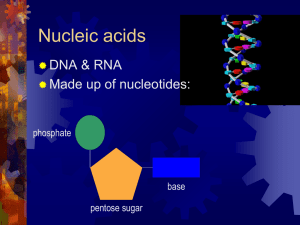
Protein Synthesis PPT
... DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), but RNA can leave the nucleus (single stranded). ...
... DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), but RNA can leave the nucleus (single stranded). ...
Stabilization of Low Affinity Protein-Protein Interactions by
... The introduction of new chemical functionalities into proteins represents a promising approach for investigating and manipulating diverse biological processes. Among a number of different approaches, the expansion of the genetic code has emerged as an eminent tool for in vivo site-specific incorpora ...
... The introduction of new chemical functionalities into proteins represents a promising approach for investigating and manipulating diverse biological processes. Among a number of different approaches, the expansion of the genetic code has emerged as an eminent tool for in vivo site-specific incorpora ...
Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab [1/13/2016]
... 13. Give examples of mutagens? 14. A simple change in an amino acid could cause what disease? ...
... 13. Give examples of mutagens? 14. A simple change in an amino acid could cause what disease? ...
Daily TAKS Connection: DNA
... will most likely occur? A The protein will be missing the first amino acid. B The amino acids that make up the protein will all be different. C The mRNA will become attached to a ribosome. D The production of the protein will be stopped. ...
... will most likely occur? A The protein will be missing the first amino acid. B The amino acids that make up the protein will all be different. C The mRNA will become attached to a ribosome. D The production of the protein will be stopped. ...
DNA and RNA - Joshua ISD
... Do these terms come to mind?? DNA contains genes or traits Genetic codes to make proteins which keep us alive! ...
... Do these terms come to mind?? DNA contains genes or traits Genetic codes to make proteins which keep us alive! ...
Chapter 8
... Anticodon • An anticodon is a set of three nucleotides that is complementary to an mRNA codon (a codon of CCC binds with an anticodon of GGG). • An anticodon is carried by a tRNA. ...
... Anticodon • An anticodon is a set of three nucleotides that is complementary to an mRNA codon (a codon of CCC binds with an anticodon of GGG). • An anticodon is carried by a tRNA. ...
anti-codon
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
... • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
BioIIch17notesRNAfilled.p pt
... -one gene codes for one polypeptide chain -polypeptide chains may combine to form 1 protein -Hemoglobin made from 2 kinds of polypeptides—thus 2 genes code for this protein -ok to say one gene codes for one protein -DNA contains instructions for making proteins, RNA actually Makes the proteins -3 ma ...
... -one gene codes for one polypeptide chain -polypeptide chains may combine to form 1 protein -Hemoglobin made from 2 kinds of polypeptides—thus 2 genes code for this protein -ok to say one gene codes for one protein -DNA contains instructions for making proteins, RNA actually Makes the proteins -3 ma ...
Worksheet: Mutations Practice
... There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution – one base-pairs is replaced by another: Example: G to C or A to G C G T C 2. Insertion – one or more base pairs is added to a sequence: Example: CGATGG –– CGAATGG GCTACC GCTTACC 3. Deletion ...
... There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution – one base-pairs is replaced by another: Example: G to C or A to G C G T C 2. Insertion – one or more base pairs is added to a sequence: Example: CGATGG –– CGAATGG GCTACC GCTTACC 3. Deletion ...
DNA Transcription – A Simulation using Corticon
... If the codon at the current position of the ribosome is other than a STOP then the amino acid attached to the corresponding tRNA will be attached to the growing protein). This process continues with the ribosome moving up the mRNA strand (in units of three) until a STOP codon is encountered Once a S ...
... If the codon at the current position of the ribosome is other than a STOP then the amino acid attached to the corresponding tRNA will be attached to the growing protein). This process continues with the ribosome moving up the mRNA strand (in units of three) until a STOP codon is encountered Once a S ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • First Step: Copying of genetic information from DNA to RNA called Transcription Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. ...
... • First Step: Copying of genetic information from DNA to RNA called Transcription Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. ...
DNA and RNA
... • tRNA carries specific amino acid to the ribosome • The specific amino acid is determined by the anticodon of tRNA • The anticodon pairs with complementary codon on mRNA (Example: codon AUG; anticodon UAC) • Peptide bonds form between amino acids, linking them into proteins • tRNAs get recycled bac ...
... • tRNA carries specific amino acid to the ribosome • The specific amino acid is determined by the anticodon of tRNA • The anticodon pairs with complementary codon on mRNA (Example: codon AUG; anticodon UAC) • Peptide bonds form between amino acids, linking them into proteins • tRNAs get recycled bac ...
Study Guide Chapter 27 Protein Metabolism 1. Define: codon
... 2. What is the codon used to start a protein sequence? To stop a protein sequence? 3. Why is the genetic code a 3 letter code? 4. If I have a tRNA with the anticodon 3'...G-C-I...5', what possible codons on an mRNA message could it bind to? What about 3'... AUU...5'? 5. If there are 61 possible amin ...
... 2. What is the codon used to start a protein sequence? To stop a protein sequence? 3. Why is the genetic code a 3 letter code? 4. If I have a tRNA with the anticodon 3'...G-C-I...5', what possible codons on an mRNA message could it bind to? What about 3'... AUU...5'? 5. If there are 61 possible amin ...
Biochemistry Exam Molecular Biology Lecture 1 – An Introduction to
... • Highly degenerate à means that there is more than one triplet that could specify the same amino acid, for example, CGU and CGC both code for arginine. • Where several different codons specify mo ...
... • Highly degenerate à means that there is more than one triplet that could specify the same amino acid, for example, CGU and CGC both code for arginine. • Where several different codons specify mo ...
Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! ...
... The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! ...
All Living things pass on their genetic heritage by common
... unwound DNA helix. Activated A, U, G and C ribonucleotide triphosphates base pair with the DNA and are linked by the RNA polymerase into RNA polynucleotides. RNA transcripts 1. rRNA, ribosomal RNA: In large and small ribosomal subunits. rRNA-ribosome protein complexes catalyze polypeptide synthesis. ...
... unwound DNA helix. Activated A, U, G and C ribonucleotide triphosphates base pair with the DNA and are linked by the RNA polymerase into RNA polynucleotides. RNA transcripts 1. rRNA, ribosomal RNA: In large and small ribosomal subunits. rRNA-ribosome protein complexes catalyze polypeptide synthesis. ...
Translation Notes 2015 - Liberty Union High School District
... process of converting mRNA into proteins. Takes place on a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains amino acids, tRNA, and ribosomes, which are all needed for protein synthesis. ...
... process of converting mRNA into proteins. Takes place on a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains amino acids, tRNA, and ribosomes, which are all needed for protein synthesis. ...
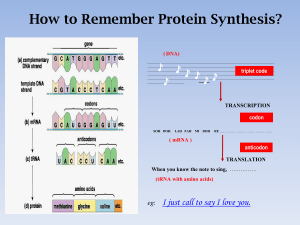
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
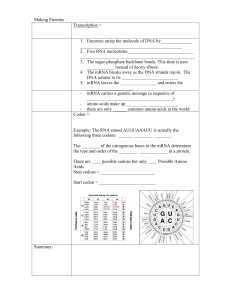
DNA Transcription
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
Protein Synthesis Poster
... Folding allows the Protein to reach its 3D (Tertiary Shape) which influences its function ...
... Folding allows the Protein to reach its 3D (Tertiary Shape) which influences its function ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.

![Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab [1/13/2016]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010042148_1-49212ed4f857a63328959930297729c5-300x300.png)