGA” is transcribed into which RNA codon? a) GUT (b) GUC (c) GCU (d) AUG 7. Which enzyme “reads” the m ...
Research Questions
... and sperm cells, which are also called germ cells). This type of mutation is present throughout a person’s life in virtually every cell in the body. When the DNA is transcribed and the RNA is processed by ribosomes, changes to the DNA means that the proteins produced are going to be different, which ...
... and sperm cells, which are also called germ cells). This type of mutation is present throughout a person’s life in virtually every cell in the body. When the DNA is transcribed and the RNA is processed by ribosomes, changes to the DNA means that the proteins produced are going to be different, which ...
notes
... polypeptide sequence via the processes of transcription (making an mRNA transcript) and translation (polypeptide synthesis) Translation uses tRNA molecules and ribosomes to join amino acids into a polypeptide chain according to the mRNA sequence (as read in codons) The universality of the genetic co ...
... polypeptide sequence via the processes of transcription (making an mRNA transcript) and translation (polypeptide synthesis) Translation uses tRNA molecules and ribosomes to join amino acids into a polypeptide chain according to the mRNA sequence (as read in codons) The universality of the genetic co ...
Gene A - Biology
... Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are lengths of DNA molecules that determine the structure of polypeptides (the building blocks of proteins) that our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino ...
... Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are lengths of DNA molecules that determine the structure of polypeptides (the building blocks of proteins) that our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino ...
6.3 Translation: Synthesizing Proteins from mRNA
... ribosome and continuously add amino acids to the polypeptide sequence. Remember, there can be three tRNAs in the ribosome because they are highly specialized for one codon. The third nucleotide of the anticodon on the tRNA is flexible in terms of what it will bind to. ...
... ribosome and continuously add amino acids to the polypeptide sequence. Remember, there can be three tRNAs in the ribosome because they are highly specialized for one codon. The third nucleotide of the anticodon on the tRNA is flexible in terms of what it will bind to. ...
Mutations
... Two categories of mutations: Germ mutation: -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
... Two categories of mutations: Germ mutation: -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
protein synthesis
... 6. mRNA attaches to ribosome 7. Ribosome reads mRNA nucleotides in sets of 3 called a Codon 8. A Start Codon (AUG) is found & amino acids are delivered to ribosome by tRNA 9. Amino acids are joined together with peptide bonds until a Stop Codon (UGA, UAA, UAG) is found 10. Assembled protei ...
... 6. mRNA attaches to ribosome 7. Ribosome reads mRNA nucleotides in sets of 3 called a Codon 8. A Start Codon (AUG) is found & amino acids are delivered to ribosome by tRNA 9. Amino acids are joined together with peptide bonds until a Stop Codon (UGA, UAA, UAG) is found 10. Assembled protei ...
Review Questions
... A second tRNA with a complementary anticodon enters the A site and binds to the second codon on the mRNA strand. (see figure on next page) The two amino acids form a peptide bond. (see figure on next page) Next, the first tRNA breaks off and moves to the E site leaving its amino acid attached to the ...
... A second tRNA with a complementary anticodon enters the A site and binds to the second codon on the mRNA strand. (see figure on next page) The two amino acids form a peptide bond. (see figure on next page) Next, the first tRNA breaks off and moves to the E site leaving its amino acid attached to the ...
Biochemistry (Macromolecules)
... 4. R group (This is the most important part as it gives each amino acid its distinctly different property. Notice all 20 amino acids have a different R group.) E. Individual Amino Acids (monomers) are bonded together by a covalent bond called a peptide bond. An amine end of one amino acid is positio ...
... 4. R group (This is the most important part as it gives each amino acid its distinctly different property. Notice all 20 amino acids have a different R group.) E. Individual Amino Acids (monomers) are bonded together by a covalent bond called a peptide bond. An amine end of one amino acid is positio ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... The process that makes an exact copy of a cell's DNA is called ___________________. What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the p ...
... The process that makes an exact copy of a cell's DNA is called ___________________. What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the p ...
bch2ibm: molecular biology end of semester 1 exam notes 2014
... -‐ It’s a ribosomal binding site in mRNA, generally located 8 basepairs upstream of AUG -‐ Exists only in prokaryotes -‐ The six-‐base consensus sequence is AGGAGGU –> this sequence helps recruit the ri ...
... -‐ It’s a ribosomal binding site in mRNA, generally located 8 basepairs upstream of AUG -‐ Exists only in prokaryotes -‐ The six-‐base consensus sequence is AGGAGGU –> this sequence helps recruit the ri ...
CHEM642-10 Powerpoint
... REGULATION OF mRNA and PROTEIN STABILITY The SsrA RNA ( a tmRNA) rescues ribosomes that translate broken mRNAs ...
... REGULATION OF mRNA and PROTEIN STABILITY The SsrA RNA ( a tmRNA) rescues ribosomes that translate broken mRNAs ...
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 6
... 8275 amino acids (1 remaining nucleotide). c) 2664 nucleotides not including the stop codon. If they include the stop codon (2667) it is fine. It is also okay if they add three for the start codon (2670) and say this methionine is sometimes cleaved off. d) Yes, there is a disparity. The start site o ...
... 8275 amino acids (1 remaining nucleotide). c) 2664 nucleotides not including the stop codon. If they include the stop codon (2667) it is fine. It is also okay if they add three for the start codon (2670) and say this methionine is sometimes cleaved off. d) Yes, there is a disparity. The start site o ...
Translation PPT
... ATP AMP bond is unstable so it can release amino acid at ribosome easily Trp C=O OH OH ...
... ATP AMP bond is unstable so it can release amino acid at ribosome easily Trp C=O OH OH ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
Slides - University of Sydney
... Aminoacyl tRNA synthesis • Need to make sure that the CORRECT amino acid is attached to a tRNA – Incorporation of amino acid is purely based on codon:anti-codon pairing – So if the wrong amino acid is on the tRNA then the wrong amino acid will be put into the protein ...
... Aminoacyl tRNA synthesis • Need to make sure that the CORRECT amino acid is attached to a tRNA – Incorporation of amino acid is purely based on codon:anti-codon pairing – So if the wrong amino acid is on the tRNA then the wrong amino acid will be put into the protein ...
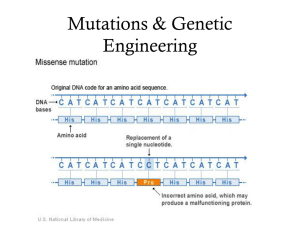
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense ...
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense ...
Modeling Protein synthesis lab
... corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called trarrsfer RNA (IRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is "read" on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in tum and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The process by ...
... corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called trarrsfer RNA (IRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is "read" on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in tum and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The process by ...
Macromolecules Part 2
... Proteins (A. K.A. Polypeptides) and Enzymes (Enzymes are a TYPE of protein.) A. These macromolecules make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight, called biomass. B. Names usually end with the suffix “lin” (i.e. Insulin) for proteins and “ase” for enzymes (i.e. Sucrase) C. The monomer “buildi ...
... Proteins (A. K.A. Polypeptides) and Enzymes (Enzymes are a TYPE of protein.) A. These macromolecules make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight, called biomass. B. Names usually end with the suffix “lin” (i.e. Insulin) for proteins and “ase” for enzymes (i.e. Sucrase) C. The monomer “buildi ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... one arm: anticodon (sequence of three bases complementary to mRNA) 3’ end has acceptor site for a particular amino acid • this recognition by tRNA of mRNA is facilitated through complimentary base pairing. every tRNA carries only one specific amino acid • therefore there must be at least 20 (20-64) ...
... one arm: anticodon (sequence of three bases complementary to mRNA) 3’ end has acceptor site for a particular amino acid • this recognition by tRNA of mRNA is facilitated through complimentary base pairing. every tRNA carries only one specific amino acid • therefore there must be at least 20 (20-64) ...
Protein Synthesis
... DNA code is a series of 4 nucleotides, A, T, C and G. Each three nucleotides in a row on a gene code for a certain amino acid in that part of the protein. ...
... DNA code is a series of 4 nucleotides, A, T, C and G. Each three nucleotides in a row on a gene code for a certain amino acid in that part of the protein. ...
Unit 4: Genetics Name: Date: Aim #23 Translation: How does DNA
... _____________________ floating in the ___________________ of the cell Once transcription in the nucleus occurs, the mRNA that is created travels to a ribosome. Step 1: ___________ leaves the ____________________ and travels to a __________________ Step 2: The ribosome travels along the mRNA strand a ...
... _____________________ floating in the ___________________ of the cell Once transcription in the nucleus occurs, the mRNA that is created travels to a ribosome. Step 1: ___________ leaves the ____________________ and travels to a __________________ Step 2: The ribosome travels along the mRNA strand a ...
Sentence Synthesis Instructions RNA polymerase Instructions, cont
... Instructions, cont’d • The other partner is the ribosome. Stay at your table and read the codons from the mRNA when it arrives. Then find the compcomplementary antianti-codon on the papers from around the room (tRNA). • String the words (amino acids) together to make sentences (proteins). ...
... Instructions, cont’d • The other partner is the ribosome. Stay at your table and read the codons from the mRNA when it arrives. Then find the compcomplementary antianti-codon on the papers from around the room (tRNA). • String the words (amino acids) together to make sentences (proteins). ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.