8 th Grade Genes and Survival Test – Study Guide
... There is test on ________________________ that covers all of the concepts on this study guide. This completed guide is due on the day of the test or you receive a zero on it! Please use your notes and textbook to locate definitions and answers for all of the following vocabulary definitions. Read pa ...
... There is test on ________________________ that covers all of the concepts on this study guide. This completed guide is due on the day of the test or you receive a zero on it! Please use your notes and textbook to locate definitions and answers for all of the following vocabulary definitions. Read pa ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Explain pH and illustrate the pH scale. What do acids form in water?/ What do bases form in water? Draw an illustration of diffusion. Describe dynamic equilibrium. What is Brownian ...
... Elements with a different number of neutrons that protons such as Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are considered______________. Explain pH and illustrate the pH scale. What do acids form in water?/ What do bases form in water? Draw an illustration of diffusion. Describe dynamic equilibrium. What is Brownian ...
Micro Quiz #3R Stu F2011 - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... 4. AT-rich DNA strands will denature (separate) at a(n): A. Higher temperature than GC-rich DNA B. Identical temperature as GC-rich DNA C. Similar temperature as GC-rich DNA, with minor variations D. Lower temperature than GC-rich DNA E. Temperature dependent upon whether it is from a prokaryote or ...
... 4. AT-rich DNA strands will denature (separate) at a(n): A. Higher temperature than GC-rich DNA B. Identical temperature as GC-rich DNA C. Similar temperature as GC-rich DNA, with minor variations D. Lower temperature than GC-rich DNA E. Temperature dependent upon whether it is from a prokaryote or ...
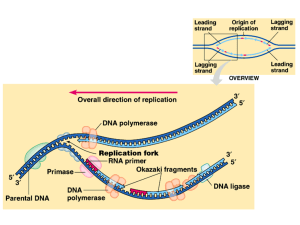
Biology, Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Study Guide 1. What two
... 16. How does transcription resemble DNA replication? 17. Contrast intron and exon. ...
... 16. How does transcription resemble DNA replication? 17. Contrast intron and exon. ...
Unit 11 web
... from sperm and 1 from egg). Total length of these molecular threads in each cell = ~2 meters ! When cells divide one strand from each ‘double thread/helix ’ goes to each new cell thus carrying the identical sequence/information. ...
... from sperm and 1 from egg). Total length of these molecular threads in each cell = ~2 meters ! When cells divide one strand from each ‘double thread/helix ’ goes to each new cell thus carrying the identical sequence/information. ...
Chapter 2 nucleic acid
... directions, one strand is oriented 5’→3’ and the other is oriented 3’ →5’. (2) The bases on the inside and the sugar-phosphate backbones (骨架)on the outside. (3) The diameter of the double helix is 2 nm, the distance between two base is 0.34 nm, each turn of the helix involves 10 bases pairs, 34 nm. ...
... directions, one strand is oriented 5’→3’ and the other is oriented 3’ →5’. (2) The bases on the inside and the sugar-phosphate backbones (骨架)on the outside. (3) The diameter of the double helix is 2 nm, the distance between two base is 0.34 nm, each turn of the helix involves 10 bases pairs, 34 nm. ...
For teachers: Get four colours of beads or rubber bands. You can
... 1. Read letters left to right in sets of three 2. Each three-letter code corresponds to an amino acid, such as “Leu” (see key) 3. T = U in the key* ...
... 1. Read letters left to right in sets of three 2. Each three-letter code corresponds to an amino acid, such as “Leu” (see key) 3. T = U in the key* ...
DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... - The “Middle-Man” between DNA (nucleus) & the ribosomes (cytoplasm). 2. Structure a. Ribose (Sugar) b. Single-stranded, not double. c. Thymine is replaced by URACIL. - Adenine binds with Uracil. d. RNA can be found inside and outside of the nucleus (DNA is always inside!) ...
... - The “Middle-Man” between DNA (nucleus) & the ribosomes (cytoplasm). 2. Structure a. Ribose (Sugar) b. Single-stranded, not double. c. Thymine is replaced by URACIL. - Adenine binds with Uracil. d. RNA can be found inside and outside of the nucleus (DNA is always inside!) ...
RNA:Structure, Function, Transcription, Translation
... a. What are the four nitrogen bases used to make RNA nucleotides? adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil b. Which base from DNA is replaced by uracil? thymine c. Is uracil a purine or a pyrimidine? single ring - pyrimidine d. What base is uracil complementary to? adenine TRANSCRIPTION: the making of RNA ...
... a. What are the four nitrogen bases used to make RNA nucleotides? adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil b. Which base from DNA is replaced by uracil? thymine c. Is uracil a purine or a pyrimidine? single ring - pyrimidine d. What base is uracil complementary to? adenine TRANSCRIPTION: the making of RNA ...
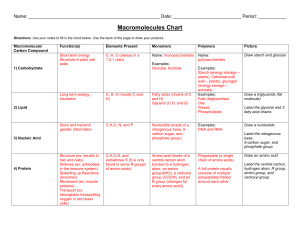
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences ...
... differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences ...
Transcription & Translation PowerPoint
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
Study Guide for LS
... - DNA is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. - In a DNA strand, the rungs (the part you step on) of the “ladder” are made of nucleotide bases. - In a DNA strand, the sides of the “ladder” are made of alternating sugar and phosphate ...
... - DNA is shaped like a double helix or a twisted ladder. - In a DNA strand, the rungs (the part you step on) of the “ladder” are made of nucleotide bases. - In a DNA strand, the sides of the “ladder” are made of alternating sugar and phosphate ...
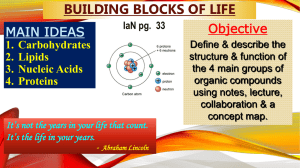
Organic Molecule Notes
... --Collagen=common structural protein in mammals. Protein Structure: --composed of long chains of amino acids. --20 different amino acids in proteins. --Polypeptide bonds link amino acids into a polypeptide chain=protein. 4 characteristics of Shape: -primary = -secondary = -tertiary = -quaternary = - ...
... --Collagen=common structural protein in mammals. Protein Structure: --composed of long chains of amino acids. --20 different amino acids in proteins. --Polypeptide bonds link amino acids into a polypeptide chain=protein. 4 characteristics of Shape: -primary = -secondary = -tertiary = -quaternary = - ...
Transcription and Translation
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
Answers - Shelton State
... 13. An enzyme that will catalyze the reaction of only one molecule has absolute specificity. 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the active site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. inhibitors 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (ful ...
... 13. An enzyme that will catalyze the reaction of only one molecule has absolute specificity. 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the active site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. inhibitors 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (ful ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.