Chemical basis of Inheritance Review KEY - Pelletier Pages
... Leading strand? Strand of DNA synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction. 13. What role do DNA polymerase and DNA ligase play in gene replication? DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragmen ...
... Leading strand? Strand of DNA synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction. 13. What role do DNA polymerase and DNA ligase play in gene replication? DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragmen ...
Chalkboard Challenge
... DNA Challenge • As a group, quietly discuss each question and agree upon one correct answer. The group with the most correct answers will win. ...
... DNA Challenge • As a group, quietly discuss each question and agree upon one correct answer. The group with the most correct answers will win. ...
Simon Rasmussen Assistant professor CBS
... A gene Gene: Stretch of DNA that gets transcribed into mRNA ...
... A gene Gene: Stretch of DNA that gets transcribed into mRNA ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis
... 18 black pentagons (deoxyribose sugar) 5 lavender tubes (uracil) 9 purple pentagons (ribose sugar) 1 large purple ribosome 3 grey tubes (peptide bonds) 3 blue three pronged pieces (tRNA) 3 black three pronged piece (amino acids) Procedure: Designate roles within your group. There should be at least ...
... 18 black pentagons (deoxyribose sugar) 5 lavender tubes (uracil) 9 purple pentagons (ribose sugar) 1 large purple ribosome 3 grey tubes (peptide bonds) 3 blue three pronged pieces (tRNA) 3 black three pronged piece (amino acids) Procedure: Designate roles within your group. There should be at least ...
SPECIFIKÁCIÓS TÁBLÁZAT Vegyszer neve Specifikáció Kiszerelés
... rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep additional dyes, for color indication for reaction setup as w ...
... rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep additional dyes, for color indication for reaction setup as w ...
Genetics Unit – Chpt. 8 Cell Reproduction
... structure and the function of the chromosomes and the genes. This would include mapping the genome, locating markers for diseases, making proteins and technology like cloning, genetic engineering and DNA fingerprinting. ...
... structure and the function of the chromosomes and the genes. This would include mapping the genome, locating markers for diseases, making proteins and technology like cloning, genetic engineering and DNA fingerprinting. ...
Cells - Salisbury University
... results from specific proteins built in the cell. Someone with sickle cell disease has slightly different DNA instructions compared to someone who does not have the disease. Our goal is to understand this better by learning about DNA structure and by learning about how DNA is passed from parents to ...
... results from specific proteins built in the cell. Someone with sickle cell disease has slightly different DNA instructions compared to someone who does not have the disease. Our goal is to understand this better by learning about DNA structure and by learning about how DNA is passed from parents to ...
Structure of Nucleic Acids
... Hydrolysis: Chemical reaction that uses water to separate polymers into monomers. (Break apart) - Exactly the opposite of Dehydration synthesis ...
... Hydrolysis: Chemical reaction that uses water to separate polymers into monomers. (Break apart) - Exactly the opposite of Dehydration synthesis ...
Cell Structure and Genetic Control
... B. There are four different types of DNA nucleotides, each of which contains one of four possible bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine; in RNA, the base uracil substitutes for the base thymine. C. DNA consists of two long polynucleotide strands twisted into a double helix. The two strands a ...
... B. There are four different types of DNA nucleotides, each of which contains one of four possible bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine; in RNA, the base uracil substitutes for the base thymine. C. DNA consists of two long polynucleotide strands twisted into a double helix. The two strands a ...
Chapters 8-10
... A base substitution mutation in a gene does not always result in a different protein. Which of the following factors could account for this? A) the fact that the mutation affects only the sequence of the protein's amino acids, so the protein stays the same B) the double-ring structure of adenine and ...
... A base substitution mutation in a gene does not always result in a different protein. Which of the following factors could account for this? A) the fact that the mutation affects only the sequence of the protein's amino acids, so the protein stays the same B) the double-ring structure of adenine and ...
Investigation 3: DNA - connorericksonbiology
... is the "outward, physical manifestation" of the organism. Which are the physical parts, the sum of the atoms, molecules, macromolecules, cells, structures, metabolism, energy utilization, tissues, organs, reflexes and behaviors. Anything that is part of the observable structure, function or behavior ...
... is the "outward, physical manifestation" of the organism. Which are the physical parts, the sum of the atoms, molecules, macromolecules, cells, structures, metabolism, energy utilization, tissues, organs, reflexes and behaviors. Anything that is part of the observable structure, function or behavior ...
Virtual Labs: Class Set Building DNA, transcription, translation
... You have successfully created a protein!” ...
... You have successfully created a protein!” ...
notes
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
File
... Created by combining three fatty acid groups with one glycerol molecule through dehydration synthesis ...
... Created by combining three fatty acid groups with one glycerol molecule through dehydration synthesis ...
Chapter 12 Test Review
... 2. Chargaff’s rules state that in DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of ______________ 3. Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of _______ = _______ & ________ = _________ 4. What is the polymer of nucleotide ____________________________________________________ 5. A DNA nucleo ...
... 2. Chargaff’s rules state that in DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of ______________ 3. Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of _______ = _______ & ________ = _________ 4. What is the polymer of nucleotide ____________________________________________________ 5. A DNA nucleo ...
Assignment 1
... c. Val-Trp-Thr d. Met-Asp-Asn Answer 9: B (Asp-Asn-Asn), This is the only ORF that shows no in-frame stop codon in the sequence given. And these are three amino acids following the first Met amino acid for this ORF. Q10. If the third base (U) of the resulting mRNA is mutated to G, then what would be ...
... c. Val-Trp-Thr d. Met-Asp-Asn Answer 9: B (Asp-Asn-Asn), This is the only ORF that shows no in-frame stop codon in the sequence given. And these are three amino acids following the first Met amino acid for this ORF. Q10. If the third base (U) of the resulting mRNA is mutated to G, then what would be ...
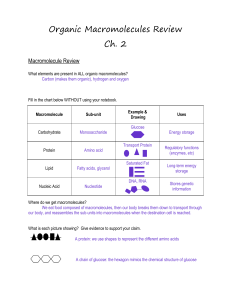
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
BELL WORK: Answer the following questions:
... c) Replaces a base with its complementary base d) Produces a codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon ...
... c) Replaces a base with its complementary base d) Produces a codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon ...
Students or teachers?
... DNA is made up of Nucleotides, that are really important for living organisms, as they are the structural components or building blocks of DNA and RNA ...
... DNA is made up of Nucleotides, that are really important for living organisms, as they are the structural components or building blocks of DNA and RNA ...
Document
... transmits genetic information in a cell is a polymer called deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA. DNA carries the instructions for making a specific protein. Ribonucleic Acid, RNA is needed to translate and copy DNA. ...
... transmits genetic information in a cell is a polymer called deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA. DNA carries the instructions for making a specific protein. Ribonucleic Acid, RNA is needed to translate and copy DNA. ...
Bell work Objectives: DNA replication DNA Replication
... The order of the pairs determines the genetic code, which controls protein synthesis or the production of proteins. 6. What do we call a set of three nitrogen bases? ...
... The order of the pairs determines the genetic code, which controls protein synthesis or the production of proteins. 6. What do we call a set of three nitrogen bases? ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.