Biological Basis PDF worksheet - UNC
... Most of the molecules found in humans and other living organisms fall into one of four categories: 1. carbohydrates (sugars and starches) 2. lipids (fats, oils, and waxes) 3. proteins 4. nucleic acids Proteins are large chain-like molecules that are twisted and folded back on themselves in complex p ...
... Most of the molecules found in humans and other living organisms fall into one of four categories: 1. carbohydrates (sugars and starches) 2. lipids (fats, oils, and waxes) 3. proteins 4. nucleic acids Proteins are large chain-like molecules that are twisted and folded back on themselves in complex p ...
D5 Phylogeny and systematics – summary of mark
... Explain the biochemical evidence provided by the universality of DNA and protein structures for the common ancestry of living organisms. ...
... Explain the biochemical evidence provided by the universality of DNA and protein structures for the common ancestry of living organisms. ...
Molecular Biology
... equivalent. Chemically adenine and guanine are purines, which have a double-ring structure, whereas cytosine and thymine (and uracil) are pyrimidines, which have a single-ring structure. The bases are held together by hydrogen bonds, two in the case of an A = T base pair and three in the case of a G ...
... equivalent. Chemically adenine and guanine are purines, which have a double-ring structure, whereas cytosine and thymine (and uracil) are pyrimidines, which have a single-ring structure. The bases are held together by hydrogen bonds, two in the case of an A = T base pair and three in the case of a G ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET (answer in COMPLETE sentences on another
... List Chargaff’s Rules (1947). What did Chargaff’s research help Watson and Crick deduce about DNA’s configuration? List the purines. List the pyrimidines. Describe the hydrogen bonding between the various nitrogen bases. What molecules make up the backbone of the DNA molecule? What does the term sem ...
... List Chargaff’s Rules (1947). What did Chargaff’s research help Watson and Crick deduce about DNA’s configuration? List the purines. List the pyrimidines. Describe the hydrogen bonding between the various nitrogen bases. What molecules make up the backbone of the DNA molecule? What does the term sem ...
Structure and Role of DNA Genetic and DNA Genetics
... 1st organisms were unicellular Oxygen was fatal to most early life forms, to survive they adapted to use oxygen for respiration Prokaryotes lack membrane bound organelles, endosymbiant theory says that early prokaryotes evolved internal cell membranes that lead to primitive eukaryotic cells. Other p ...
... 1st organisms were unicellular Oxygen was fatal to most early life forms, to survive they adapted to use oxygen for respiration Prokaryotes lack membrane bound organelles, endosymbiant theory says that early prokaryotes evolved internal cell membranes that lead to primitive eukaryotic cells. Other p ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
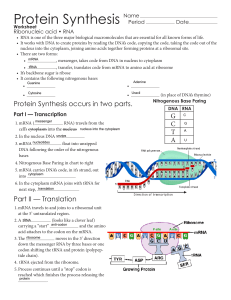
Create a comic strip to illustrate and explain protein synthesis
... Create a comic strip to illustrate and explain protein synthesis. Explain what happens during transcription, RNA splicing, and translation (Explanations are worth 3 points each). The comic strip should begin with a sequence of DNA and end with a protein, illustrating and explaining the steps in betw ...
... Create a comic strip to illustrate and explain protein synthesis. Explain what happens during transcription, RNA splicing, and translation (Explanations are worth 3 points each). The comic strip should begin with a sequence of DNA and end with a protein, illustrating and explaining the steps in betw ...
No Slide Title
... 2. Introns = DNA or RNA that does not have information for protein 3. Exons = DNA or RNA DNA or RNA containing information for proteins 4. Must splice out introns for RNA to function mRNA Splicing ...
... 2. Introns = DNA or RNA that does not have information for protein 3. Exons = DNA or RNA DNA or RNA containing information for proteins 4. Must splice out introns for RNA to function mRNA Splicing ...
Lecture 7
... • How many amino acids would one protein contain if it was translated from an mRNA that is 690 nucleotides long? ...
... • How many amino acids would one protein contain if it was translated from an mRNA that is 690 nucleotides long? ...
DNA Replication
... entire strand is copied Result is two strands of DNA Semi-Conservative Replication - Each strand is 50% new and 50% old DNA ...
... entire strand is copied Result is two strands of DNA Semi-Conservative Replication - Each strand is 50% new and 50% old DNA ...
Biomolecules Review
... 18. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? Which way will it move during electrophoresis? 19. The site on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. ...
... 18. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? Which way will it move during electrophoresis? 19. The site on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. ...
Biology 12 DNA Functions Functions of DNA: 1. To replicate or make
... 4. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome. (3 bases on tRNA called an anticodon). Anticodons match with codons. Amino Acids link through peptide bonds. 5. ribosome travels down mRNA, tRNA’s continue to bring amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. ...
... 4. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome. (3 bases on tRNA called an anticodon). Anticodons match with codons. Amino Acids link through peptide bonds. 5. ribosome travels down mRNA, tRNA’s continue to bring amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. ...
Name: Genetics Study Guide
... What does codominance mean in genetics? How is it different from Incomplete dominance? Know the difference between a hybrid and a purebred. In what decade was the DNA structure discovered? Who discovered the structure of DNA? What is the scientific name of the DNA structure? Which is the correct ord ...
... What does codominance mean in genetics? How is it different from Incomplete dominance? Know the difference between a hybrid and a purebred. In what decade was the DNA structure discovered? Who discovered the structure of DNA? What is the scientific name of the DNA structure? Which is the correct ord ...
DNA - hdueck
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? What amino acid would this tRNA carry? Amino acid tRNA mRNA DNA ...
... Some proteins are modified further before they do their specific jobs What are some of the possible roles for these proteins? The following tRNA has the anticodon UAC. What is the DNA base code for this tRNA? What amino acid would this tRNA carry? Amino acid tRNA mRNA DNA ...
Unit 8 - Macromolecules Processes
... Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid double helix sugar-phosphate backbone made up of subunits called NUCLEOTIDES ...
... Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid double helix sugar-phosphate backbone made up of subunits called NUCLEOTIDES ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.