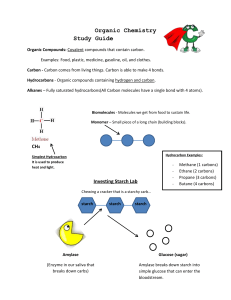
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... Lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fatsoluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others. ...
... Lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fatsoluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others. ...
Ribonucleic acids are found in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm
... Transfer RNA serves as the carrier molecule for amino acids to be used in protein synthesis, and is responsible for decoding the mRNA. In addition, many other classes of RNA are now known. DNA, structure and replication DNA molecules are large, with RMMs up to one trillion (1012). Experimental work ...
... Transfer RNA serves as the carrier molecule for amino acids to be used in protein synthesis, and is responsible for decoding the mRNA. In addition, many other classes of RNA are now known. DNA, structure and replication DNA molecules are large, with RMMs up to one trillion (1012). Experimental work ...
Biochemistry Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... 6. What is the process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals? a. cohesion c. chemical reaction b. adhesion d. dissolving 7. Glycerol and fatty acids make up_________> a. carbohydrates. c. nucleic acids. b. lipids. d. protein. 8. Which of the following foods is least likely ...
... 6. What is the process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals? a. cohesion c. chemical reaction b. adhesion d. dissolving 7. Glycerol and fatty acids make up_________> a. carbohydrates. c. nucleic acids. b. lipids. d. protein. 8. Which of the following foods is least likely ...
Buffers - Philadelphia University
... • (H,C,N,O,P,S,Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca). – Chemical makeup appears to be determined partly by the availability of raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49% ...
... • (H,C,N,O,P,S,Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca). – Chemical makeup appears to be determined partly by the availability of raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49% ...
Single molecule derivation of base pair free energies in
... reaction that makes possible to disrupt the bonds that hold molecular structures in nucleic acids and proteins. In this way, for example, a double stranded DNA molecule can be converted into two individual single strands by pulling apart the two strands (molecular unzipping)2 . The capability of sin ...
... reaction that makes possible to disrupt the bonds that hold molecular structures in nucleic acids and proteins. In this way, for example, a double stranded DNA molecule can be converted into two individual single strands by pulling apart the two strands (molecular unzipping)2 . The capability of sin ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA - Northwestern High School
... • Different enzymes to try and stop transformation. • Deoxyribonuclease , no transformation. • Taking place in the DNA!!! ...
... • Different enzymes to try and stop transformation. • Deoxyribonuclease , no transformation. • Taking place in the DNA!!! ...
DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
Biology Vocabulary 8, test on Thursday, 1/19/17
... having more than two alleles that code for a specific trait substance or situation, such as a chemical or exposure to radiation, that causes mutations permanent change in a cell's DNA, ranging from changes in a single base pair to deletions of large sections of chromosomes cell division in which the ...
... having more than two alleles that code for a specific trait substance or situation, such as a chemical or exposure to radiation, that causes mutations permanent change in a cell's DNA, ranging from changes in a single base pair to deletions of large sections of chromosomes cell division in which the ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... DNA, numerous viruses exist, in which genetic information can be in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single- or double-stranded RNA (ssRNA or dsRNA), as well as in the form of duplex DNA (dsDNA). However, viruses are not living things because they cannot replicate autonomously, without the ...
... DNA, numerous viruses exist, in which genetic information can be in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single- or double-stranded RNA (ssRNA or dsRNA), as well as in the form of duplex DNA (dsDNA). However, viruses are not living things because they cannot replicate autonomously, without the ...
DNA Webquest - Jackson School District
... 3. Franklin worked with Raymond Gosling and was able to get photos of DNA fibers. What did she conclude from these photos (two things)? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Go to ...
... 3. Franklin worked with Raymond Gosling and was able to get photos of DNA fibers. What did she conclude from these photos (two things)? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Go to ...
DNA-The Alphabet of Life
... This is an example of a genetic code that may be found in your body. ...
... This is an example of a genetic code that may be found in your body. ...
Revised Chapter 4 and 5
... • Genetic material that stores information for its own replication and for the sequence of amino acids in proteins. ...
... • Genetic material that stores information for its own replication and for the sequence of amino acids in proteins. ...
What is BIOLOGY?
... are important to living things? Be able to give the symbol for these. (EX: C = carbon; Na+ = sodium) What makes water important to cells? What are polar and non-polar molecules? Give examples. Which parts of a phospholipid molecule are polar? Non-polar? What is the difference between hydrophobic and ...
... are important to living things? Be able to give the symbol for these. (EX: C = carbon; Na+ = sodium) What makes water important to cells? What are polar and non-polar molecules? Give examples. Which parts of a phospholipid molecule are polar? Non-polar? What is the difference between hydrophobic and ...
DNA Replication, Translation, Transcription, & Protein
... • When a cell divides into two cells, each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. • REPLICATION is the process by which all of the DNA is copied before the cell divides. ...
... • When a cell divides into two cells, each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. • REPLICATION is the process by which all of the DNA is copied before the cell divides. ...
13 4 (a) Genetic modification of organisms uses a
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
Phar lecture 6
... nucleotides in the human genome. Each day ~10 000 glycosidic bonds are cleaved from these purines in a given cell under physiological conditions. The conclusion: your cells contain some nasty little compounds. There are 130 genes which encode proteins responsible for repair in the human genome. Even ...
... nucleotides in the human genome. Each day ~10 000 glycosidic bonds are cleaved from these purines in a given cell under physiological conditions. The conclusion: your cells contain some nasty little compounds. There are 130 genes which encode proteins responsible for repair in the human genome. Even ...
ANSWERS - midterm study guide
... What is the monomer of DNA called? NUCLEOTIDE 3. What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? SUGAR, PHOSPHATE, AND BASE 4. What are the 4 nucleotide bases of DNA? Which bases pair together? ADENINE – THYMINE, GUANINE - CYTOSINE 5. What type of bond holds the bases together in a DNA molecule? HYRDOGEN_____ ...
... What is the monomer of DNA called? NUCLEOTIDE 3. What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? SUGAR, PHOSPHATE, AND BASE 4. What are the 4 nucleotide bases of DNA? Which bases pair together? ADENINE – THYMINE, GUANINE - CYTOSINE 5. What type of bond holds the bases together in a DNA molecule? HYRDOGEN_____ ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.