asdfs - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Series of genes that controls development and differentiation in the developing embryo Hox genes ...
... Series of genes that controls development and differentiation in the developing embryo Hox genes ...
Transcription and Translation
... 20 amino acids are arranged in different orders to make a variety of proteins Assembled on a ribosome ...
... 20 amino acids are arranged in different orders to make a variety of proteins Assembled on a ribosome ...
Transcription and Translation
... 20 amino acids are arranged in different orders to make a variety of proteins Assembled on a ribosome ...
... 20 amino acids are arranged in different orders to make a variety of proteins Assembled on a ribosome ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
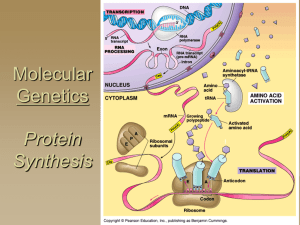
Molecular Genetics
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
Central Dogma
... 2. If the number of bacteria continued to increase at the same rate as the pond continued to warm, what would the measurement be at 30 degrees? A. 400 B. 640 C. 860 D. 1270 3. Based on the information presented, the number of which of the following substances is not determined by the pond's temperat ...
... 2. If the number of bacteria continued to increase at the same rate as the pond continued to warm, what would the measurement be at 30 degrees? A. 400 B. 640 C. 860 D. 1270 3. Based on the information presented, the number of which of the following substances is not determined by the pond's temperat ...
In 1953 Watson and Crick developed a double helix model for DNA
... The two nucleic acid strands are _______________________ to each other. That means that one strand is “_____________________” compared to the other. The 2 nucleic acid strands are held together by ____________ _ _____________ between the nitrogen bases. When the nitrogen bases bond together they fol ...
... The two nucleic acid strands are _______________________ to each other. That means that one strand is “_____________________” compared to the other. The 2 nucleic acid strands are held together by ____________ _ _____________ between the nitrogen bases. When the nitrogen bases bond together they fol ...
DNA-drug interactions and charge transfer processes in DNA.
... Some organic molecules can bind to DNA and thus interfere with DNA replication, transcription and gene expression process, or even direct nucleic acid cleavage. These small molecules can thus act as therapeutic agents in cancer cure. These drug molecules can bind to DNA by different mechanisms. The ...
... Some organic molecules can bind to DNA and thus interfere with DNA replication, transcription and gene expression process, or even direct nucleic acid cleavage. These small molecules can thus act as therapeutic agents in cancer cure. These drug molecules can bind to DNA by different mechanisms. The ...
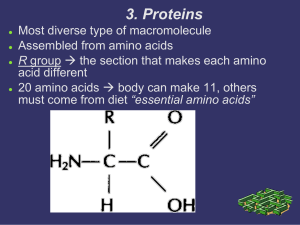
3. Proteins
... Exposing a protein to excess heat, radiation or a change in pH will alter its shape • Denaturation • Occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing an often permanent change in shape • ex. X-ray radiation or nuclear radioactivity can disrupt protein structure and can lead to cancer or gen ...
... Exposing a protein to excess heat, radiation or a change in pH will alter its shape • Denaturation • Occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing an often permanent change in shape • ex. X-ray radiation or nuclear radioactivity can disrupt protein structure and can lead to cancer or gen ...
Slide 1
... purebred red is crossed with a purebred white cow and results in a cow that is roan in colorhas both red and white hair) ...
... purebred red is crossed with a purebred white cow and results in a cow that is roan in colorhas both red and white hair) ...
lesson viii - MisterSyracuse.com
... you wouldn’t just rip it out of your cookbook and hand it over! You’d make a copy of it. This is what we’re going to learn about today. There are two words that sound alike mean very different things. You have to keep these straight in your head. Transcription is going from one language to the same ...
... you wouldn’t just rip it out of your cookbook and hand it over! You’d make a copy of it. This is what we’re going to learn about today. There are two words that sound alike mean very different things. You have to keep these straight in your head. Transcription is going from one language to the same ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
DNA and genetic information
... • "words" (codons or triplets) are 3 letters long in genetic code • each group of 3 nucleotides corresponds to one amino acid. • A nucleotide sequence (sequence of codons) can be “translated” into an amino acid sequence, i.e., a peptide or protein ...
... • "words" (codons or triplets) are 3 letters long in genetic code • each group of 3 nucleotides corresponds to one amino acid. • A nucleotide sequence (sequence of codons) can be “translated” into an amino acid sequence, i.e., a peptide or protein ...
Introduction to bioinformatics
... proteins. At this time, it is still unknown what the other 98% does => is this “junk” DNA? We have around 20,000 genes in our genome. This is not much when you think that a worm with 350 brain cells has barely fewer genes. Therefore the hot question is: how many proteins are really encoded in those ...
... proteins. At this time, it is still unknown what the other 98% does => is this “junk” DNA? We have around 20,000 genes in our genome. This is not much when you think that a worm with 350 brain cells has barely fewer genes. Therefore the hot question is: how many proteins are really encoded in those ...
Transcription and Translation
... • Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a DNA sequence (gene) • RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and separates the DNA strands • Complementary ribonucleotides align opposite complementary base pairs • RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together with covalent bonds • ...
... • Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a DNA sequence (gene) • RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and separates the DNA strands • Complementary ribonucleotides align opposite complementary base pairs • RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides together with covalent bonds • ...
What is a protein?
... •The ______________________ binds with a ribosome where it is decoded. Since this is where the DNA language is changed to the protein language, this is called Translation. •The code on the m-RNA is read _______ bases at a time. This is called a triplet code or __________________. •Each codon stands ...
... •The ______________________ binds with a ribosome where it is decoded. Since this is where the DNA language is changed to the protein language, this is called Translation. •The code on the m-RNA is read _______ bases at a time. This is called a triplet code or __________________. •Each codon stands ...
Advanced Organic Chemistry of Nucleic Acids
... nucleic acids to Moscow University chemistry majors already with a solid organic and physical chemistry background. To teach this particular subject was most exciting at the time when virtually every year was marked by stunning discoveries in the field of nucleic acids. We still derive a great deal ...
... nucleic acids to Moscow University chemistry majors already with a solid organic and physical chemistry background. To teach this particular subject was most exciting at the time when virtually every year was marked by stunning discoveries in the field of nucleic acids. We still derive a great deal ...
Biology Common Assessment Name
... 6. Code created during transcription from the DNA blueprint a. Replication b. gene ...
... 6. Code created during transcription from the DNA blueprint a. Replication b. gene ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.