Introduction to biotechnology - Indiana University School of Informatics
... 2. DNA cloning either through the use of cloning vectors or the polymerase chain reaction, whereby a single DNA molecule can be copied to generate many billions of identical molecules. 3. Nucleic acid hybridization, which makes it possible to find a specific sequence of DNA or RNA with great accurac ...
... 2. DNA cloning either through the use of cloning vectors or the polymerase chain reaction, whereby a single DNA molecule can be copied to generate many billions of identical molecules. 3. Nucleic acid hybridization, which makes it possible to find a specific sequence of DNA or RNA with great accurac ...
answers
... What is a purine? NITROGEN BASE WITH 2 RINGS What is a pyrimidine? NITROGEN BASE WITH ONE RING What is the shape of a DNA molecule? DOUBLE HELIX= “TWISTED LADDER” Which molecules for the backbone of the DNA molecule? PHOSPHATES__ & __SUGARS_______ What molecules form the “steps of the ladder”? ___NI ...
... What is a purine? NITROGEN BASE WITH 2 RINGS What is a pyrimidine? NITROGEN BASE WITH ONE RING What is the shape of a DNA molecule? DOUBLE HELIX= “TWISTED LADDER” Which molecules for the backbone of the DNA molecule? PHOSPHATES__ & __SUGARS_______ What molecules form the “steps of the ladder”? ___NI ...
Protein Synthesis
... DNA into mRNA (Transcription) • Then, decode those DNA instructions (now in the form of mRNA) to construct correct amino acids into a protein. (Translation) ...
... DNA into mRNA (Transcription) • Then, decode those DNA instructions (now in the form of mRNA) to construct correct amino acids into a protein. (Translation) ...
Genetics and Heredity
... Contains the genes that code for inherited traits Stored in the nucleus of an organisms cells Organized into chromosomes Carried by DNA ...
... Contains the genes that code for inherited traits Stored in the nucleus of an organisms cells Organized into chromosomes Carried by DNA ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... o Purines have a ________________________-ring structure and include the bases ________________________ and _________________________. o Pyrimidines have a ________________________-ring structure and include the bases ________________________ and _________________________. o DNA takes on the shape o ...
... o Purines have a ________________________-ring structure and include the bases ________________________ and _________________________. o Pyrimidines have a ________________________-ring structure and include the bases ________________________ and _________________________. o DNA takes on the shape o ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... RNA polymerase complex binds to “promoter” region of DNA and opens helix Promoter region is upstream for a specific gene. Promoter region contains two specific sets of nucleotide sequences. P252 Fig. 6.6 For each gene only ONE strand of the double-stranded DNA molecule is transcribed-this is c ...
... RNA polymerase complex binds to “promoter” region of DNA and opens helix Promoter region is upstream for a specific gene. Promoter region contains two specific sets of nucleotide sequences. P252 Fig. 6.6 For each gene only ONE strand of the double-stranded DNA molecule is transcribed-this is c ...
Chapter 5 - glenbrook s hs
... 2 or more polypeptide chains aggregated into 1 macromolecule √collagen (connective tissue) √hemoglobin ...
... 2 or more polypeptide chains aggregated into 1 macromolecule √collagen (connective tissue) √hemoglobin ...
DNA & RNA
... RNA molecules that carry copies of these instructions are known as mRNA Proteins are assembled on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of several dozen proteins as well as a form of RNA called rRNA During protein construction, a third type of RNA molecule transfers each amino acid to the ribos ...
... RNA molecules that carry copies of these instructions are known as mRNA Proteins are assembled on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of several dozen proteins as well as a form of RNA called rRNA During protein construction, a third type of RNA molecule transfers each amino acid to the ribos ...
DNA
... • The result is that each new copy of DNA produced by this process is made up of ½ original DNA molecule and ½ new DNA molecule. This makes the process semi-conservative. ...
... • The result is that each new copy of DNA produced by this process is made up of ½ original DNA molecule and ½ new DNA molecule. This makes the process semi-conservative. ...
• Double helix -- twisted ladder shape of DNA, like spiral staircase
... Which letters bind with which? A - T, G - C ...
... Which letters bind with which? A - T, G - C ...
DNA Unit Test Study Guide extra added
... The messenger RNA is fed through a protein assembly line and the “factory” that runs the assembly line is the ribosome. The ribosome is a cell organelle made up of RNA and protein. It is the site of where the proteins are built or synthesized. 10. Mutations: 3 types, effects of mutations A. Substitu ...
... The messenger RNA is fed through a protein assembly line and the “factory” that runs the assembly line is the ribosome. The ribosome is a cell organelle made up of RNA and protein. It is the site of where the proteins are built or synthesized. 10. Mutations: 3 types, effects of mutations A. Substitu ...
HEREDITY AND GENETICS vocabulary terms and
... A mathematical diagram used to calculate the frequencies of different genotypes and phenotypes among the offspring of a cross ...
... A mathematical diagram used to calculate the frequencies of different genotypes and phenotypes among the offspring of a cross ...
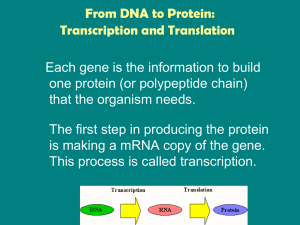
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... one protein (or polypeptide chain) that the organism needs. The first step in producing the protein is making a mRNA copy of the gene. This process is called transcription. ...
... one protein (or polypeptide chain) that the organism needs. The first step in producing the protein is making a mRNA copy of the gene. This process is called transcription. ...
Biochemistry
... macromolecules in the cell. They are composed of linear polymers called polypeptides, which contain amino acids connected by peptide bonds. ...
... macromolecules in the cell. They are composed of linear polymers called polypeptides, which contain amino acids connected by peptide bonds. ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 4. Of what are chromosomes composed? 5. Why did most scientists think the protein was the genetic material prior to the research of Griffith, Avery, and Hershey/Chase? 6. Understand Hershey and Chase’s experiment. 7. What information led to the discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule? 8. What ...
... 4. Of what are chromosomes composed? 5. Why did most scientists think the protein was the genetic material prior to the research of Griffith, Avery, and Hershey/Chase? 6. Understand Hershey and Chase’s experiment. 7. What information led to the discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule? 8. What ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
... using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four bases found in the DNA molecule. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.