View/Open - Oregon State University
... 2. The information in mRNA is encoded as the Genetic Code. The genetic code specifies how nucleic acid information is converted to make a protein. Information in mRNA is encoded in groups of three nucleotides (called a codon or a triplet). There are 64 possible codons. 61 of them code for amino acid ...
... 2. The information in mRNA is encoded as the Genetic Code. The genetic code specifies how nucleic acid information is converted to make a protein. Information in mRNA is encoded in groups of three nucleotides (called a codon or a triplet). There are 64 possible codons. 61 of them code for amino acid ...
10.3 Protein Synthesis
... • The language of mRNA is called the Genetic Code (A, G, U, C) (contains only 4 letters) • It is the matching of the RNA sequence to the correct amino acid to make proteins. • It is based on codons, which are 3 bases together on an mRNA chain. • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • There a ...
... • The language of mRNA is called the Genetic Code (A, G, U, C) (contains only 4 letters) • It is the matching of the RNA sequence to the correct amino acid to make proteins. • It is based on codons, which are 3 bases together on an mRNA chain. • Each codon codes for a specific amino acid • There a ...
8.5
... are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The mRNA message is read as a series of non-overlapping codons, a sequence of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. In general, codons that code for the same amino acid share the same first tw ...
... are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The mRNA message is read as a series of non-overlapping codons, a sequence of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. In general, codons that code for the same amino acid share the same first tw ...
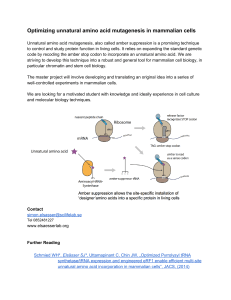
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
rsc prize and award lecture
... genomic DNA. In the cell, DNA is copied to messenger RNA, and triplet codons (64) in the messenger RNA are decoded - in the process of translation - to synthesize polymers of the natural 20 amino acids. This process (DNA RNA protein) describes the central dogma of molecular biology and is conserved ...
... genomic DNA. In the cell, DNA is copied to messenger RNA, and triplet codons (64) in the messenger RNA are decoded - in the process of translation - to synthesize polymers of the natural 20 amino acids. This process (DNA RNA protein) describes the central dogma of molecular biology and is conserved ...
Revealing the Genetic Code
... Gene = sequence of nucleotides (bases) Protein = sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases determines sequence of amino acids (protein’s primary structure) Protein’s primary structure determines its secondary & tertiary (3D) structures Protein’s 3D structure determines its function!! ...
... Gene = sequence of nucleotides (bases) Protein = sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases determines sequence of amino acids (protein’s primary structure) Protein’s primary structure determines its secondary & tertiary (3D) structures Protein’s 3D structure determines its function!! ...
Protein Synthesis
... 19. How many binding sites do ribosomes have? 20. One site holds the __________ transcript, while the other sites hold __________ with their attached amino acid. 21. Polypeptide formation begins when a ribosome attaches to what mRNA codon? 22. What amino acid does the start codon code for? 23. Amino ...
... 19. How many binding sites do ribosomes have? 20. One site holds the __________ transcript, while the other sites hold __________ with their attached amino acid. 21. Polypeptide formation begins when a ribosome attaches to what mRNA codon? 22. What amino acid does the start codon code for? 23. Amino ...
Document
... Objective: To know the major steps in protein synthesis and the RNAs and proteins involved in this process. To understand the mechanism by which proteins are targeted to specific cimpartments. I. Genetic code A. Three nucleotides make one codon B. "Universal" C. Degenerate D. Commaless II. Translati ...
... Objective: To know the major steps in protein synthesis and the RNAs and proteins involved in this process. To understand the mechanism by which proteins are targeted to specific cimpartments. I. Genetic code A. Three nucleotides make one codon B. "Universal" C. Degenerate D. Commaless II. Translati ...
Diapositiva 1 - Programma LLP
... In the early sixties, molecular biologists were able to "decrypt" the genetic code. ...
... In the early sixties, molecular biologists were able to "decrypt" the genetic code. ...
10 DNA Vocabulary - Petal School District
... 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that copies the DNA 7. template strands—the original strands of DNA 8. messenger RNA (mRNA)—copies DNA code 9. ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—makes up ribosomes 10. transfer RNA (tRNA)—carries a specific amino a ...
... 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that copies the DNA 7. template strands—the original strands of DNA 8. messenger RNA (mRNA)—copies DNA code 9. ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—makes up ribosomes 10. transfer RNA (tRNA)—carries a specific amino a ...
translation ppt
... There are three types of RNA. mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. The Genetic Code represents 64 possible codons corresponding to 20 different amino acids, start signal and stop signals. The process of TRANSLATION takes place within the cytoplasm on a ribosome. The process of TRANSLATION involves: initiation, elon ...
... There are three types of RNA. mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. The Genetic Code represents 64 possible codons corresponding to 20 different amino acids, start signal and stop signals. The process of TRANSLATION takes place within the cytoplasm on a ribosome. The process of TRANSLATION involves: initiation, elon ...
Do Now: Wednesday, March 19
... for the protein that is needed is unwound Step 2: RNA polymerase (enzyme) uses the DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA ...
... for the protein that is needed is unwound Step 2: RNA polymerase (enzyme) uses the DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA ...
Hydrophobic: tending to repel and not absorb water
... formed by a combination of smaller molecules. ...
... formed by a combination of smaller molecules. ...
One Gene -One polypeptide
... Overview of Protein Synthesis2 main parts 1.Transcription -nucleus a sequence of DNA nucleotides (a gene) is converted to a single-stranded RNA molecule (mRNA) mRNA leaves the nucleus to go to the ribosomes. DNA remains in the nucleus. 2.Translation –ribosomes mRNA is translated into amino ...
... Overview of Protein Synthesis2 main parts 1.Transcription -nucleus a sequence of DNA nucleotides (a gene) is converted to a single-stranded RNA molecule (mRNA) mRNA leaves the nucleus to go to the ribosomes. DNA remains in the nucleus. 2.Translation –ribosomes mRNA is translated into amino ...
Players in the protein game
... microscope but in order to see the DNA you have to have a high powered mircroscope ...
... microscope but in order to see the DNA you have to have a high powered mircroscope ...
Document
... • Use a table of mRNA codons and their corresponding amino acids to deduce the sequence of amino acids coded by a short mRNA strand of known base sequence ...
... • Use a table of mRNA codons and their corresponding amino acids to deduce the sequence of amino acids coded by a short mRNA strand of known base sequence ...
Transparency master
... complements the codons on the mRNA Codon - a group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid Transcription – process by which mRNA molecules are copied from the DNA Translation – when codons in mRNA are decoded into a sequence of amino acids DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid, double-stranded h ...
... complements the codons on the mRNA Codon - a group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid Transcription – process by which mRNA molecules are copied from the DNA Translation – when codons in mRNA are decoded into a sequence of amino acids DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid, double-stranded h ...
Albert Libchaber Detlev W. Bronk Professor The Rockefeller
... In the fascinating puzzle of the origin of life, two main phenomena distinguish biology from non-equilibrium thermodynamic processes: the presence of a code and the ability of machines to self-reproduce. - In the RNA world of the early soup we are studying how a genetic code could originate, buildin ...
... In the fascinating puzzle of the origin of life, two main phenomena distinguish biology from non-equilibrium thermodynamic processes: the presence of a code and the ability of machines to self-reproduce. - In the RNA world of the early soup we are studying how a genetic code could originate, buildin ...
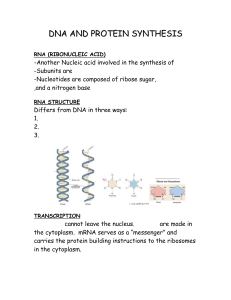
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
General Biology Notes CH 12: TRANSLATION A.K.A. PROTEIN
... into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins. ...
... into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins. ...
Codon Practice
... CCG CCU GTC GUA AUA Tryptophan TGT UAG 8. Given the DNA code ATTCGCTTT, what would the mRNA code be? How many codons are there? What are the codons? What are the amino acids? 9. Given the DNA code TCGAATGGTTTT, what would the mRNA code be? How many codons are there? What are the codons? What are the ...
... CCG CCU GTC GUA AUA Tryptophan TGT UAG 8. Given the DNA code ATTCGCTTT, what would the mRNA code be? How many codons are there? What are the codons? What are the amino acids? 9. Given the DNA code TCGAATGGTTTT, what would the mRNA code be? How many codons are there? What are the codons? What are the ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.