* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Dna code - Winston Knoll Collegiate
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
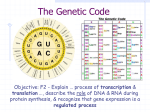
THE DNA CODE The Key to Protein Synthesis The Question of DNA DNA stores information to build proteins in sequences of nucleotides - DNA nucleotides contain one of 4 nitrogen bases A T C G - there are 20 different amino acids used to build protein Problem: How to code for 20 amino acids with only 4 nitrogen bases? Solution: Use groups of 3 nucleotides to code for each amino acid Why are 3 nucleotides required? Using one nucleotide can only code for 4 amino acids Using pairs of nucleotides produces 16 combinations – can code for 16 amino acids Using groups of three nucleotides produces 64 different combinations – can code for all 20 amino acids - several different groups can each code for the same amino acid THE DNA CODE The DNA code is: - universal to all living things -the groups of nucleotides code for the same amino acid in all living things 3 DNA nucleotides = Triplet - one triplet = one amino acid Examples – TCA = Serine CTG = Aspartic Acid THE CODE CONTINUED 3 mRNA nucleotides = Codon - codon is the complement of a triplet - codon codes for the same amino acid as the triplet it is complementary to Example: DNA triplet = CTG = Aspartic Acid mRNA codon = GAC = Aspartic Acid Triplet Codon Transcription Amino Acid Translation DNA Triplet mRNA Codon Amino Acid CTG GAC Aspartic Acid CGC GCG Alanine THE CODON CHART – FROM CODON TO AMINO ACID Codon = UGC Cysteine Codon = CAC Histidine Codon = AAA Lysine Codon = GCG Alanine